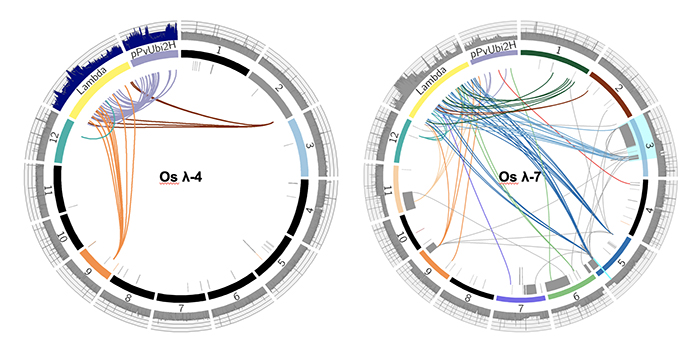
Impact of Biolistic Transformation on the Genome
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLiu et al. show that biolistic transformation can cause extensive damage and rearrangements, including deletions, duplications, chromosome fusions, and copy number variations. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00613
By Jianing Liu and R. Kelly Dawe, Department of Genetics, University…
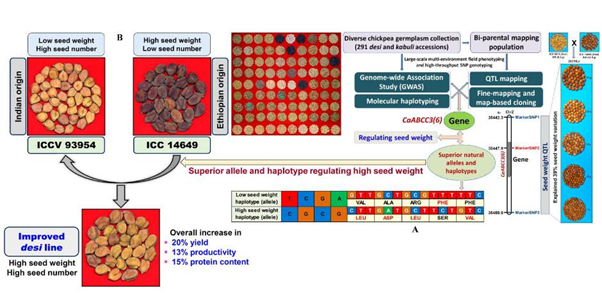
ABC transporter-mediated transport of glutathione conjugates enhances seed yield and quality in chickpea (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIdentifying the genetic determinants of yield and quality traits is essential for crop improvement. Chickpea is the third-most cultivated legume species and is a prominent source of protein to global consumers. Genetic improvement of chickpea, in terms of enhancing its seed size and weight, has been…
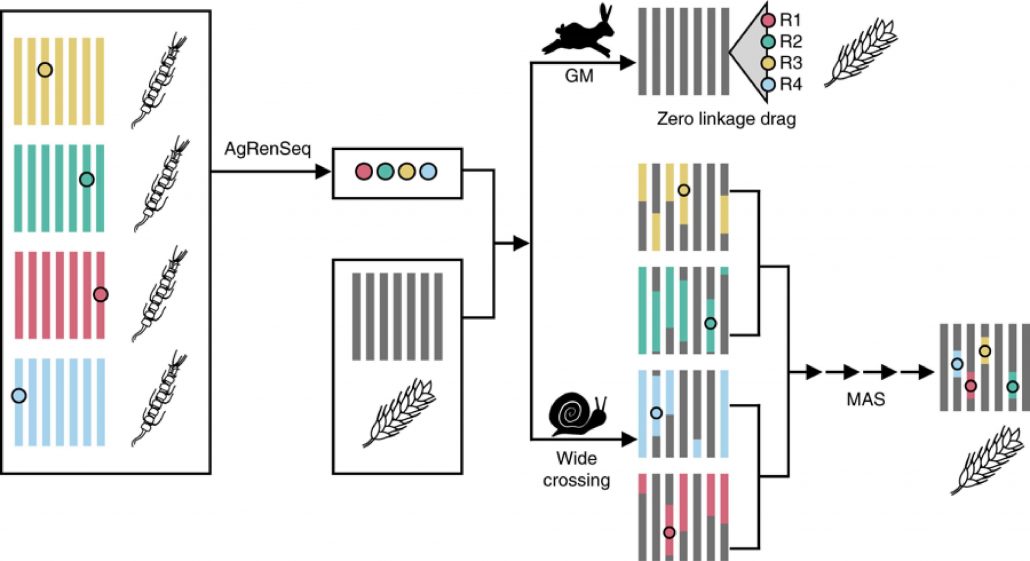
Tapping into the genetic diversity of wild crops for engineering disease resistance (Nature Biotech)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLack of sequence information makes harnessing the diversity of disease resistance (R) genes in wild crops highly challenging. Arora and Steuernagel et al. report AgRenSeq, a reference genome-free technique, for rapid cloning of nucleotide binding/Leucine-rich repeat (NLR) resistance genes from wild…
