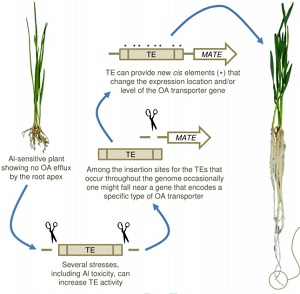
Review: Transposable elements have role in aluminum resistance (J Exp Bot)
Phytotoxic aluminum can drastically harm plant roots, leading to decreased nutrient uptake, water absorption and yields. Many plant species efflux organic anions into the rhizosphere to reduce the toxic effects of aluminum. Some of the genes that encode transporter proteins which mediate organic anion…
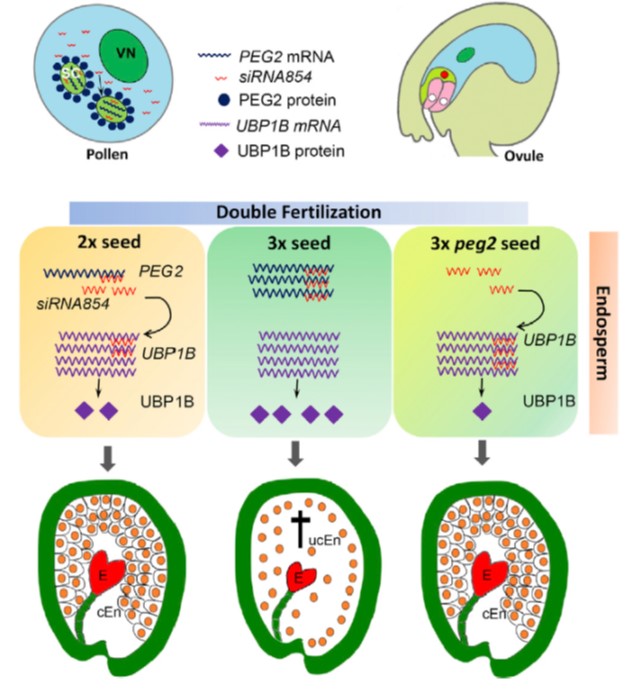
The imprinted gene PEG2 acts as a sponge for the transposon-derived siRNA854, inducing postzygotic reproductive isolation (Devel. Cell)
Closely related species that have different numbers of chromosomes (e.g., 2n versus 4n) are reproductively isolated, and this can arise as a consequence of an unbalancing in the expression levels of maternally- and paternally-imprinted genes. Wang et al. have identified a fascinating mechanism that explains…
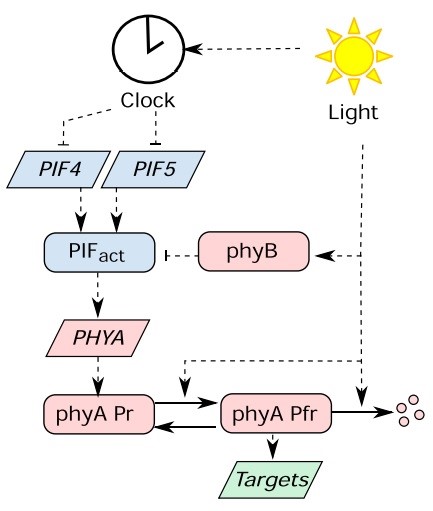
Dawn and photoperiod sensing by phytochrome A ($) (PNAS)
Plants perceive the change of seasons based on measuring the duration of daylight. Flowering is a major seasonal response that depends on photoperiod. In this study, Seaton et al. looked at the role of phytochrome A (phyA) in photoperiod sensing. PHYA is the direct target of PIF4 and PIF5 transcription…
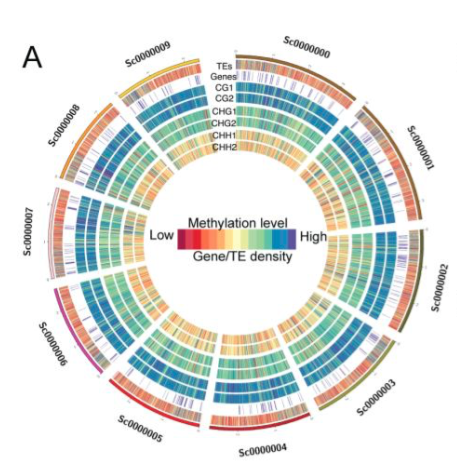
Tea genome expansion linked to TE bursts (Plant Biotechnol. J.)
