
Avoiding Shade to Grow Taller but Not Always Stronger: Phytochrome–Jasmonic Acid Interplay
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe environment plays a major role in determining whether, when, and how growth occurs, and resource allocation towards growth is an important factor in many contexts. For example, plants whose defenses against pathogens are activated often grow less, and plants that must grow taller to reach the light…
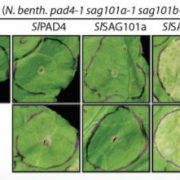
Die Another Way: An EDS1-SAG101 Complex Mediates TNL Immunity in Solanaceous Plants
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefDisease resistance (R) receptors detect pathogen effector-mediated host manipulation and induce effector-triggered immunity (ETI) that is often associated with programmed cell death. R proteins are generally conserved across plants, consisting of nucleotide-binding site and leucine rich repeat (NBS-LRR)…
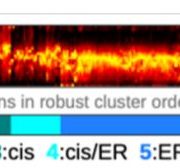
To Golgi and Beyond!
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe Golgi apparatus is the central sorting station of the eukaryotic secretory pathway. Protein and lipid cargoes are received at its cis face from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and may undergo various modifications including glycosylation before being trafficked onwards from the trans face to their…
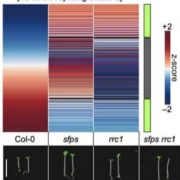
In the Pale Red Light: Control of pre-mRNA Splicing by RRC1 and SFPS
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPlants have armed themselves with a battalion of photoreceptors to cope with changes in light quantity, quality and direction. Light perception is especially critical when the seedling first emerges from the darkness of the soil and engages the red/far-red light photoreceptors phytochromes (phys). An…
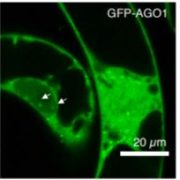
Small RNAs in the maillot jaune: transcriptional analysis of the plant cell cycle
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe cell cycle is a tightly coordinated dance with the ultimate goal of dividing one cell into two. Eukaryotic cells tend to divide in the same general pattern, broadly reduced to four phases; cells increase organelle content in the G1 phase, DNA replication occurs in S phase, cells grow in size and…
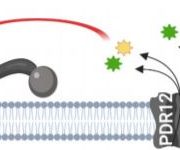
Resistance on Tap: PDR Transporters Direct Antimicrobial Metabolites Towards Invading Pathogens
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIn Arabidopsis thaliana and related species within the Mustard family (Brassicaceae), the tryptophan (trp)-derived antimicrobial metabolite camalexin (3-thiazol-2-yl-indole) plays a central role in defense against bacterial, fungal, and oomycete pathogens. Upon pathogen attack, cytochrome P450 monooxygenases…
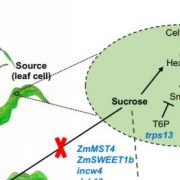
Senescence: the genetics behind stay-green corn
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefSenescence results from two ineluctable laws of nature: every living entity will eventually die and when it does, nothing will be lost, as everything will be recycled. At the organism level, senescence is an integral part of the plant life cycle, under strict age-dependent genetic control. This dismantlement…
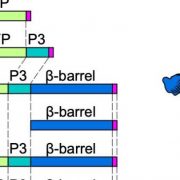
Barreling down the Chloroplast Highway: Protein Sorting of Outer-Membrane β-Barrel Proteins
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefModern-day chloroplasts are the descendants of a photosynthetic cyanobacterium that took up residence inside the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Since this initial cohabitation agreement, the cyanobacterial endosymbiont has dumped most of its genome into the host eukaryotic genome. This creates an engineering…

Designer PPR Proteins as Tools to Explore RNA Binding in vivo
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefTechniques to isolate the RNA molecules bound to a specific protein, via co-immunoprecipitation, for instance, have been available for years. The converse—methods to identify the proteins bound to a specific RNA—have been harder to come by, in part because of difficulty in elucidating the determinants…

