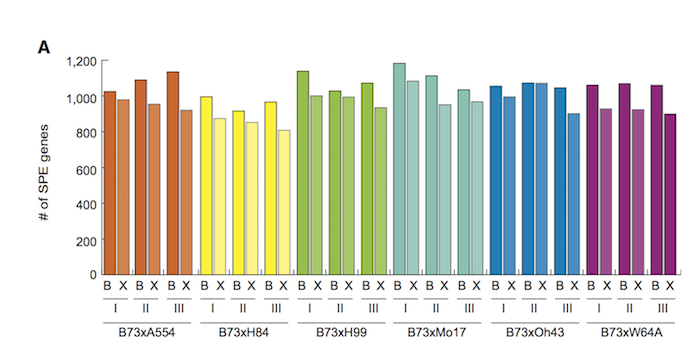
Single Parent Expression (SPE) of non-syntenic genes in maize hybrids (Curr. Biol.) ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogIn maize, it has long been known that the crossing of two inbred lines can produce a hybrid offspring with higher yield than the parents. Baldauf and collaborators have studied the gene expression of 6 hybrid lines coming from 7 distantly related inbred lines. One line, B73, was chosen as the common…
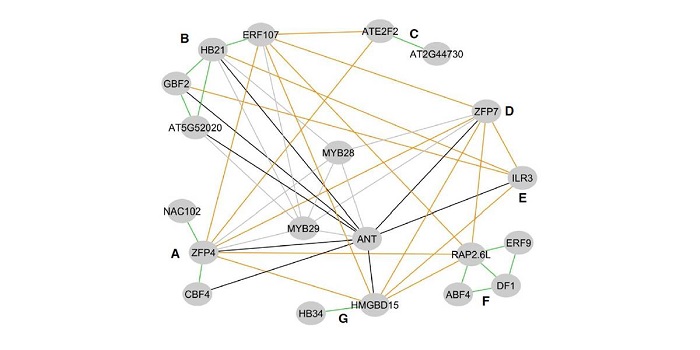
Network-guided discovery of transcription factors epistasis in glucosinolate biosynthesis (Plant Cell)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlant Cell. Li et al. studied epistatic (non-additive) interactions amongst the network of transcription factors controlling aliphatic glucosinolate biosynthetic pathways, which are well-described and have diverse roles in plant defense. Specifically, the authors measured metabolite levels and transcript…
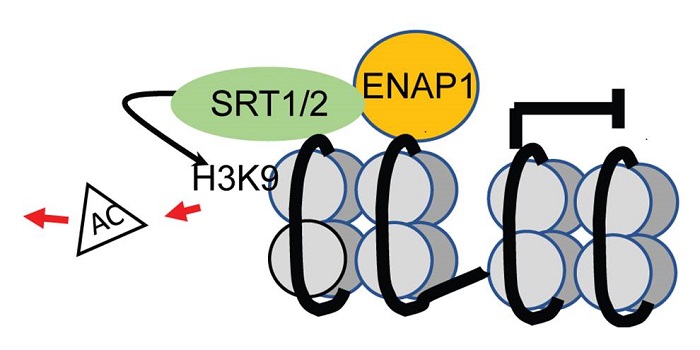
Ethylene Represses Gene Transcription via Histone Deacetylases
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefApproximately half of all ethylene-responsive genes are downregulated in the presence in ethylene (Chang et al, 2013), but this repression has received relatively little attention compared to the ethylene-mediated activation of expression. The known positive regulators of ethylene signaling include ETHYLENE…
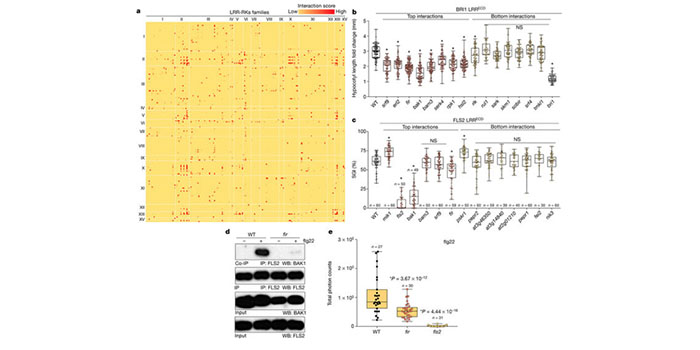
An extracellular network of Arabidopsis leucine-rich repeat receptor kinases
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogNature. Through the activity of hundreds of membrane receptors, plants can sense the extracellular environment and tune their growth and responses to abiotic and biotic stimuli in an elegant and complex way. Despite their pivotal role, only a dozen of receptors have been characterized in plants and very…

Chloroplasts Use Bacterial Mechanism to Recognize Start Codons
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellScharff et al. investigate function of anti-Shine-Dalgarno sequence in chloroplast ribosomes https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00524
