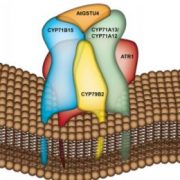
A Plant Metabolon Efficiently Mass-produces Phytochemical Defenses
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefWhen plants are under attack, they activate defense programs including the biosynthesis of chemical defense compounds. The biosynthesis of these phytochemicals has to occur rapidly and represents a major sink of nutrients and amino acids. How plants optimize the mass production of chemical weapons remains…
The same but different: CoMoVa, an algorithm to identify functional variation in cis regulatory elements
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefTranscription factors (TFs) act through TF binding sites (TFBSs) to control the transcription of associated genes. TFBSs are short and degenerate sequences that are often depicted using a Position Weight Matrix, which contain invariant nucleotides that are crucial for TF binding and variable nucleotides…
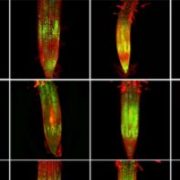
Moving on Up: An MCTP-SNARE Complex Mediates Long-distance Florigen Transport
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefFlowering plants integrate endogenous and external cues to accurately time the transition from vegetative to reproductive growth (Cho et al., 2017). Many plants, including Arabidopsis thaliana, sense changes in day length (photoperiod) to transition to flowering as the season changes. Decades of careful…
Developmental timing is everything (part II): gating of high temperature responses by the circadian clock
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefArabidopsis thaliana seedlings exposed to heat stress (>42ºC) suffer high lethality rates unless exposed to milder heat (37ºC) beforehand. This pre-exposure distinguishes basal from acquired thermotolerance and has been extensively studied over the years. However, experimental conditions used to…

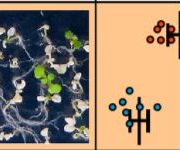
Promoting production: UPL3 promoter variation modulates seed size and crop yields
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIdentifying natural genetic variation, understanding how it influences traits, and utilizing it for crop improvement is a major objective in plant science. Miller et al. (2019) have identified genetic variation in the promoter region of BnaUPL3.C03 from a panel of Brassica napus accessions that can influence…
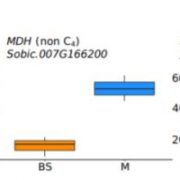
Comparative Cell-Specific DNaseI-Seq Reveals Transcription Factor Binding Landscape in C3 and C4 Grasses
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefNearly every aspect of growth, morphogenesis, physiology, and stress response is influenced by cell/tissue-type specific gene expression. Transcription factors (TFs) recognize cis-regulatory elements and signal transcription machinery for gene regulation, and the interaction between TFs and their target…
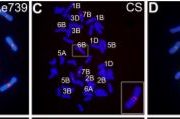
Polyploid Pairing Problems: How Centromere Repeat Divergence Helps Wheat Sort It All Out
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefBy Jennifer Mach, Science Editor
I don’t know how polyploids get their chromosomes paired correctly in meiosis— I can’t even sort my socks. Sometimes I give up and pair random socks, but plants can’t go with random pairings, because that’s a route to death, and with genomes in the dozens…
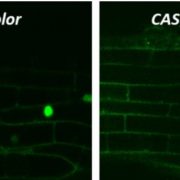
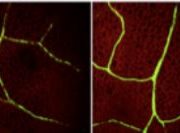
Perception of Ectomycorrhizal Signals by Poplar Induces Root Colonization
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefBy Gregory Bertoni
Symbiotic associations with microorganisms are widespread among both woody and herbaceous plant species, including most agronomic crops (Brundrett and Tedersoo, 2018). Mycorrhizal fungi provide their hosts with mineral nutrients absorbed from the soil in exchange for fixed carbon…
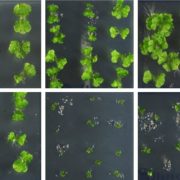
Some Things Never Change: Conserved MYC-family bHLH Transcription Factors Mediate dinor-OPDA Signaling in Liverworts
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe lipidic phytohormone jasmonyl-isoleucine (JA-Ile) is a key mediator of stress-versus-growth signaling in vascular plants. Upon it’s accumulation, JA-Ile is detected by the F box receptor protein COI1 (CORONATINE INSENSITIVE1), which in turn leads to the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation…

