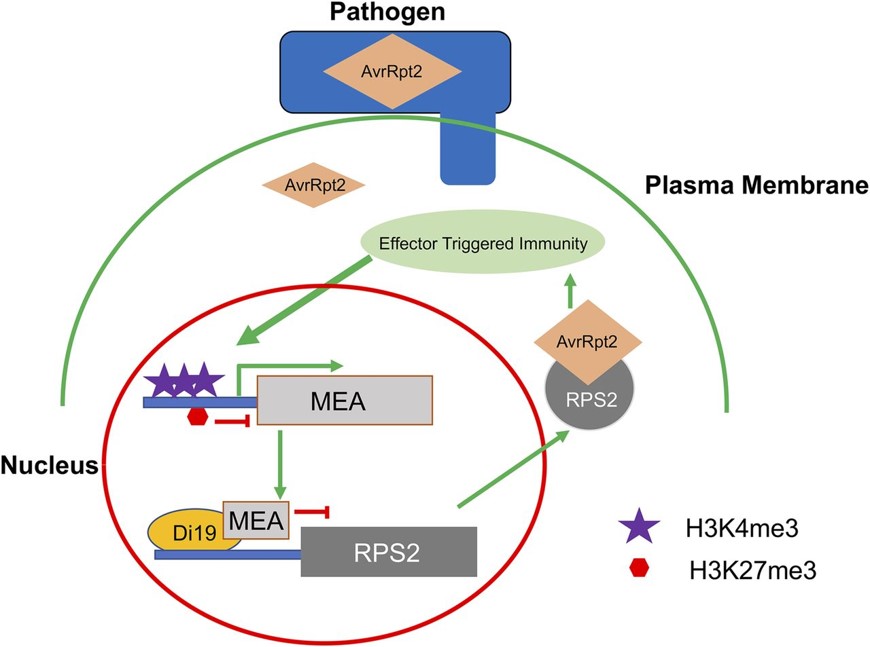
Polycomb Group Transcriptional Repressor: Suppress to Sustain
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsEvidence of epigenetic gene regulation in plant immunity was first reported in 1975 (Guseinov et al., 1975) with the demonstration that cytosine methylation is altered in response to pathogen infection. Since then, it has been established that pathogen infection influences DNA methylation and histone…

A New Epigenetic Switch Regulating Histone Modification
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellMateo-Bonmatí et al. have found novel components of the Arabidopsis epigenetic machinery. Plant Cell (2018). https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00300
By Eduardo Mateo-Bonmatí, Lucía Juan-Vicente, Riad Nadi, and José Luis Micol
Background: In multicellular organisms, most cells contain the same…
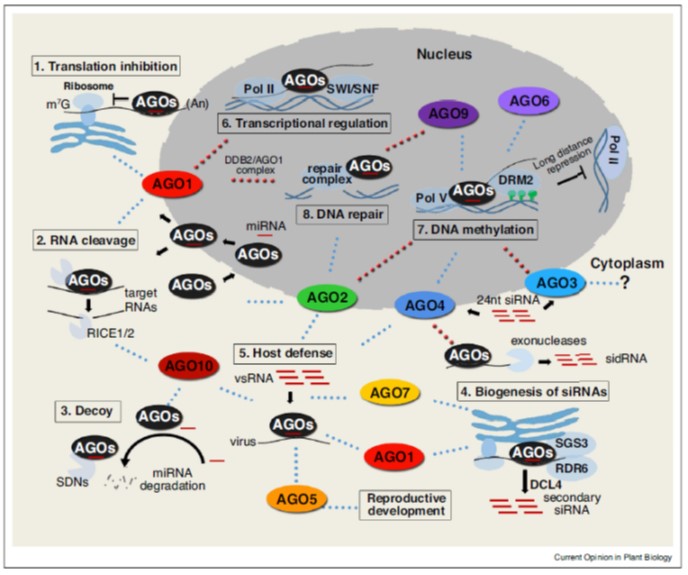
Review. Actions of plant Argonautes: Predictable or unpredictable? (COPB $)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe Arabidopsis genome encodes nine Argonaute proteins and an AGO pseudogene. The nine functional proteins fall into three clades based on sequence. Ma and Zhang update what we know about these proteins. It turns out, the simple assumptions made early on have not entirely been borne out. For example,…
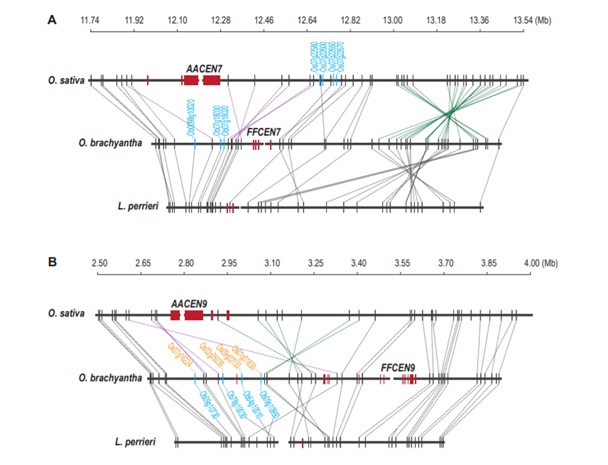
Chen Mingsheng's research team found an evolutionary trend of genes fleeing the centromere region
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: NewsArticle source: http://theworldseeds.cn/index.php?p=152804 (Translated by Google Translate)
The centromere and its surroundings are the fastest-evolving and most complex areas of the plant genome. The centromere and near centromere regions not only undergo rapid sequence changes and structural remodeling,…
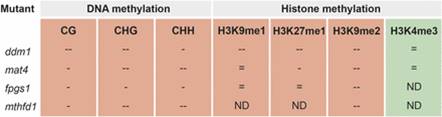
Powering Epigenetics through the 1C Pathway
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsBy Lisa Smith and Nathan Butler
