
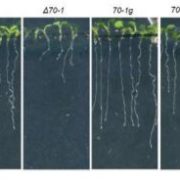
Double Crossed: CDKG1 Regulates Crossover Formation by Stabilizing Meiotic and Somatic Recombination Intermediates
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefGenetic recombination is the process by which novel genotypes are generated from the genetic material of both parents. In eukaryotes, homologous chromosomes synapse and recombine during meiotic prophase I, during which double-stranded breaks (DSBs) are formed by DNA topoisomerases such as SPO11. If large…
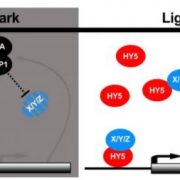
Chimeric Activators and Repressors Define HY5 Activity
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefEarly during seedling development and throughout their lives, plants sense and adapt to their constantly changing environment. Germinated seedlings perceive light which triggers a major developmental switch ultimately leading to photoautotrophic growth. This complex process, referred to broadly as photomorphogenesis,…
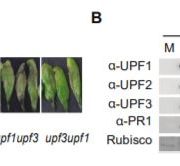
Security Notice: This Plant Immunity is under mRNA Surveillance
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefEvery manufacture relies on a quality control process to ensure that the released product is without defects. Similarly, each transcript leaving the eukaryotic nucleus is subjected to mRNA surveillance, which helps to ensure that only flawless mRNAs are directed to translation. For example, transcripts…
A Roadmap Toward Large-Scale Genome Editing in Crops
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIf the planet does not turn to ash before 2050, farmers will need to produce twice as much on roughly the same available arable land to feed the ever-growing world population. But since the Green Revolution of the 1950s and 1960s, progress in crop yield has been incremental. And for good reason: most…
Twin-Positive Motifs Function as Specific Plastid Targeting Signals
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPrecise trafficking of proteins to their proper destinations in the cell, whether to an organelle, a membrane, or the cytoplasm, is required for optimal cellular function. Because most plastid proteins are nucleus-encoded and translated in the cytoplasm, proper targeting and import relies on the presence…
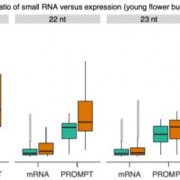
Exosome-Deficient Mutants Reveal Rare Promoter Upstream Transcripts (PROMPTs) in Arabidopsis
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIn eukaryotes and archaea, protein-coding DNA is transcribed to messenger RNA (mRNA) via a preinitiation complex (PIC) composed of over 100 proteins, among them regulatory proteins, numerous transcription factors, and RNA polymerase II—the enzyme that produces precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA). Although…
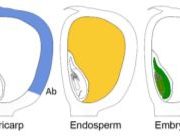
The Way Out: A Transcriptionally Unique Group of Endosperm Cells Implicated in Nutrient Export to the Embryo
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefSuccessful development of the maize (Zea mays) kernel requires proper nutrient transport and signaling among its genetically distinct components: the embryo that gives rise to the next generation, the endosperm that nourishes the embryo, and the maternal tissues that surround the embryo and the endosperm…
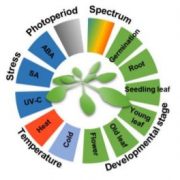
The R-loop: An Additional Chromatin Feature for Gene Regulation in Arabidopsis
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefR-loops are three-stranded nucleic acid structures composed of a DNA-RNA hybrid and a displaced single-stranded DNA. R-loops are stable structures as they form an intermediate A/B conformation of the RNA-DNA hybrid that is more stable than the B form of dsDNA or A form of the dsRNA. Recent evidence reveals…
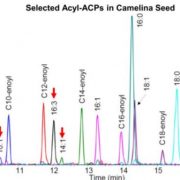
A Closer Look at Acyl-ACPs in Lipid Metabolism
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefAcyl lipids are a wide range of compounds that have diverse functions in membrane synthesis, energy storage, and signal transduction. Fatty acids are key building blocks of acyl lipids that are synthesized by the fatty acid synthase complex via sequential condensation of two-carbon units to reach lengths…

