Plant Science Research Weekly: August 28, 2020
WWR Full PostReview: Extending Plant Defense Theory to Seeds ($)
Plants have developed multiple mechanisms to deal with the natural enemies they encounter through their life. In consequence, the Plant Defense Theory has arisen to assess how plants allocate resources to this purpose. However, much of the efforts…

Summer Webinars on the Plant Science Decadal Vision
Blog, Plant Science Research NetworkWith society summer conferences going online, the Plant Science Research Network has hosted a series of virtual discussions on the new Plant Science Decadal Vision 2020 - 2030.
On August 26, BTI President Dr. David Stern presented on the Plant Science Decadal Vision 2020–2030, a holistic vision for…

Self-Incompatibility Can Cause Death in Vegetative Cells
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideSelf-incompatibility (SI) is a mechanism used by flowering plants to prevent self-fertilization. It is controlled by a multi-allelic S-locus that allows self/non-self-recognition between pistil and pollen. In several SI systems, when male and female S-determinants match, self pollen is recognized and…

Recognizing Plant Direct authors: Zainab ALJbory
Plant Direct, Plant Direct: Author ProfilesZainab ALJbory, first author of Differential Localization of Hessian Fly Candidate Effectors in Resistant and Susceptible Wheat Plants
Current Position: Postdoc. Research Associate
Education: B.S. in Plant Protection and M.S. in Entomology from University of Baghdad- Iraq. Ph.D. in Molecular Entomology,…

OsGSK2 integrates jasmonic acid and brassinosteroid signalling in rice
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPlant defenses against herbivore or pathogen attack involve the coordination of multiple hormone-mediated signalling networks, including the jasmonate (JA) and brassinosteroid (BR) pathways. Jasmonate is an oxylipin phytohormone that triggers the transcription of defence-related proteins and secondary…
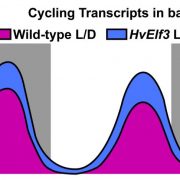
The rhythm of the light: how light and the clock drive cycling of transcript levels in barley
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchCircadian rhythms are ubiquitous among living things. A core set of so-called clock genes and their products assemble an oscillatory network that provides a rhythm to anticipate dawn and dusk (Hsu and Harmer, 2014). The circadian clock regulates the day/night rhythms of plants and light itself has many…
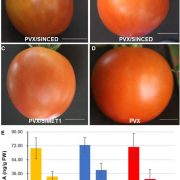
METHYLTRANSFERASE1 and Ripening in Vivipary
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideDuring fruit ripening in tomato and other flowering plants, the seeds contained within the fruit normally become dormant. However, under certain physiological conditions, seeds can germinate within fruits, a phenomenon called vivipary. Vivipary can substantially reduce yield and product quality in vegetables,…

The Multifaceted Roles of UPF1 in Gene Regulation
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellRaxwal et al. uncover the roles of the RNA helicase and ATPase UPF1 in regulating gene expression. The Plant Cell (2020) https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00244
By Vivek K. Raxwal and Karel Riha
CEITEC Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic
Background: Gene expression, i.e., the…
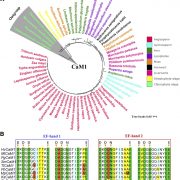
Calmodulin and Salt Tolerance
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideSalt stress is a major abiotic factor restricting crop growth and productivity. Excess sodium (Na+) causes ion toxicity and ion imbalances. Maintaining lower Na+ accumulation in shoots is crucial for salt tolerant plant species and genotypes under salt stress. Lower shoot Na+ accumulation in plants…

