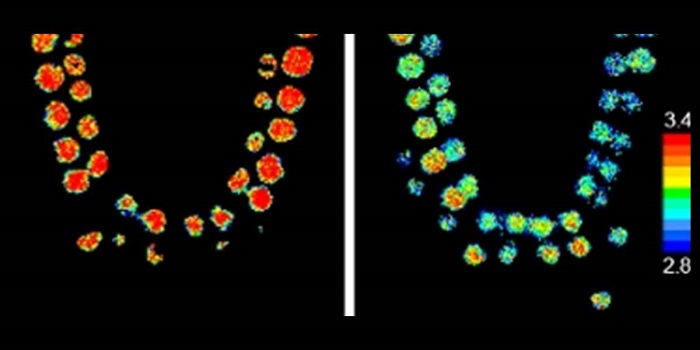
In vivo FRET–FLIM reveals cell-type-specific protein interactions in Arabidopsis roots ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research Blog0 Comments
/
Long et al. examined transcription factor complex formation in vivo in Arabidopsis roots using a technique that combines FRET (Förster Resonance Energy Transfer) and FLIM (Fluorescence Lifetime imaging Microscopy). Using this method, the authors were able to observe cell-type specific complex formation…

Cytokinin induces genome-wide binding of the type-B response regulator ARR10 to regulate growth and development in Arabidopsis ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogCytokinin, one of the major plant hormones, is involved in many aspectis of plant growth and development. Over the last few decades, the biosynthetic and signaling pathways have been discovered. The mechanistic explanation to control a myriad array of gene expression is still a black box. Zubo et al.…
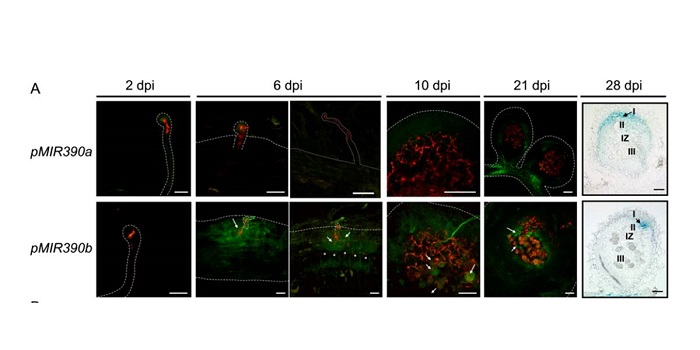
A MicroRNA Switch that Controls Lateral Root Growth and Nodulation
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogLegume roots form two types of organs, lateral roots and symbiotic nodules, which participate, respectively, in the uptake of water and mineral nutrients and in nitrogen fixation. Since both organs have considerable impacts on plant growth, understanding the mechanisms underlying the development of lateral…

Special Issue: Plant epigenomics
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe current issue of Genome Biology features a collection of review and research articles on the topic of plant epigenomics, with an overview editorial by Köhler and Springer. This collection "highlights advances in our understanding of the functions of epigenetic modifications, and the application…
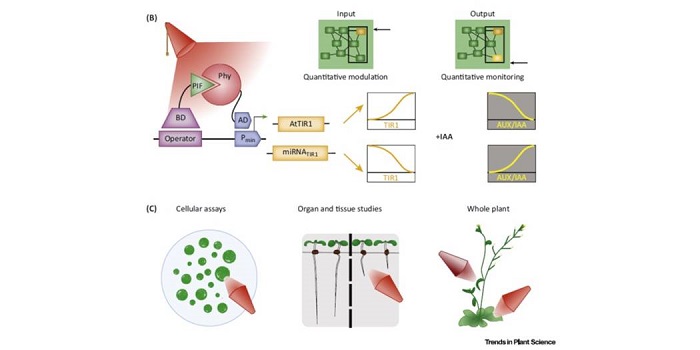
Review: Quantitative monitoring and control of plant signalling through novel theoretical–experimental approaches
Plant Science Research WeeklySamodelov and Zurbriggen describe approaches to exquisitely fine-tune protein and metabolite expression levels through a variety of synthetic and semi-synthetic biology approaches. For example, optigenetics tools enable gene expression to be activated precisely via a light beam; when combined with downstream…
