
Multiple metabolic innovations and losses are associated with major transitions in land plant evolution (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe colonization of land by a single streptophyte algae lineage around 450 million years ago culminated in the evolution and radiation of all terrestrial flora, the embryophytes. Adapting and thriving in the land environment required many morphological and physiological innovations, as well as the acquisition…
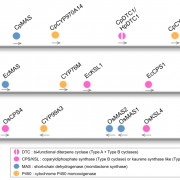
Genomic evidence for convergent evolution of gene clusters for momilactone (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants produce a rich diversity of chemical compounds. In fungi, the genes encoding specialized biosynthetic pathways are frequently arranged in contiguous loci forming biosynthetic gene clusters (BGC). In plants, BGCs are not common, however, some cases have been found in angiosperms. Among the known…
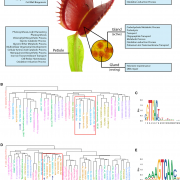
Repurposed genes and the evolution of plant carnivory (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCarnivorous plants attract, trap, digest, and import nutrients from small animal prey, enabling these plants to thrive in nutrient-poor soil. Palfalvi et al. sequenced, annotated, and compared draft genomes from the family Droseraceae for the Venus flytrap (Dionaea muscipula), the waterwheel plant (Aldrovanda…
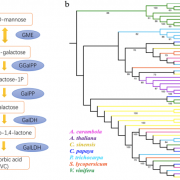
Dissecting the genome of star fruit (Averrhoa carambola L.) (Hort. Res.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStarfruit is a sweet and sour fruit that has a shape of a five-point star. It belongs to the Oxalidaceae family and is a fruit of Averrhoa carambola, a species of tree native to tropical Southeast Asia. The fruit is consumed in many parts of the world and is known for its many economic, medicinal and…
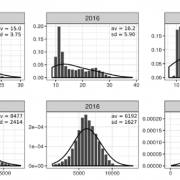
Improvement of predictive ability in maize hybrids by including dominance effects and marker x environment models ($) (Crop Sci.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHeterosis is phenomenon that occurs when crossbred individuals show qualities (such as such as size, growth rate, fertility, and yield) that are superior to those of both parents. In maize, heterosis can be explained in terms of hybrid vigor, and this has been well studied using traditional breeding.…
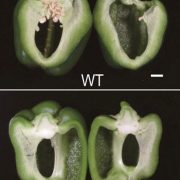
A gene knock-out that leads to seedless parthenocarpic fruits in Solanaceae plants ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyParthenocarpy, or the ability to make fruit without fertilization, is desirable for many reasons including the opportunity to make seedless fruits and a greater resiliency in crop production in the face of climate change. Matsuo et al. identified a new gene involved in parthenocarpy, starting with a…
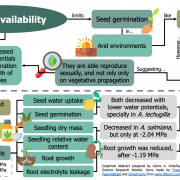
Water availability effects on germination, membrane stability and initial root growth of Agave lechuguilla and A. salmiana (Flora)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLow water availability limits seed germination in arid environments, such as the ones that Agave plants inhabit. As a result, vegetative propagation has been considered their most effective and successful method of reproduction. However, agaves produce several hundreds of seeds, and their natural populations…
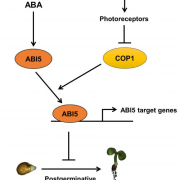
Post germination seedling establishment by ABA in response to light (Plant J.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAbscisic acid (ABA), is implicated in reversible inhibition of seed germination (emergence of radicle) and post-germination seedling establishment (formation of green open cotyledons) during unfavorable conditions. Yadukrishnan et al. analyzed the role of light in ABA- mediated inhibition of post germination…
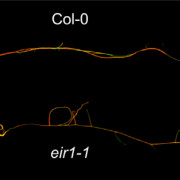
PIN FORMED 2 modulates the transport of arsenite in Arabidopsis thaliana (Plant Comms.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPIN FORMED (PIN) proteins are known for their directional auxin transport capacity. Ashraf et al. found that auxin transporter PINs have sequence similarity to bacterial arsenite transporter arsB, yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae arsenite transporter SsAcr3, and arsenic hyperaccumulator fern Pteris vittata…

