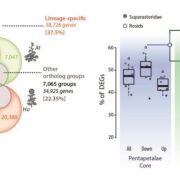
All Together Now: Phylotranscriptomics Reveals Core Responses to Fungal Infection Across the Pentapetalae
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefOver 450 million years of land plant evolution has led to the acquisition of diverse and often overlapping sets of defense responses that limit pathogen infection. Decades of research has uncovered canonical immune pathways that provide resistance to specialist (hemi)-biotrophic pathogens relying on…
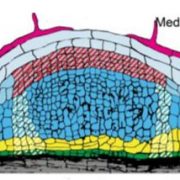
A Nod to Their Ancestors: Mutation of MtNOOT1 Highlights Conserved Nodule Development
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefNitrogen is an essential component of amino acids, nucleic acids, and even chlorophyll. Plants cannot grow without it. However, acquiring nitrogen is difficult as plants cannot use the most common form, atmospheric nitrogen (N2). To solve this, a select group of flowering plants have evolved to harness…
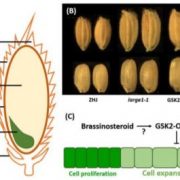
When Less is More: GSK2-OML4 Module Negatively Regulates Grain Size in Rice
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefSeed size is a major component of seed yield. Unveiling the control of seed size provides a theoretical foundation for developing new strategies to boost crop production in the context of global food security. How plants determine their seed size is also a fascinating question in developmental biology.…
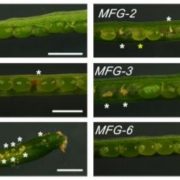
Stop the FUSS: BPCs restrict FUSCA3 transcription to promote ovule and seed development
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefTightly controlled genetic programs regulate developmental phase transitions within distinct tissues and cells. This is especially true for the vegetative-to-reproductive and reproductive-to-seed developmental phase changes that ensure the production of gametes capable of generating viable seed upon…
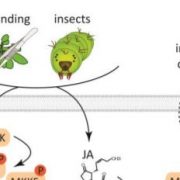
Defense, fast and slow: activation of different MAPK pathways in response to wounding
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIn a world full of herbivores and mechanical stresses, the ability to sense and respond to wounding is crucial for plants, as injuries open doors for phytopathogen entry and allow uncontrolled evaporation. Wounding triggers local and systemic defenses that heal injuries, make plants taste unpleasant…
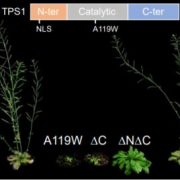
Life is Sweeter with Trehalose 6-Phosphate
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefBesides making our daily lives sweeter, sugars are the most important energy source in all organisms. Balancing their availability and regulating their partitioning between tissues are major determinants for growth and development. In plants, sucrose is the main product of photosynthesis and is transported…
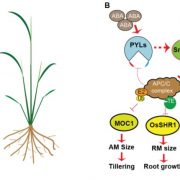
APC/CTE Shapes Rice Architecture from Top to Bottom
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefGibberellins (GAs) and abscisic acid (ABA) affect plant development in an opposite manner. GA is generally considered a growth promoting hormone, whereas ABA signaling, triggered in response to stress, counteracts the GA effects and restricts growth under suboptimal conditions (Vanstraelen and Benkova,…
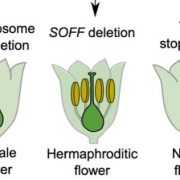
Y keep your X? Insights into the genetic basis of plant sex chromosome evolution
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefContrary to animals, sex chromosomes in flowering plants (angiosperms) have evolved at least hundreds of times independently, providing an opportunity to unravel the mechanisms underlying their repeated evolution.
In the XY system, the Y chromosome dominantly confers male identity: XY individuals…
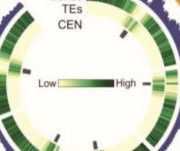
On the Importance of Variation: A High-Resolution Map of Copy Number Variants in Arabidopsis
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefLinking genotype to phenotype is a major challenge in plant biology. Phenotypic variation observed between individuals of a same plant species is the consequence of a vast array of genetic variation, including Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) and small or large structural variants including Copy…

