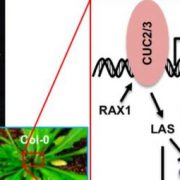
Activate, Breakdown, Branch Out: CUC2/3-DA1-UBP15 Controls Axillary Meristem Initiation
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefShoot architecture is a key ecological and agricultural trait that impacts biomass, the potential to harvest light, planting density, and the reproductive success of a plant. Branching is a prominent feature of plant shoot architecture. A shoot branch develops from an axillary bud, which is located in…
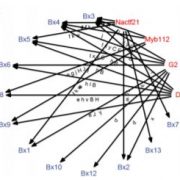
Drawing in the Net: Forty-Five Maize Gene Regulatory Networks from Over 6,000 RNA-Seq Samples
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefEukaryotic gene expression is largely governed by transcription factors (TFs), the nuclear proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences and determine when and where genes are turned on. Transcriptional gene regulatory networks (GRNs) that modulate developmental processes and environmental responses consist…
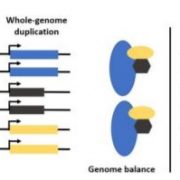
Gene Dosage Balance Immediately Following Whole-Genome Duplication in Arabidopsis thaliana
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefFlowering plants have witnessed multiple cycles of whole-genome duplication (WGD) over the past 200 million years of evolution. Typically, WGD increases genome size and gene content, followed by gene loss, or fractionation, depending on functional categories. Certain classes of genes are retained as…
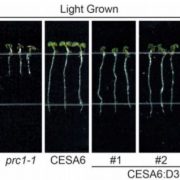
Another Brick in the Plant Cell Wall: Characterization of Arabidopsis CSLD3 Function in Cell Wall Synthesis
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPlant cell walls are one of the great engineering feats of nature, providing immense structural strength and durability. The core components of plant cell walls (pectin, hemicellulose, and cellulose) can occur in different proportions and vary in their structure and assembly, thus allowing cell walls…
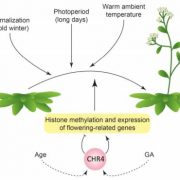
Remodeling Flowering: CHROMATIN REMODELING 4 Promotes the Floral Transition
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPlants that fail to flower at the right time will lose out on seed production. Hence, the transition from vegetative growth to the reproductive phase depends strongly on environmental signals. Cold winter temperatures and long days are seasonal cues that stimulate flowering through vernalization and…
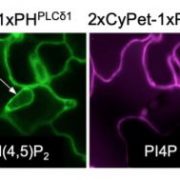
Good Fats, Bad Fats: Phosphoinositide Species Differentially Localize to Plant-Pathogen Interfaces and Influence Disease Progression
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefMany filamentous pathogens invade living plant cells with specialized intracellular infection structures (haustoria) that promote microbial growth. Cytological studies demonstrate that the haustoria of fungal and oomycete pathogens are separated from host cell cytoplasm by a highly differentiated and…
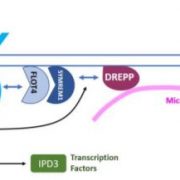
DREPP in Nanodomains Regulates Microtubule Fragmentation during Symbiotic Infection
Research, The Plant Cell: In BriefIn the legume-rhizobium root nodule, nitrogen fixing rhizobia are accommodated inside plant cells. In the Medicago – Sinorhizobium model system, the internalization of rhizobia into the host plant is triggered by Nod factors secreted from the symbiotic bacteria. The signals are perceived by the host…
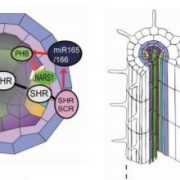
It’s All in the Neighborhood: SHORTROOT-mediated Intercellular Signals Coordinate Phloem Development in the Root
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIn all multicellular organisms, tissue patterning and organogenesis are governed by asymmetric cell divisions (ACDs) and the cellular exchange of positional cues. Plants, unlike animals, undergo post-embryonic organogenesis due to the maintenance of stem cells in specialized niches. One such niche, the…
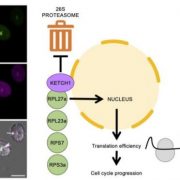
KETCHing up with gametogenesis: nucleocytoplasmic import and cell cycle control
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIn eukaryotes, active import of large signaling molecules and proteins over 40kD in the nucleus is mediated by aptly named “importin” proteins. As there are considerably fewer importins than there are cargos, determining how cargo-transporter specificity is mediated constitutes a challenging issue…

