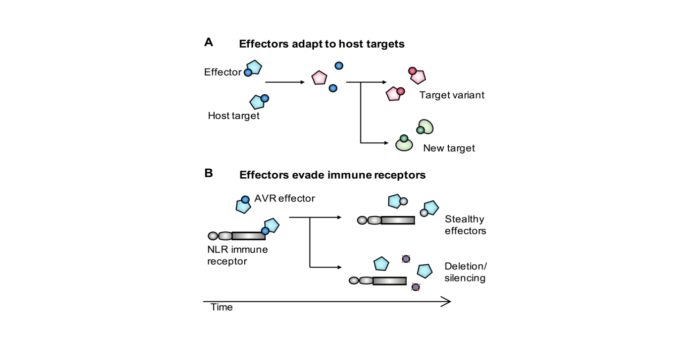
Review. The coming of age of EvoMPMI: evolutionary molecular plant-microbe interactions across multiple timescales
Plant Science Research WeeklyOften, a wide gap exists between evolutionary research, that is focused on theoretical approaches and organism evolution across multiple timescales, and molecular research aspiring to solve mechanistic puzzles of how particular systems work. Plant Biology is no exception to this, and much can be learnt…

Conservation of Genomic Imprinting during Wheat Polyploidization
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellYang et al. discover conservation of genomic imprinting between closely related Triticum and Aegilops species. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00837
By Guanghui Yang and Mingming Xin
Background: Genomic imprinting causes genes to be differentially expressed depending on their parent-of-origin, which…
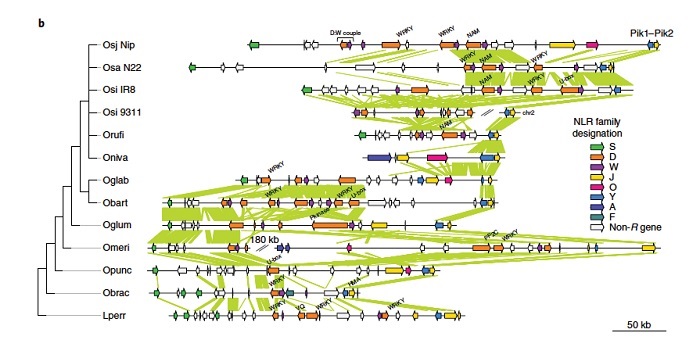
Genetic conservation, turnover and innovation across the genus Oryza (Nature Genetics)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogIn order to use wild rice relatives for future crop improvement, the differences and similarities between wild and domesticated genomes need to be understood. Stein and colleagues sequenced the genomes of two domesticated varieties and seven wild species, unraveling 15 million years of evolutionary history…
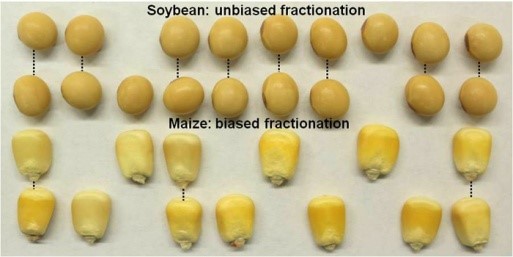
Duplicate Genomes Evolved Differently in Maize and Soybean
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZhao et al. demonstrate that duplicated genomes in maize and soybean followed distinct trajectories over millions of years https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00595
By Meixia Zhao, Biao Zhang, Damon Lisch, and Jianxin Ma
Background: Over evolutionary time, many organisms, particularly plants, have periodically…
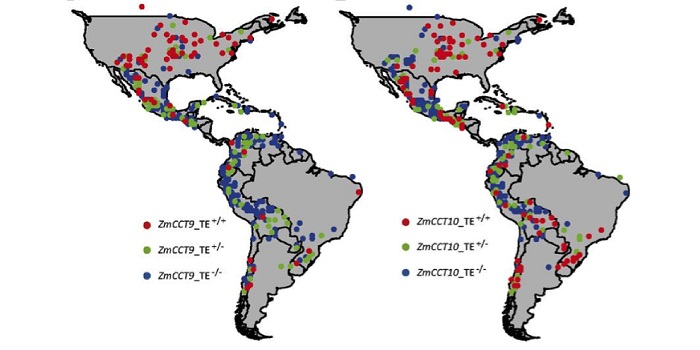
Maize adaptation to higher latitudes has been facilitated by transposon activities.
