
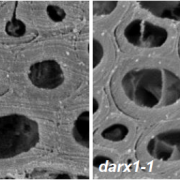
A Role for Autophagy in Plant Lipid Homeostasis
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefAutophagy is the conserved eukaryotic mechanism by which cytoplasmic components such as macromolecular complexes, organelles, and cytosol are degraded in the lysosome or vacuole (Reggiori and Klionsky, 2013). Basal autophagy ensures that obsolete organelles and misfolded proteins are removed from the…
Methionine-Derived Glucosinolates: The Compounds that Give Brassicas their Bite
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe compounds that give wasabi (Eutrema japonicum) its kick and bok choy (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis) its distinctive flavor are breakdown products of glucosinolates derived from not so pungent amino acids. These zesty phytochemicals help Brassica plants adapt to their many environmental niches worldwide…

The White Stripes Featuring ALBOSTRIANS, a Chloroplast-Localized CCT Domain Protein
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefVariegation in different organ types has been of great interest to biologists. The study of pigment variegation in maize kernels led to the discovery of transposable elements (McClintock, 1950), whereas the study of eye pigment variegation in Drosophila has led to interesting insights into chromatin…

Letting Sleeping DOGs Lie: Regulation of DOG1 during Seed Dormancy
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe auspicious timing of seasonal germination is crucial to plant fitness and survival. Consequently, seed dormancy is tightly regulated by both developmental and environmental cues, which are integrated via crosstalk between several phytohormone signaling pathways including gibberellins, abscisic acid…
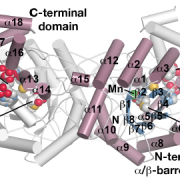
Cell Wall Polymers: The Importance of Deacetylation
Research, The Plant Cell: In BriefMany of the polysaccharides that make up the plant cell wall carry acetate side groups. Notably, the degree of such acetylation is not always the same—even within the same species, it changes over the course of development and is different between tissues. While the mechanism for adding acetyl groups…

A growing reputation for FRUITFULL genes
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe sub-functionalization and neo-functionalization of duplicated MADS-domain containing transcription factor coding genes has driven angiosperm evolution. These transcription factors control almost every facet of reproductive development in plants and are key breeding targets for crop yield improvement.…
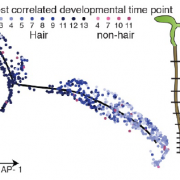
The Future is Now: Gene Expression Dynamics at Single Cell Resolution
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefFor the past 10 years, a popular method to study global gene expression changes has been RNA sequencing of bulk tissues. However, an inherent limitation of this approach is the confounding of multiple cell types or multiple developmental stages. By contrast, new technologies enable transcriptional profiling…
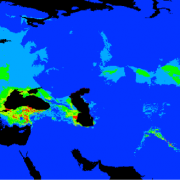
Loss-of-Function, a Strategy for Adaptation in Arabidopsis
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefWhen thinking about adaptive processes, the concept of genetic innovation comes to mind. At the genomic scale, a lot of attention has been given to gene introgression, duplication, and novel functionalization to uncover the bases of adaptation. However, as the majority of genes are non-essential, both…
Shedding New Light on the Ancient Process of Photosynthesis in Cyanobacteria
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefAll photosynthetic organisms, from cyanobacteria to flowering plants, must continuously adjust to changing light conditions to maximize photosynthetic efficiency while protecting their delicate photochemical centers. During photosynthesis, light energy is preferentially captured by photosystem I (PSI)…

