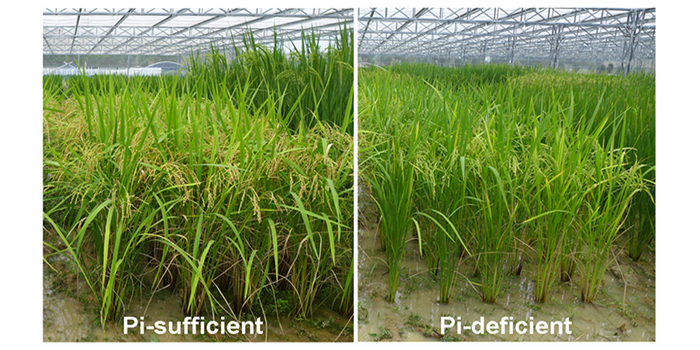
Rice Leaf Erectness Tied to Phosphorus Efficiency
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellRuan et al. discover a protein module that regulates rice leaf inclination in response to soil Pi availability. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00738
Background: As an essential element for plant growth, phosphorus (P) is taken up by plant roots as inorganic Pi (Pi) from the soil solution.…

Adjusting Boron Transport by Two-Step Tuning of Levels of the Efflux Transporter BOR1
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsBoron is an essential plant micronutrient with the narrowest optimal range in the soil of any micronutrient. At neutral pH, boron is present as uncharged boric acid, B(OH)3, which can freely penetrate membranes. Boron plays an important role in cross-linking cell wall components, but boron starvation…

Nitrate Ahoy! Shoot Cytokinin Signals Integrate Growth Responses with Nitrogen Availability
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefNutrients are rarely distributed homogenously in soil. Consequently, plants have local and long-distance signaling systems in place to monitor and coordinate both demand and supply of essential macronutrients such as nitrogen (N). The “N-demand” long distance signal emanates from a section of the…
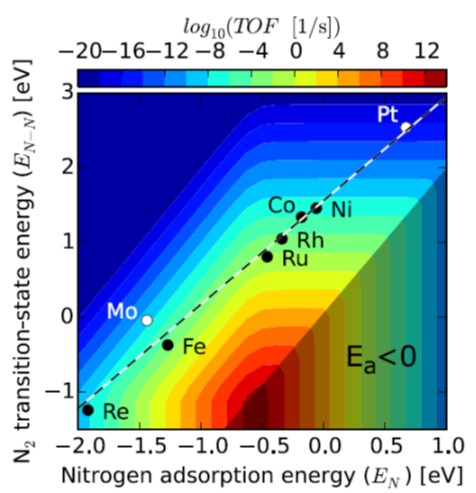
Review: Beyond fossil fuel–driven nitrogen transformations ($) (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyObtaining the high yields needed to feed the human population depends on the application of nitrogen-containing fertilizers to non-leguminous crops, yet the production of these compounds consumes 1 – 2% of global energy output. Plant scientists are familiar with the conversion of N2 to NH3 by nirogenase…

Developing High-Yield Early-Maturation Crops by Manipulating Nitrogen Utilization
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellWang et al. investigate the function of OsNRT1.1A in rice. Plant Cell (2018). https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00809.
By Wei Wang, Bin Hu and Chengcai Chu
Background: To cope with an increasing global population and decreasing availability of arable land, improving crop yield is a major agricultural…
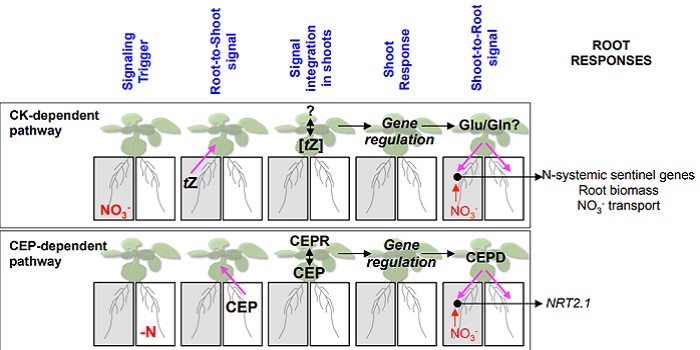
The cytokinin trans-Zeatin plays a role in long distance nitrogen signaling ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants modify gene expression and physiological processes to overcome temporal and spatial variations in nitrogen availability. These modifications rely on complex root-shoot-root signaling networks which are triggered by cytokinin biosynthesis. Poitout and colleagues use mutant analysis, transcriptome…

Sulfur partitioning between glutathione and protein synthesis determines plant growth (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklySulfur is incorporated into the amino acid cysteine (Cys) and also the reactive-oxygen scavenger glutathione (GSH). Speiser et al. investigated the effect of restricting both Cys and glutathione production through a double-mutant analysis in Arabidopsis; sir1-1 is a slow-growing sulfite-reductase deficient…
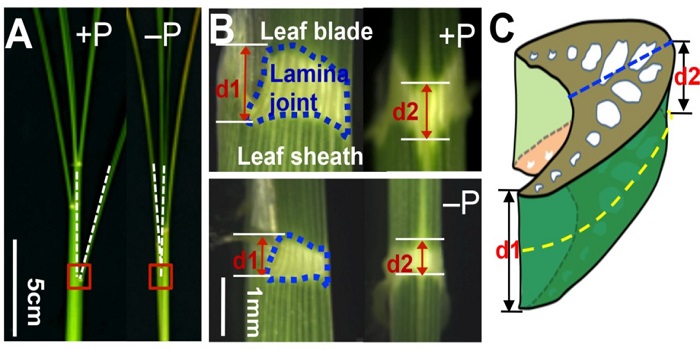
So Inclined: Phosphate Status and Leaf Angle in Rice
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefWhen plants have plenty of room, they can maximize the incoming light by spreading their leaves. However, in modern agricultural fields, plants that hold their leaves upright to decrease mutual shading can be grown at high density. Leaves serve as a reservoir for nitrogen that can be re-mobilized to…
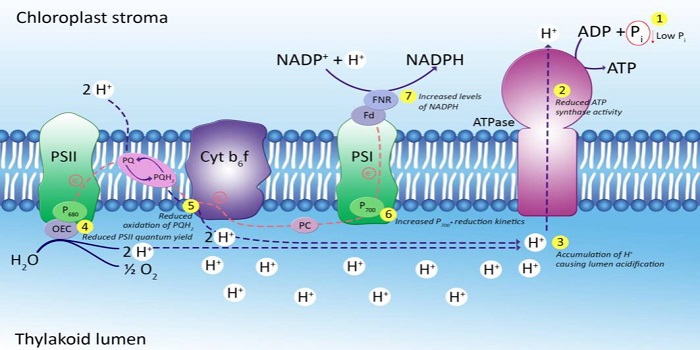
Phosphorous Deficiency and Photosynthesis
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchPhosphorus (P) is an essential macronutrient, and P deficiency limits plant productivity. P influences many aspects of photosynthesis P-deficient plants typically remain green and do not develop leaf chlorosis and yet P starvation immediately affects CO2 assimilation. Specifically, P deficiency is believed…

