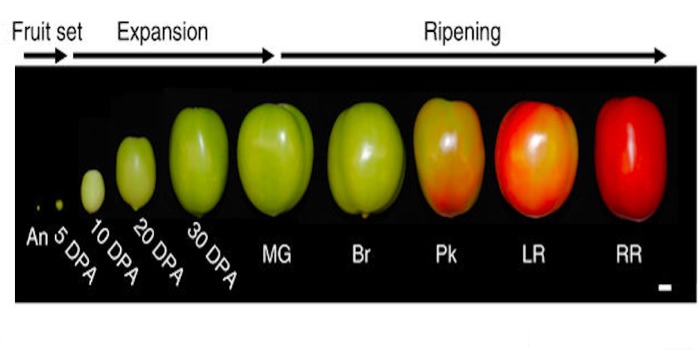
Transcriptome mapping of tomato fruit development and ripening (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTomato (Solanum lycopersicum) is today the main model to study fleshy fruit development. Until now, most tomato growth and ripening studies are focused on a single tissue, the pericarp, and do not take into consideration the development of internal tissues. Shinozaki et al. provide an extensive spatiotemporal…
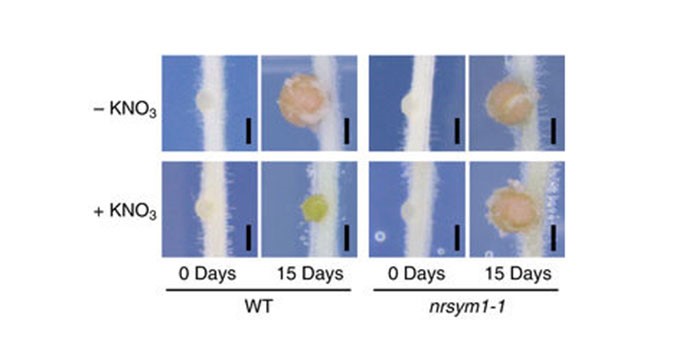
A NIN-LIKE PROTEIN mediates nitrate-induced control of root nodule symbiosis in Lotus japonicus
Plant Science Research WeeklyLegumes form root endosymbioses with Rhizobium bacteria in a special structure called nodule. In this symbiotic relationship, on one hand the plant provides the microbe with sugars and in exchange it receives fixed atmospheric nitrogen, the main limiting element for plant growth. Nevertheless, when nitrogen…
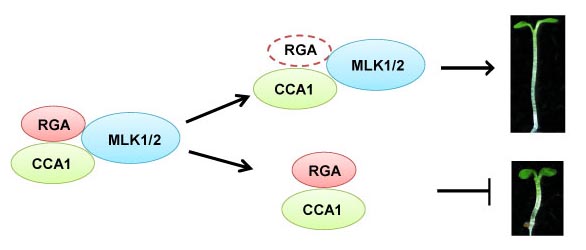
Combining Forces for Hypocotyl Elongation: Histone Modifications, GA, and the Circadian Clock
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZheng et al. discover proteins that mediate interactions between gibberellins and the circadian clock https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00830
By Han Zheng and Yong Ding
Background: Hypocotyl elongation helps the shoot emerge from the soil surface. The gibberellin (GA) signaling protein RGA inhibits…
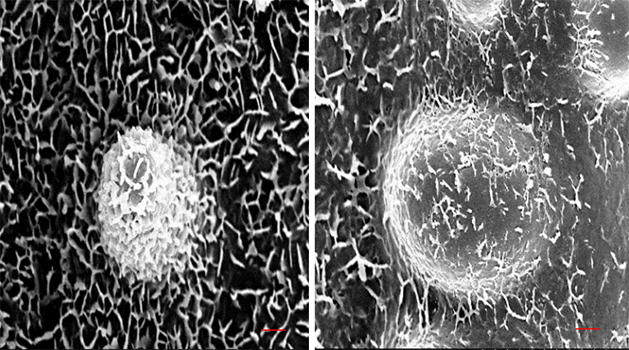
Wax Protects Rice from Drought Stress
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellWang et al. investigate how two proteins work oppositely to regulate wax contents and drought stress response in rice https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00823
By Zhenyu Wang and Qingyun Bu
Background: Rice is a staple food for world populations and its production is threatened by drought stress. Cuticular…

Snapshot of a TF Network in Plants
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLi et al. investigate a transcription factor network that transmits environmental signals to regulate secondary metabolism in plants. The Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00805.
By Baohua Li and Daniel Kliebenstein
Background: Plants produce specialized secondary metabolites to survive…

Ribosome Production Under Surveillance
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellMaekawa et al. find a ribosome production monitoring system in Arabidopsis thaliana Plant Cell (2017) https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00778
By Shugo Maekawa, Tetsuya Ishida, Shuichi Yanagisawa
Background: Protein is produced by ribosomes consisting of a number of proteins and several RNAs (ribosomal…

The Phytohormone Ethylene and Transcriptional Repression
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZhang et al. investigate histone deacetylase in the ethylene response. Plant Cell (2017). https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00671
By Fan Zhang
Background: Ethylene is the only gaseous hormone in plants, and is a key hormone controlling plant growth and resistance to stress. Epigenetic mechanisms are…
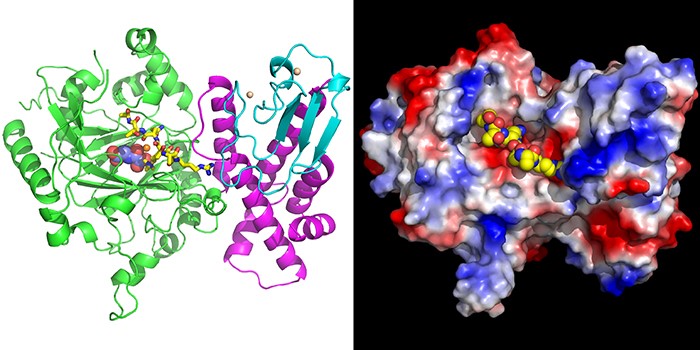
Structure of KDM5 Gives Insight to Histone Demethylation
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellYang et al. reveal a conserved H3K4me3 recognition mechanism shared by both plant and animal KDM5 histone demethylases. The Plant Cell (2017). https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00666
By Z. Yang, Q. Qiu, X. Cao and J. Du
Background: Histone methylation is a conserved gene regulation mechanism in plants…
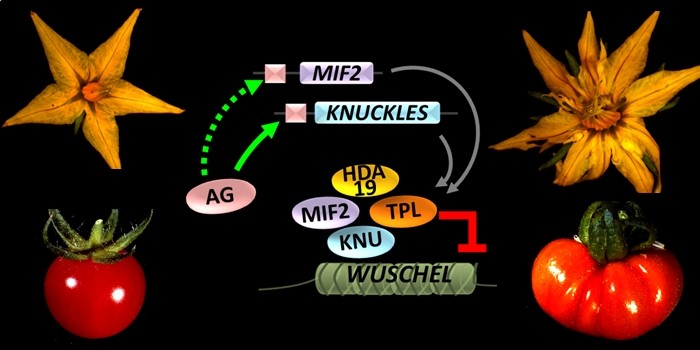
When Mini Protein Makes Big Fruit
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellBollier et al. investigate locule number control in Arabidopsis thaliana and tomato. The Plant Cell 2018 https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00653.
By N. Bollier and M. Hernould
Background: During flower development, production of a defined number of floral organs is due to the determinate fate of floral…