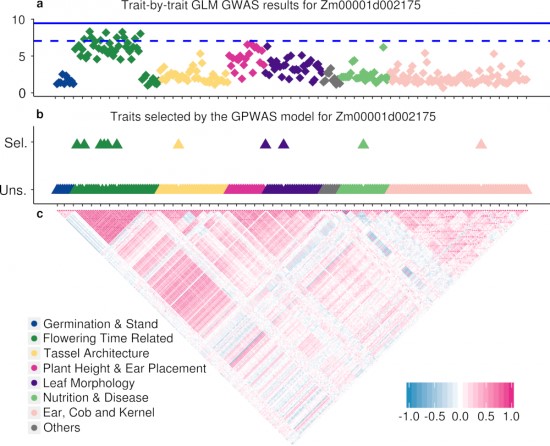
Distinct characteristics of genes associated with phenome-wide variation in maize (Zea mays) (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHigh-throughput plant phenotyping is growing rapidly and enables the collection of dozens or hundreds of traits of the same plant genotype efficiently. The development of this technology expands the diversity of plant phenotypes and brings an opportunity for reexamining the connections between genotype…

AP2-like transcription factor SUPERNUMERARY BRACT controls rice seed shattering and seed size (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNon-shattering seed, or seed that stays attached to the stem when mature, is a key domestication trait that makes harvesting easier. Previous studies have identified several domestication genes that suppress the formation of the seed's abscission zone, thus preventing shattering. Jiang et al. used a…
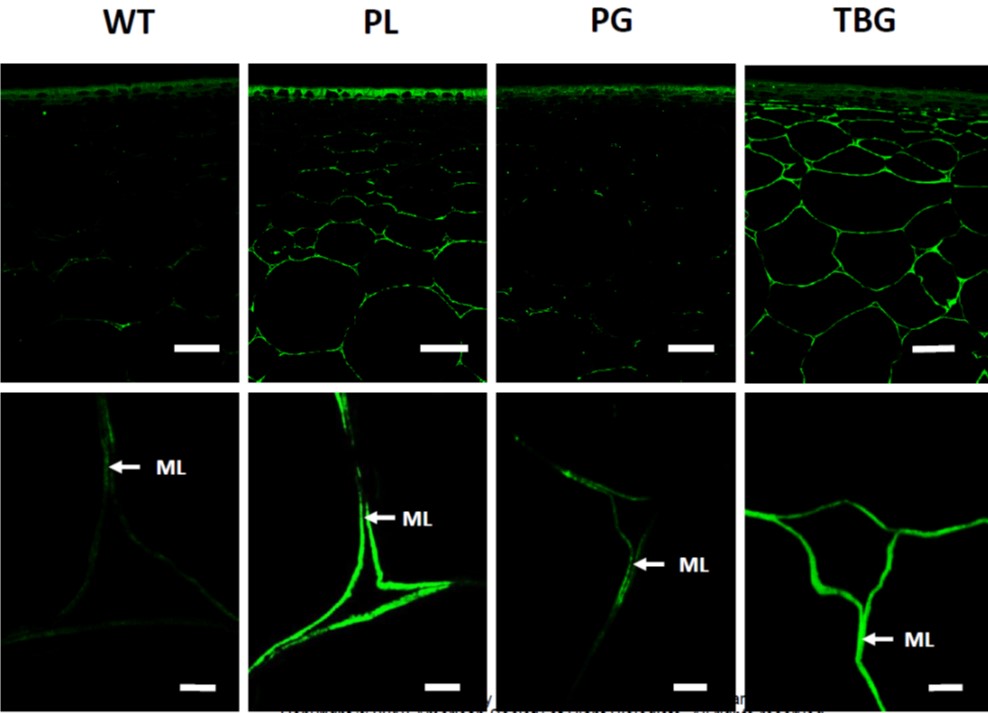
CRISPR Mutants Shed Light on Pectin’s Role in Tomato Fruit Softening
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideTomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruits undergo pronounced softening during ripening. Softening is important for flavor development and overall palatability, but also impacts fruit storage, transportability, and shelf life. Shelf life is a particularly important quality trait of tomato fruits affected by…
