
Plants (RNA) Editors: Testing for Conservation in RNA Editing in moss and angiosperms
Research, The Plant Cell: In BriefWhen I was a kid, I remember keeping a bottle of wite-out with my pens for the inevitable spelling mistake. Now, in the digital age, I either let my word processor autocorrect spelling errors or wait for the red squiggly line under suspicious words.
On any given day, a single (plant) cell by far out-writes…
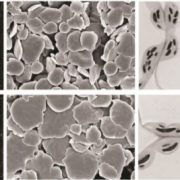
Which Factors Control Starch Granule Initiation?
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefStorage and remobilization of sugar molecules play important roles for the growth and survival of living organisms. Besides a few exceptions, animals store carbohydrates in the form of soluble glycogen while green plants and algae bank glucans as insoluble starch. Starch forms the basis of human nutrition…

Comparative profiling examines roles of DNA regulatory sequences and accessible chromatin during cold stress response in grasses
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPhysical access to regulatory DNA, including cis-regulatory sequences found within proximal promoters and distal enhancer elements, is a vital property of chromatin. In turn, their access is determined by nucleosome occupancy and post-translational modification of histone proteins. A continuum of chromatin…

Close Encounters of the ARF Kind: Proximity-based ARF1 GTPase Activity Regulates Vesicle Trafficking
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefADP-RIBOSYLATION FACTOR (ARF) proteins play essential roles in vesicle trafficking by regulating the formation of membrane vesicles that move cargo throughout the cell. Their activity is controlled by specific guanine exchange factors (ARF-GEFs) that activate ARFs by catalyzing a GDP to GTP exchange…
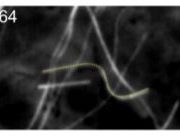
FRA1 Kinesin Prevents Cell Wall Deposition from Going Off the Rails
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefCellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin are the brick and mortar of the plant kingdom, and how they are laid has substantial impacts on plant morphology. Plant cell shape is dictated by the interplay between turgor pressure and heterogeneity in cell wall composition, whereby localized cell wall loosening…
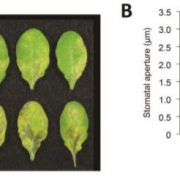
No Entry: SIF2 Closes Stomatal “Doors” to Bacteria by Making Guard Cells SLAC(1)
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefBacteria use stomatal pores as a point of entry to invade plant leaves. As a first line of defense, plants attempt to counteract this attack by restricting bacterial entry simply by closing the stomata. This happens via reduction in turgor pressure of the two guard cells flanking the stomatal pore, the…

ASTREL Projection: Comparative Phylogenomics Uncovers Novel Genes Co-eliminated with the EDS1 Immune Pathway
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe plant immune system is largely centered around immune receptors that monitor for pathogen-derived signatures. Extracellular immunity is afforded through cell-surface receptors recognizing common microbial motifs like bacterial flagellin or fungal chitin (Boutrot and Zipfel, 2017). By contrast, intracellular…
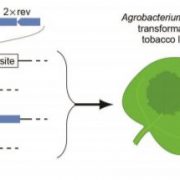
Shooting for the STARRs: A Modified STARR-seq Assay for Rapid Identification and Evaluation of Plant Regulatory Sequences in Tobacco Leaves
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefA single genome gives rise to different cell types and organs in response to precise temporal and spatial regulation of gene expression, driven by developmental and environmental cues. These expression patterns are orchestrated by cis-regulatory elements, distal enhancers and gene-proximal promoters.…
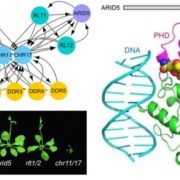
Remodeling Chromatin in an ARID Environment
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe control of gene expression is of fundamental importance for cellular life. In Eukaryotes, linear DNA is wrapped around nucleosomes that constitute a physical barrier to active transcription. Chromatin remodeling complexes modulate the composition, stability and positioning of nucleosomes therefore…