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogProc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. Flowering is a major determinant of crop adaptation to new environments. Starting from its tropical origins and requirement for short-day conditions to flower, natural selection and breeding have allowed maize to adapt to long-day environments and thus be grown over a wider…
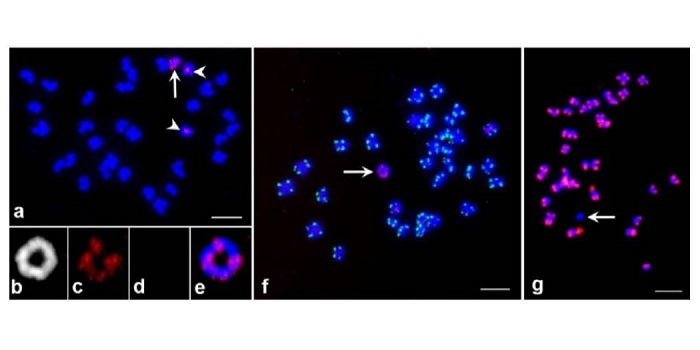
Gene duplication and aneuploidy trigger rapid evolution of herbicide resistance in common waterhemp
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlant Physiol. Herbicide resistance is a serious problem in contemporary agriculture. One of the most widely used herbicides, glyphosate, interferes with the activity of EPSPS (5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase). Koo et al. previously showed that glyphosate-resistant waterhemp (Amaranthus tuberculatus,…
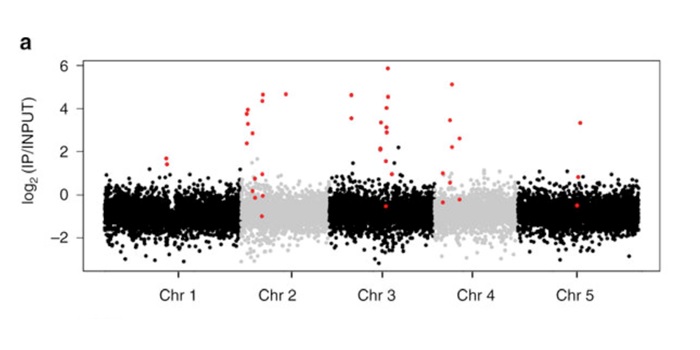
Evolution of transposon-encoded anti-silencing factors in Arabidopsis ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogTransposable elements (TEs) are a major component of eukaryotic genomes. Their activity is silenced by epigenetic mechanisms such as chromatin modifications and DNA methylation in order to avoid deleterious effects on host genome stability. Nevertheless, how TEs overcome silencing by the host and propagate…
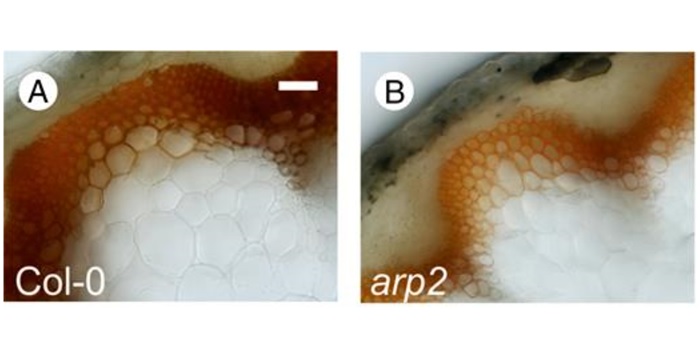
What We're Reading: January 5th
Blog, Research, Research Blog, WWR Full PostGuest Editor: Alecia Biel
Alecia is a graduate student at The Ohio State University in the US and has been a Plantae Fellow since September 2017. Her research focuses on elucidating hormone signaling pathways and the role of the nucleus during this process, particularly throughout plant abiotic…
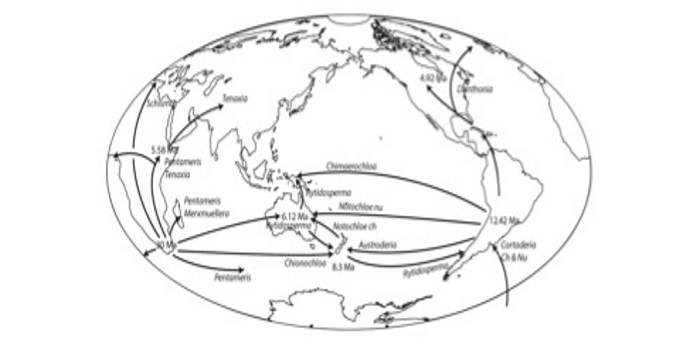
Review. Grasses: The original Vikings ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe Vikings were notorious raiders for centuries, pillaging and looting the shores throughout the northern hemisphere. Through their successful raids, the Vikings established colonies that grew into states and countries, among these Normandy, England, Sicily, and Russia. The success of the Vikings is…