By Lars B. Scharff
BACKGROUND: Cells of plants contain three different systems for protein synthesis: in the cytosol, in plastids, and in mitochondria. Proteins in the…
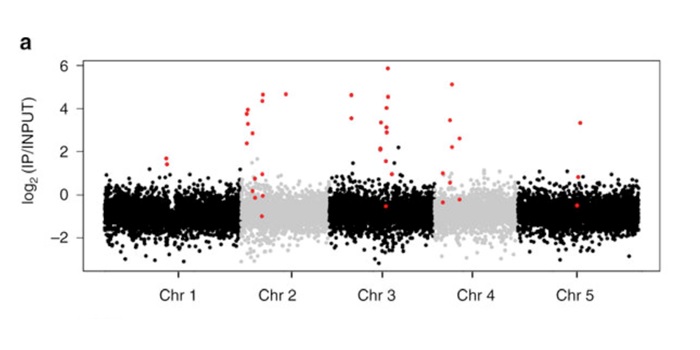
Evolution of transposon-encoded anti-silencing factors in Arabidopsis ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogTransposable elements (TEs) are a major component of eukaryotic genomes. Their activity is silenced by epigenetic mechanisms such as chromatin modifications and DNA methylation in order to avoid deleterious effects on host genome stability. Nevertheless, how TEs overcome silencing by the host and propagate…
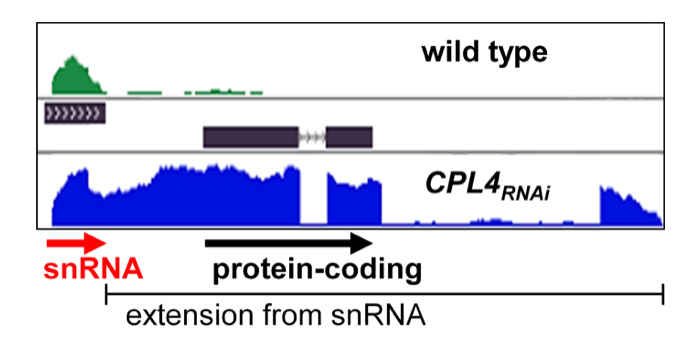
Transcriptional Switching Makes New Messages
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellFukudome et al. explore the significance of Pol II C-terminal phosphorylation https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00331
By Akihito Fukudome and Hisashi Koiwa
Background: In animals and plants, gene expression begins with an enzyme called RNA polymerase II (Pol II), which produces ribonucleic acid (RNA)…

Multiple Mediator Subunits Impact Metabolism
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellDolan et al. examine how a complex that regulates gene expression alters the production of phenylpropanoids https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00282
By Whitney Dolan and Clint Chapple
Background: Plants produce a vast array of compounds known as phenylpropanoids from the amino acid phenylalanine.…
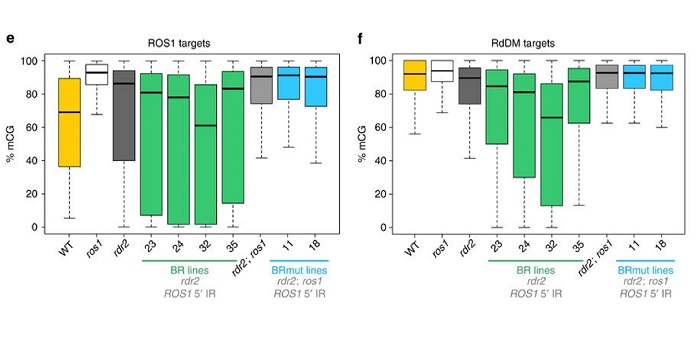
Methylome robustness in plants is conferred by a methylation-sensitive system.
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogDNA methylation is instrumental in promoting transcriptional silencing at repetitive elements, inhibiting illegitimate recombination and establishing genomic imprinting. In plants, DNA methylation profiles are stably inherited over generations through the activities of cytosine DNA methyltransferases…

