
Mediator Skills: MED16 Controls Endoreduplication
The discovery of Mediator began with the observation that two transcriptional activators could interfere with each other’s function in vitro, even though they did not bind to the same promoter (Kelleher, Flanagan and Kornberg, 1990). The hypothesis, since then well-validated, was that each transcription…
Setting Time for a Hot Date: Paused Embryo Development and Protective Organogenesis Allow Dates to Cope with the Desert Environment
Adaptive developmental plasticity, in which changing environmental conditions modulate morphogenesis, can help organisms survive harsh conditions. Common examples include the protection of shoot apical meristems by transient arrest and sequestration into bud-like structures in wintering evergreens (e.g.…
State of (in)flux: Action of a CNGC Ca2+ channel in defense against herbivory
Plants have evolved highly sophisticated signalling systems that enable them to coordinate growth and development and respond rapidly to environmental fluctuations. These long-range signals can take the form of mobile small molecules such as phytohormones and RNAs, but can also be electrical signals…
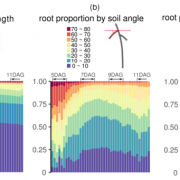
Unearthing Root Growth Dynamics Through 3-D Time-lapse Imaging
Plants blindly probe the soil for ever-changing pockets of water and nutrients and continuously adjust their root system architecture (RSA) accordingly. Whether they invest more energy in growing existing roots or sending out new lateral roots depends on both genetic programs and environmental factors.…
Fear Not the Unknown: OPENER as a Study in Shedding Light on Genes with Unknown Function
Genome sequencing has become (relatively) cheap and easy, but assigning functions to the genes identified remains challenging—even in exhaustively studied species such as Arabidopsis thaliana, where functions of ~30% of genes remain unknown. Many of these genes likely have functions that are essential,…

Looking Over Allopolyploid Clover
The allotetraploid species white clover (Trifolium repens) resulted from hybridization of two diploid European species whose extant relatives are found only in limited regions–– T. occidentale is a creeping clover found only in saline areas near the shores of Western Europe and T. pallescens is found…

Six Days, Seven Nights: The Transcriptional Speed of Seed Development
The development of the seed is a complex dance of cell division and differentiation, including transcriptional and genomic repatterning. Measuring gene expression by high-throughput RNA-Seq is routine in laboratories, and numerous seed transcriptomes and microarrays have long been published for maize…
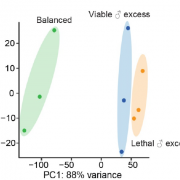
Father Knows Best? Small RNA Pathway Controls Endosperm Response to Paternal Genomic Dosage
In flowering plants, seed viability is dependent upon the endosperm, a triploid tissue produced by fertilization of a diploid central cell by a haploid sperm. Most endosperm genes are expressed in a 2:1 maternal to paternal ratio reflecting the genomic DNA content. Consequently, balance between maternal…
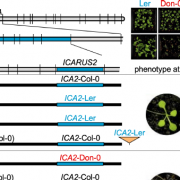
Too Close to the Flame: Duplicated ICARUS Genes and Growth at Higher Temperatures
Plants can adjust their growth and reproduction cycles according to the local climate they experience, but how will they respond when ambient temperatures rise? Most Arabidopsis accessions respond by increasing cell elongation and accelerated flowering, but some cannot cope with higher temperatures and…

