The Lure of Lignin: Deciphering High-value Lignin Formation in Seed Coats
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefLignin is a major functional component of plant secondary cell walls and the second most abundant biological polymer on Earth after cellulose. Understanding the biosynthesis of lignin has huge practical implications because lignin is a major by-product of processes that use cellulosic biomass for industrial…

Ripe for the Picking: Finding the Gene Behind Variation in Strawberry Fruit Color
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefSweet ripe strawberries (Fragaria spp.) come in colors ranging from deep burgundy to white and everything in between. Such variation attracts consumers and gardeners alike, making fruit color an important breeding target. Strawberry fruit receptacles vary in color due to different levels of anthocyanins.…
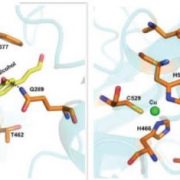
Fine Tuning Floral Morphology: MADS-Box Protein Complex Formation in Maize
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPlant floral organ development is orchestrated by master regulatory genes that control the differentiation of meristem tissue. According to the ABC(DE) model of flower development (Bowman et al., 1989; nicely summarized by Irish, 2017), different floral organs form in concentric whorls (verticils) in…
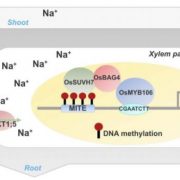
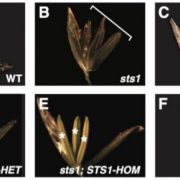
A DNA Methylation Reader with an Affinity for Salt Stress
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefHigh levels of soil salinity lead to toxic accumulation of sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-) ions in plants, which adversely affect plant growth and yield. Plants use several strategies to cope with salt stress. These include removal and compartmentalization of toxic ions, and maintenance of growth and…
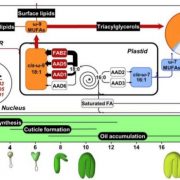
Lipid Synthesis and Beyond: SAD Fatty Acid Desaturases Contribute to Seed Development
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefFatty acid (FA) desaturases have long been recognized as key enzymes in synthesizing lipids containing unsaturated FAs, which constitute the majority of seed oil. As a major class of FA desaturases, stearoyl-acyl carrier protein desaturases (SADs) catalyze the first desaturation step, producing the monounsaturated…
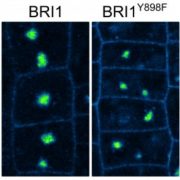
Get it Sorted: A Classic Endocytic Sorting Mechanism in Mammals is Conserved in Plants
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe plasma membrane (PM) is an exquisitely dynamic structure. It has to be, since it serves as the interface between the cell and the ever-changing environment. PM-associated signaling proteins shuttle quickly between the PM and the cell’s interior to help the organism respond to whatever comes its…
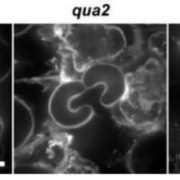
Let’s stick together – a pectin biosynthetic mutant reveals the interconnectedness of plant cell walls
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe plant cell wall is vital for plant survival—it mediates defence against pathogens, provides structural stability and controls growth to produce final plant form. Plant cell walls are composite structures formed mainly from cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectins, and the interactions of these components…
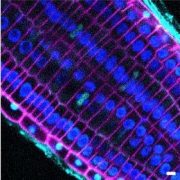
Follow that Protein: SNAP-tagging Permits High-resolution Protein Localization
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefProtein analysis relies heavily on the production of ‘tagged’ proteins, i.e. recombinant proteins that contain both a functional peptide sequence and a peptide or chemical label (the ‘tag’). Common tags include fluorescent proteins (FPs), which make tagged proteins easier to detect, as well as…

Tracking the Courier: In Planta Imaging of NADH/NAD+ Ratios with a Genetically Encoded Biosensor
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe movement of electrons between molecules and organelles via redox reactions is a cornerstone of cellular metabolism. Electron carriers such as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and its phosphorylated form NADP mediate reduction or oxidation reactions via their own conversion between reduced…