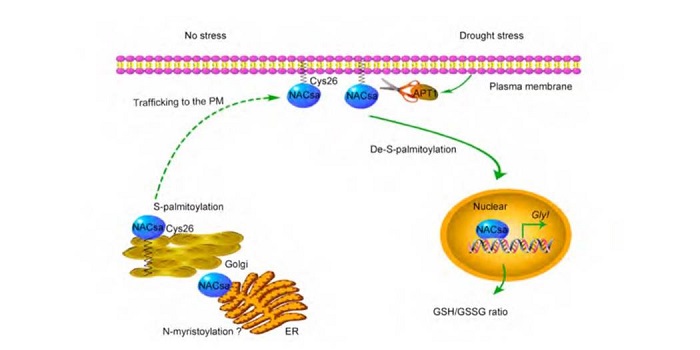
A lipid-anchored NAC transcription factor translocates into nucleus to activate GlyI gene expression involved in drought stress
Plant Science Research WeeklyRegulation of transcription factor (TF) localization is a common strategy for gene expression regulation. Wang et al. identified a membrane-anchored TF, MfNACsa, as contributing to drought stress responses. In unstressed plants, MfNACsa is anchored to the plasma membrane through covalent-attachment…
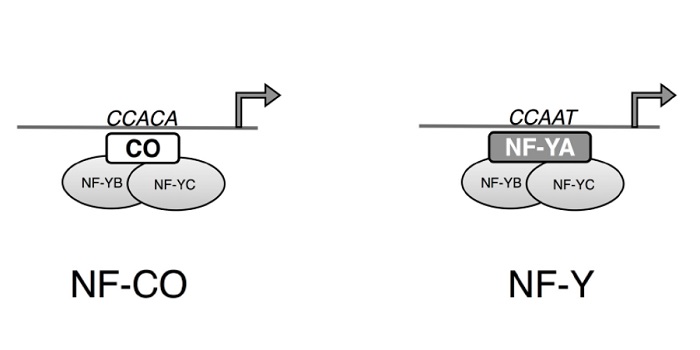
CONSTANS Companion: CO Binds the NF-YB/NF-YC Dimer and Confers Sequence-Specific DNA Binding
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefOne of the central players in the complex regulation of flowering, CONSTANS (CO) functions as a center for integration of the various signals that determine the timing of flowering. As output, CO regulates the expression of FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) and other genes (reviewed by Shim et al., 2017). CO contains…
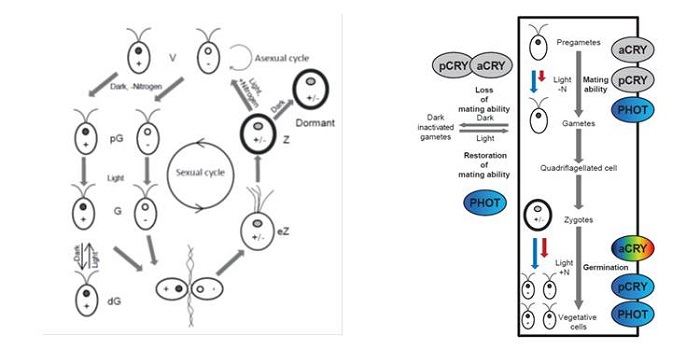
A plant cryptochrome controls key features of the Chlamydomonas circadian clock and its life cycle
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAnimals and plants have divergent sets of blue light receptors, called Cryptochromes. However, green alga Chlamydomonas has both animal-like and plant cryptochrome (pCRY). The presence of multiple cryptochrome suggests specific roles in different pathways in respective organisms. In this paper, Müller…
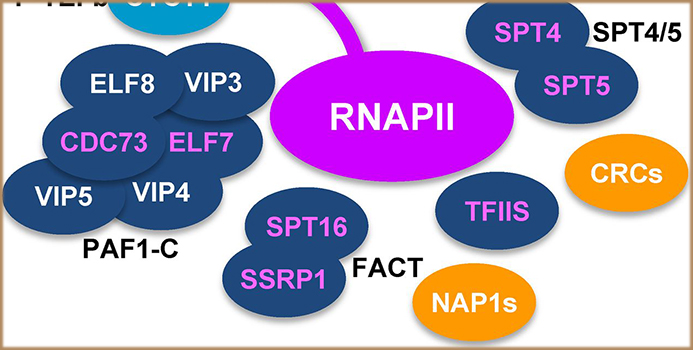
The composition of the Arabidopsis RNA Polymerase II Transcript Elongation Complex reveals the interplay between elongation and mRNA processing factors
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchGene expression is regulated at multiple levels such as genome, transcription, RNA processing and nuclear export, translation, and post-translation. Functional mRNA levels are regulated at transcription stage where RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) controls initiation and elongation of mRNA. In particular,…

