
Special Science Issue: Plants and Heat
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe June 12 issue of Science has a focus on plants and heat that includes several excellent review and research articles. In a very interesting review, Singh Yadav et al. discuss the complex and fascinating question of how plants sense temperature, emphasizing both the biophysical nature of temperature…

Theme issue: Crops under stress
Plant Science Research WeeklyThey May 29 issue of Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. B. similarly addresses the pressing questions of how crop plants will continue to feed the world in spite of the rapidly changing climate. This issue covers some of the same topics as the Science special issue on heat stress but goes beyond heat to cover drought…
Review. Going beyond the model: When different plants have different plans
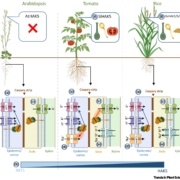
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn a recent review, Nieves-Cordones and Rubio highlight the species-specific strategies used by Arabidopsis and crop plants to regulate potassium (K⁺) and sodium (Na⁺) transport, which challenges the universality of Arabidopsis thaliana research. In Arabidopsis, K⁺ uptake is largely mediated by…

Multimerization of IAA3 via ROS suppresses lateral root formation in air gaps
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoot growth and branching is strongly tuned to environmental conditions including soil compaction, nutrient availability, and the presence of water, with auxin having a major role in regulating root architecture. Here, Roy et al. have demonstrated how auxin contributes to a suppression of root branching…
Identity is Everything : MYB68 regulates endodermal differentiation and suberin patterning
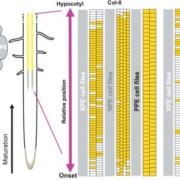
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoot cells are organized into concentric layers that facilitate the movement of water and nutrients. Among these, the endodermis overlays the root vasculature, allowing it to play a major role in selective uptake. To perform this function, endodermal cells undergo two distinct stages of differentiation.…
The shape of adaptation: Evolution of venation patterns in plants
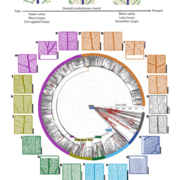
Plant Science Research WeeklyLeaf venation patterns display remarkable diversity across both living and fossil plant lineages, yet key questions remain about when and how these architectural differences emerged and what functional roles they serve. In their recent review, Mantos et al. explored the evolutionary history of venation…
PIN auxin transporters facilitate polar transport of synthetic phenoxyacetic acid herbicides
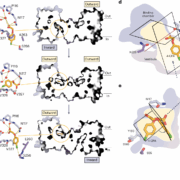
Plant Science Research WeeklySynthetic herbicides are widely used in agriculture to control weeds, often by targeting the physiological pathways regulated by auxins, plant hormones that induce root growth and development. PIN-FORMED (PIN) auxin transporters facilitate the polar transport of natural auxins such as indole-3-acetic…
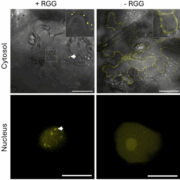
Artificial condensates can boost metabolic engineering
Plant Science Research WeeklyNicotiana benthamiana is widely used to reconstruct complex, multi-step metabolic pathways for research or industrial purposes. This is enabled by rapid and high-level protein expression after agroinfiltration. Within cells, as well as membrane-bound organelles, nonmembrane-bound biomolecular condensates…
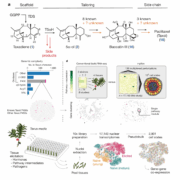
Elucidation and recreation of the biosynthetic pathway for taxol
Plant Science Research WeeklyPaclitaxel (sold as Taxol) is taxane diterpene natural product of yew trees (Taxus spp.) and a potent stabilizer of microtubules that is effective in treatment of cancers. However, it has proven difficult to elucidate its biosynthetic pathway, and commercial production still relies on extracting an…

