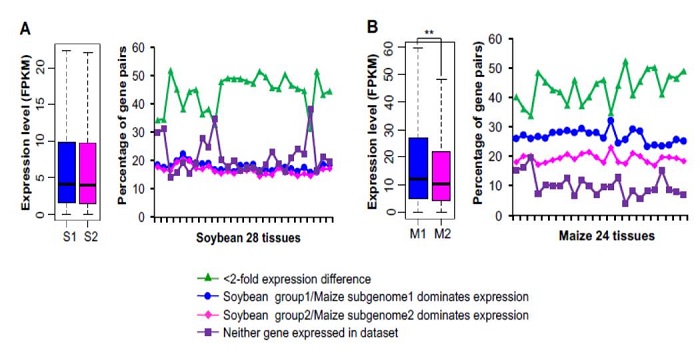
Patterns and consequences of subgenome differentiation provide insights into the nature of paleopolyploidy in plants
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogMany plants are polyploid, meaning that instead of the normal, diploid “2n” complement of chromosomes (one from each parent), they have more than 2n. Following whole-genome duplication, redundancy can allow the duplicated regions to diverge or become silenced. In some cases, silencing occurs preferentially…
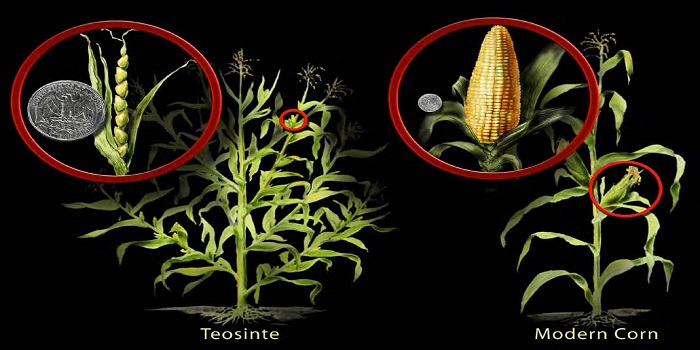
Review. Artificial evolution: Creating genetic diversity in the lab ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogHumans have been domesticating plants for 10,000 years, having an impact on the gene pools of multiple species chiefly through selective breeding approaches. Although plant domestication ensured food availability to early civilizations, plants were, and still are, mainly selected based on their morphology…
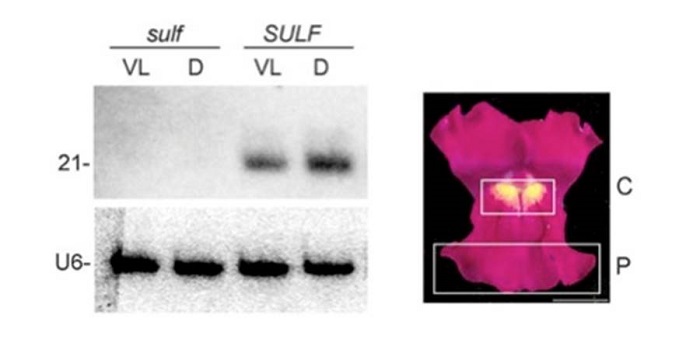
Regulatory small RNAs responsible for natural variation in snapdragon flower color patterning ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogFlower color pattern is a major trait influencing pollinator attraction, but underlying regulatory mechanisms are still poorly understood. Using co-existing Snapdragon subspecies displaying different flower pigmentation motifs, Bradley et al. investigated the molecular basis of flower color patterning.…

J. Exp. Bot. Special Issue. The plant cuticle: old challenges, new perspectives ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogThe cuticle is a cell-wall polymer that protects against desiccation, pathogens and UV light. Domínguez et al. provide an open-access editorial that describes this fine collection of articles covering all aspects of the plant cuticle, from its evolutionary origins to its ecological significance. Within…

Mycorrhizal fungi shaped the evolution of terrestrial plants
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogMutualistic associations between plants and fungi are incredibly widespread, occurring in 90% of extant land plants, and likely are the most ecologically important symbiotic relationships on Earth. Fungi played an integral part in land plant evolution; roots only evolved after early land plants colonised…
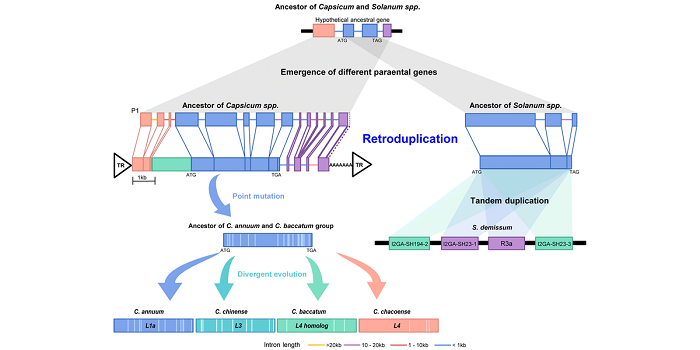
Amplification of plant disease-resistance genes in pepper is intimately linked to transposon activity
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPeppers are an economically and ecologically important crop plants, but genomic resources are rather scarce. The authors provide here new reference genome sequences for three species of hot pepper (Capsicum baccatum, C. chinense and C. annuum), identifying evolutionary forces that have shaped pepper…

How asparagus recently changed its lifestyle from hermaphroditism to distinct males and females
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogSex determination in the animal kingdom has been relatively well studied, with two main systems responsible for the sexes in mammals, insects, birds, reptiles and fish; XY and ZW sex-determination. Although much is still unknown about these systems, with many exceptions being discovered to previously…
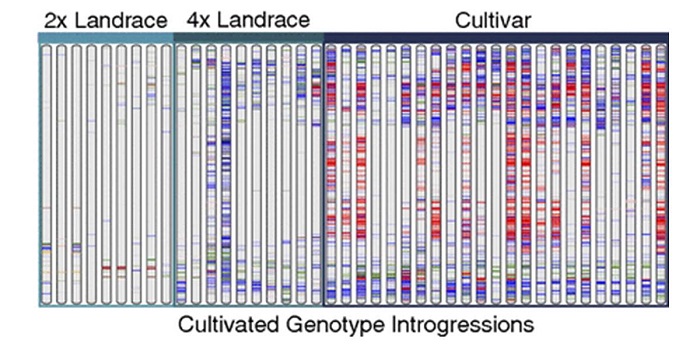
Complex evolutionary history and targets of domestication in the cultivated potato
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPotatoes originated in the Andes of southern Peru, and are now the third most important crop for direct human consumption. Hardigan et al. sequenced 67 potato relatives, including South American landraces, North American cultivars and wild-diploid species to learn about the genetics of modern potato’s…

Earth’s very first trees ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogLong ago, the dinosaurs roamed amongst majestic forests of ancient tree ferns, cycads and conifers. But longer ago still, prior to the birth of both the kings of the animal and plant kingdoms, majestic forests of gigantic trees were unimaginable, with the landscape covered in small plants lacking leaves,…

