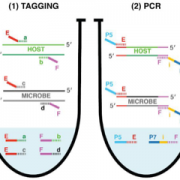
Measuring both microbial load and diversity with a single amplicon sequencing library (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAmplicon sequencing of microbial DNA is a gold standard for analyzing the relative abundance of microbes in host-associated microbiomes. To gain more accurate insights into microbiome changes, it is crucial to know the absolute abundance of microbes, which can be analyzed by integrating relative abundance…
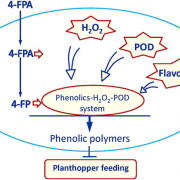
A chemical elicitor, 4- fluorophenoxyacetic acid suppresses insect pest populations and increases crop yields (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant strengtheners, synthetic chemical elicitors, have been shown to enhance plant resistance against various insect pests without toxic effects on the environment, but evidence is lacking for a significant increase in crop growth and yield after using these elicitors. To address this, Wang et al. studied…
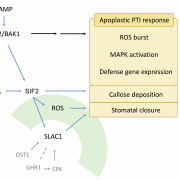
STRESS INDUCED FACTOR 2 regulates arabidopsis stomatal immunity through phosphorylation of the anion channel SLAC1 ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants detect microbes by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that sense common conserved structures called microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) and trigger the innate immunity responses. Chan et al. identified a new player in the Arabidopsis immune response known as STRESS INDUCED FACTOR 2…

Plant Science Research Weekly: June 5th
WWR Full PostReview: Functions of anionic lipids in plants
Moving materials within and out of cells requires that membranes carry identification labels, but when the membrane itself moves, that ID label must be updated. These requirements are met ingeniously by the anionic lipids, which are both a modifiable information…

Recognizing Plant Physiology authors: Nat Graham
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Author ProfilesNat Graham, first author of Plant genome editing and the relevance of off-target changes
Current Position: Molecular Biology Scientist at Pairwise – Durham, North Carolina, USA
Education: Ph.D. in Biology, University of Missouri - Columbia
Non-scientific Interests: brewing beer, cooking, hiking
Brief…

Recognizing Plant Cell authors: Anindya Ganguly
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: Author ProfilesAnindya Ganguly, first author of FRA1 Kinesin Modulates the Lateral Stability of Cortical Microtubules Through Cellulose Synthase-Microtubule Uncoupling Protein
Current Position: Research Assistant Professor, Molecular Physiology and Biological Physics, University of Virginia, USA
Education: BS and…

Recognizing Plant Physiology authors: Chenyong Miao
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Author Profiles
Chenyong Miao, first author of Increased power and accuracy of causal locus identification in time-series genome-wide association in sorghum
Current Position: PhD candidate in the Schnable lab at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln
Education:
Ph.D. in Agronomy (in progress ) at the University…

Recognizing Plant Cell authors: Sabine Brumm
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: Author ProfilesSabine Brumm, first author of Coordinated activation of ARF1 GTPases by ARF-GEF GNOM dimers is essential for vesicle trafficking in Arabidopsis
Current Position: Post-Doc, Sainsbury Laboratory University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK
Education: Ph.D. from University of Tübingen, ZMBP, developmental…

Recognizing Plant Physiology authors: Matthew Neubauer
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Author ProfilesMatthew Neubauer, first author of Loss of the Arabidopsis Acetyltransferase NAA50 Induces ER Stress and Immune Responses and Suppresses Growth
Current Position: Postdoctoral Researcher, Department of Plant and Microbial Biology, North Carolina State University
Education: B.S., Biology, Loyola University…