Expansion of plant genomes is thought to be linked to massive bursts of transposable elements activity. This implies consequences on the distribution of epigenetic modifications required for the silencing of the causative transposons. Consequences of transposon bursts have been extensively described…
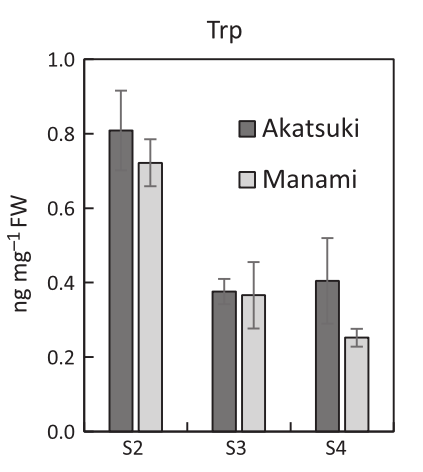
Stony hard phenotype in peach due to transposon insertion into YUCCA ($) (Plant J)
Fruit softening in melting-flesh peaches is triggered by a major accumulation of ethylene at the late stage of ripening. Existence of stony hard peaches showing inhibition of fruit softening has been correlated with low levels of indole-3-acetic-acid inducing low levels of ethylene, but the underlying…

Sweet and Juicy: Identification and Origins of the Dry Alleles in Sorghum
Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) is the fifth most important cereal crop globally and is considered to be the “camel among crops” due to its ability to flourish in low-nutrient soils and to withstand prolonged drought. Cultivated varieties are phenotypically and morphological diverse. Consequently, sorghum…
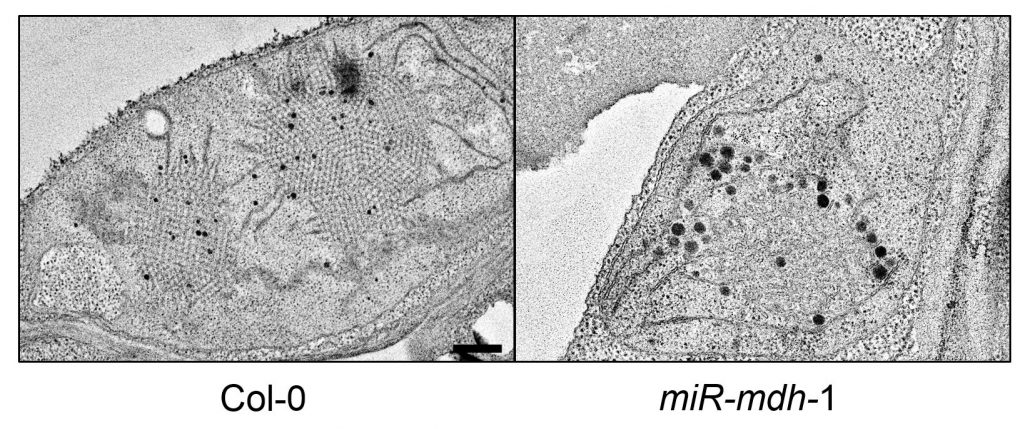
Moonlighting Role of Plastidial NAD-MDH
Schreier et al. investigate the role of a plastid malate dehydrogenase in early chloroplast development. Plant Cell 30: 1745-1769
Background: Malate dehydrogenases (MDH) are enzymes that are widespread in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. MDH interconverts oxaloacetate and malate, using either NAD or…
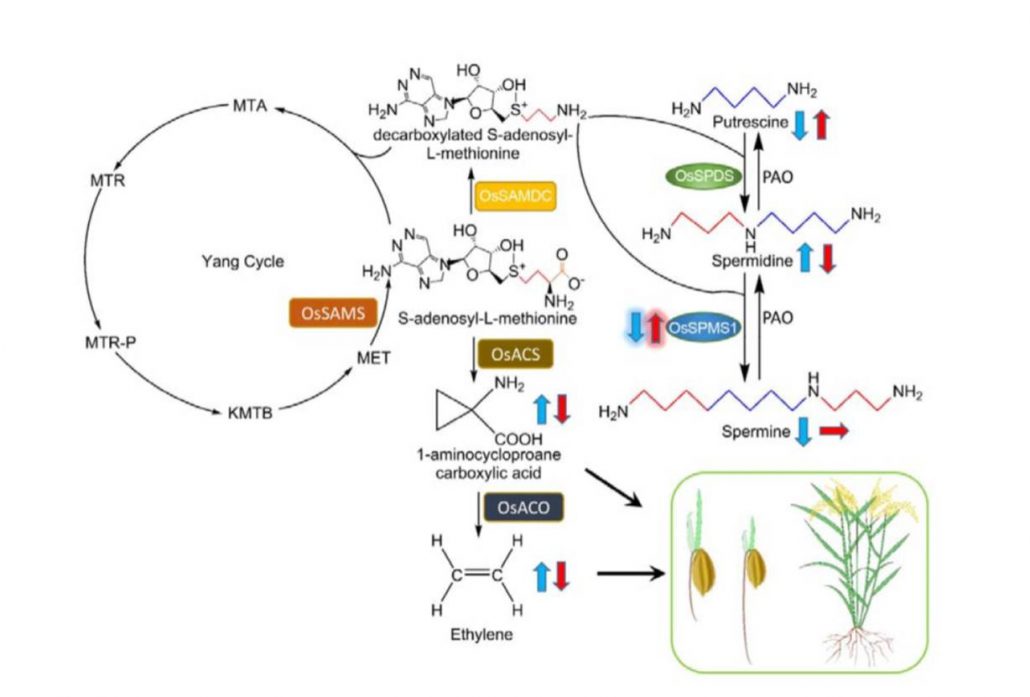
The spermine synthase OsSPMS1 regulates seed germination, grain size, and yield (Plant Physiol)
Polyamines including spermine and spermidine are present in all eukaryotes and have diverse roles. In plants they have been implicated in responses ranging from abiotic and biotic stresses to grain filling. Tao et al. examined the function of OsPMS1, encoding a spermine synthase, through genetic methods…
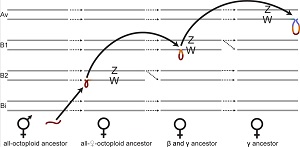
Plant sex regions can “jump” in strawberry (PLOS Biol.)
Sex chromosome restructure has happened frequently during the evolution of eukaryotes, often resulting in highly differentiated sex chromosomes. However, little is known about this process in plants. The wild North American octoploid strawberries (Fragaria) have separate sexes with homomorphic, female…

