
The AREB1-ADA2b-GCN5 Complex Regulates Gene Expression during Drought Stress
Abiotic stresses constitute a global threat to agricultural crop production and natural ecosystems. One of the most prominent abiotic stresses is drought, which dramatically alters plant physiology and morphology. Studies in model organisms have shed light into how plants respond to drought stress, including…
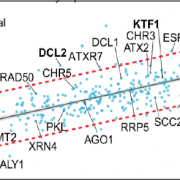
Blocking the Guards: The ALY1 Nuclear Export Protein Is Required for DNA Methylation Machinery to Function
Plants constantly face the threat of attack from many directions. Organisms like bacteria, viruses, and fungi must be blocked from entering a plant’s cells, or quickly targeted for destruction once inside. Within the plant genome itself, transposable elements lie in wait for reactivation. In addition,…
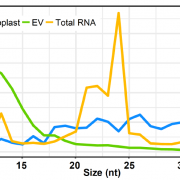
tyRNA Bubbles: Extracellular Vesicles Carry 10–15-nt Small RNAs and Specific Groups of MicroRNAs
Plant and animal cells produce various types and sizes of extracellular vesicles (EVs). Mammalian EVs function in intercellular communication and plant EVs carry defense compounds, defense-related proteins, and RNAs and participate in the defense against fungal pathogens (reviewed in Hansen and Nielsen,…
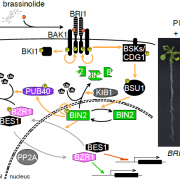
Plants on (Brassinos)steroids: Degradation of the Transcription Factor BZR1 by the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase PUB40
Brassinosteroids (BR) are the only plant hormones with an animal counterpart: steroid hormones. Analysis of BR signaling demonstrated that steroid receptors could reside at the plasma membrane and modulate growth and gene expression, an observation that is now becoming appreciated in non-plant systems…
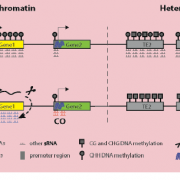
Meiocyte-specific Small RNAs and Meiotic Recombination: Questions and Anthers
Small RNAs regulate gene expression and epigenetic modifications (via RNA-directed DNA methylation), and therefore play key roles in plant development (reviewed in Borges and Martienssen, 2015). Moreover, emerging evidence indicates that small RNAs may have a role in the repair of double-stranded breaks…
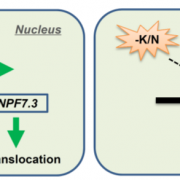
It’s an Uphill Battle: The MYB59-NPF7.3 Regulatory Module and its Role in Nutrient Transport
Fertilizer use in agriculture is one of the essential strategies in improving crop productivity and ensuring global food security. Two primary nutrients in fertilizers are potassium (K+) and nitrate (NO3-), which are vital for proper plant function. In order to formulate better approaches in optimizing…
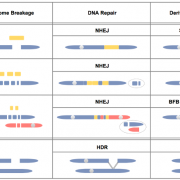
Smashing barriers in biolistic plant transformation
A foundation of modern biotechnology is the ability to stably introduce foreign DNA into an organism. The two most widely used methods, Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and biolistics, are both steeped in a rich history of creative exploration into the molecular unknown. Agrobacterium research accelerated…
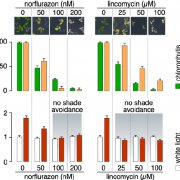
The shade of things to come: plastid retrograde signaling and shade avoidance
Plants compete with each other over finite resources like water and nutrients, but also for sunlight when they grow in each other’s shadow. Light filtered through leaves is rich in far-red light and initiates responses, known as shade avoidance syndrome (SAS), that aim to out-compete neighbors by promoting…
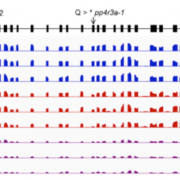
The Protein Phosphatase 4 Complex Functions in miRNA Biogenesis in Arabidopsis
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short (typically 21–22 nucleotide), single-stranded noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression, mainly via posttranscriptional gene silencing. The miRNA biogenesis pathway is complex, involving numerous proteins, and is highly conserved in plants. If this pathway is hampered,…

