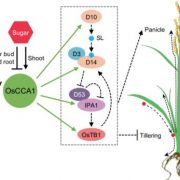
Sugars Inform the Circadian Clock How to Shape Rice Shoots via the Strigolactone Pathway
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefCircadian clocks act as universal timekeepers to harmonize internal processes with external day-night rhythms. Genetic feedback loops gear these inner clocks by approximating time in response to dawn-dusk cycles. In plants, development, growth, hormone action, metabolism and other downstream events are…
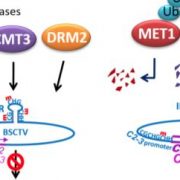
The Great Escape: How a Plant DNA Virus Hijacks an Imprinted Host Gene to Avoid Silencing
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPlant viruses are a major threat to global food security. The large family of geminiviruses has a broad pathogenic impact on economically important crops such as maize, tomato, and cassava and causes millions of tons of losses per year worldwide (Rojas et al., 2005). Geminiviruses possess a circular…

More Than Just a FAD(5): Unsaturated Fatty Acids in Chloroplasts Elicit Protective Autoimmunity
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefArabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) chloroplast-division mutants that have abnormally large chloroplasts have been around for quite some time, not only because they can be identified relatively easily through screening (Pyke & Leech 1991) and because their spectacular morphology sparks intrigue, but…
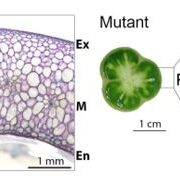
Tempting Fate: A Guanylate-Binding Protein Maintains Tomato Fruit Cell Differentiation
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefTissues are composed of specialized cell types. As a cell matures, it acquires the characteristics associated with a specific identity, or fate. This process is called cell differentiation and is crucial for proper organ development. However, after a differentiation program is initiated, the mechanisms…

Peripheral? Not Really! The Extracellular Arabinogalactan Proteins Function in Calcium Signaling
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefArabinogalactan proteins (AGPs) are a family of extracellular proteoglycans that existed in land plants and algae (Johnson et al., 2017). AGPs are part of the hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein (HRGP) superfamily that also includes extensins and proline-rich proteins. Based on the protein sequence, a glycosylphosphatidylinositol…
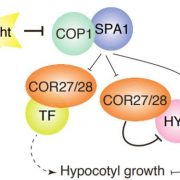
How COR27 and COR28 Promote Hypocotyl Growth: Bind to COP1 And Suppress HY5 Activity
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefSeedling growth and development rely on the successful integration of information from external signals, such as light and temperature, and endogenous processes, such as the rhythmic ticking of the circadian clock. Together, these signaling pathways tune hypocotyl elongation to allow seedlings to escape…
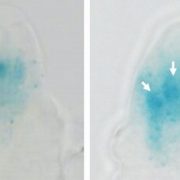
The Sounds of Silence: Cell Fate Restriction and RNA Silencing in Plant Ovules
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefGamete formation in sexually reproducing plants begins with formation of a “mother cell” that undergoes meiosis to generate haploid spores. Haploid spores further develop into gametophytes within which gametes differentiate. In flowering plants (angiosperms), including crop systems, the female mother…

On UPF Proteins, Baking Cookies, and the Many Targets of Nonsense-Mediated RNA Decay
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefWhen we cut out cookies from rolled-out dough, we often end up with unwanted dough scraps, and sometimes the dough sticks to the cookie-cutter, resulting in misshapen cookies. Just like these misshapen cookies, faulty or aberrant RNAs can arise in cells due to mistakes during transcription, RNA processing,…

A damascene moment: the genetic basis of complex petals in Nigella
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefFrom the flat white sheets of our favourite weed Arabidopsis thaliana to the colourful cups and spirals of orchids, petals come in a spectacular array of shapes, sizes, colours and textures. These elaborate forms have often evolved to attract pollinators. For example, bee orchids produce petals that…