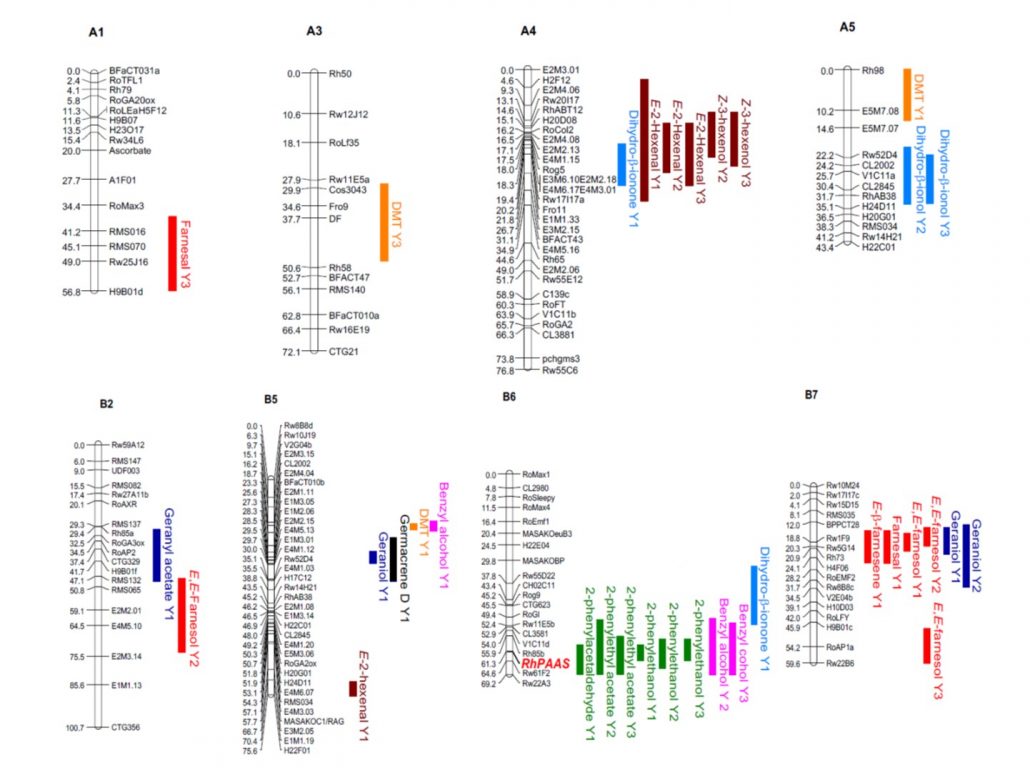
Genetics of rose petal fragrance: RhPAAS and 2-phenylethanol (Plant Phys)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn Romeo and Juliet, Shakespeare wrote, “that which we call a rose, by any other word would smell as sweet,” but the truth is, most roses today don’t smell as sweet as the ones Shakespeare described; selection for prolonged cut flower life has largely been at the expense of fragrance. Roccia seek…
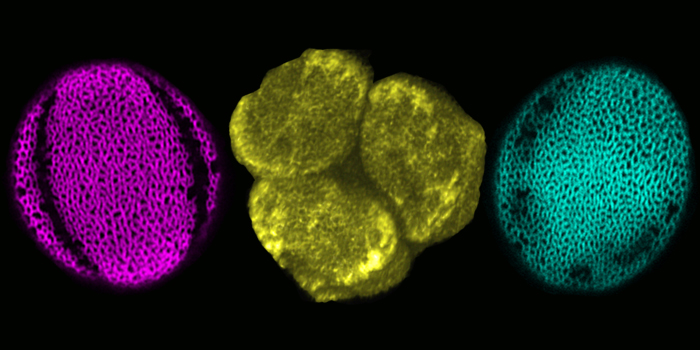
Exploring Pollen Patterns to Learn How Cells Create Distinct Domains
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLee et al. identify a protein involved in pollen aperture development and the formation of distinct membrane domains in microspores. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00442
By Byung Ha Lee and Anna Dobritsa
Background: Pollen grains are famous for their ability to develop various intricate patterns…

APE2 Acts in DNA Demethylation
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellLi et al. demonstrate that APE2 and the DNA 3′ phosphatase ZDP play overlapping roles in active DNA demethylation in Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Cell (2018).
By Jinchao Li and Weiqiang Qian
Background: DNA methylation, the addition of a methyl group to the C-5 position of cytosine, is a…