Epigenetic modifications in plants repress transposable elements to maintain genome stability and facilitate adaptation to changing environmental conditions by regulating the expression of some genes. Furthermore, conditions such as disease stress can alter the epigenetic…

Variability of paternally imprinted gene expression linked to hybridization failure in Capsella (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHybrid seed lethality represents a major reproductive barrier in angiosperms and facilitates species divergence over evolutionary times. Hybrid seed lethality is mainly due to defective endosperm development, leading to embryo arrest. Hybrid seed defects show a parent-of-origin effect, but the underlying…
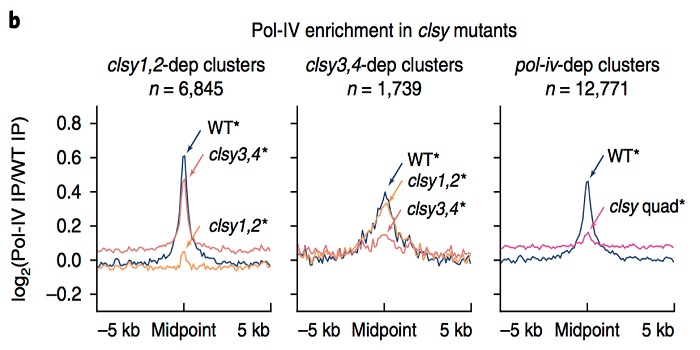
Stay CLASSY: Control of locus-specific de novo DNA methylation by the CLASSY family ($) (Nature Genet.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyDNA methylation is fundamental for genome function and stability, including regulation of gene expression, silencing of transposable elements and control of recombination. While the processes involved in maintenance of DNA methylation are generally well understood, the factors required for locus-specific…
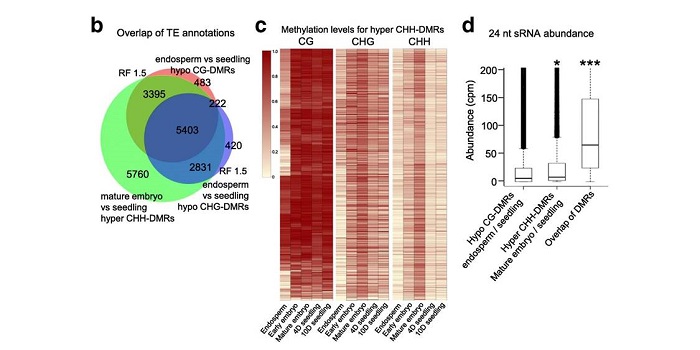
DNA methylation dynamics during early plant life
Plant Science Research WeeklyDNA methylation is extensively reprogrammed in the early embryo and germlines of mammals, whereas flowering plants do not show such extensive resetting except in the endosperm. Active DNA demethylation in the central cell and reduced activity of DNA methyltransferases leads to global hypomethylation…
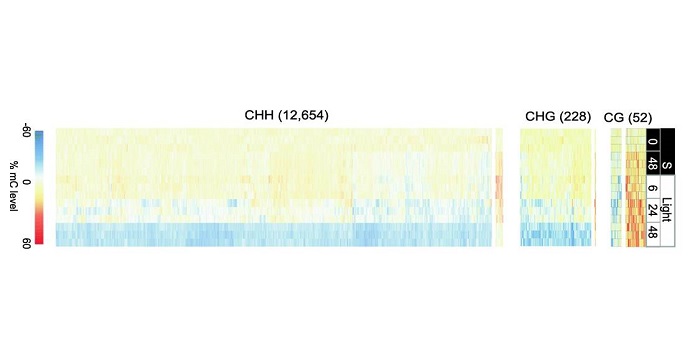
Extensive transcriptomic and epigenomic remodelling occurs during Arabidopsis thaliana germination
Plant Science Research WeeklyUnderstanding the complex regulatory mechanisms that contribute to germination and seedling establishment requires integration of gene-expression, transcription factors (TFs), DNA methylation, smallRNA data, and their interactions. Narsai et al. describe the first dynamic transcription factor network…

