
Field-based species identification of closely-related plants using real-time nanopore sequencing
DNA sequencing was slow before the development of high throughput sequencing. Portable DNA sequencing, which would make sequencing on-site a reality, was impossible until recently. Parker et al. report on the on-site use of MinION from Oxford Nanopore Technologies for DNA barcoding, which yields data…

Emergence of subgenome dominance across time and ploidy
0 Comments
/
Many plants are not simple diploids (two copies of each chromosome) but are instead are the result of various forms of polyploidization (for example, whole-genome duplication or interspecific hybridization). Polyploidization can disrupt well-established controls over gene expression levels, transposon…
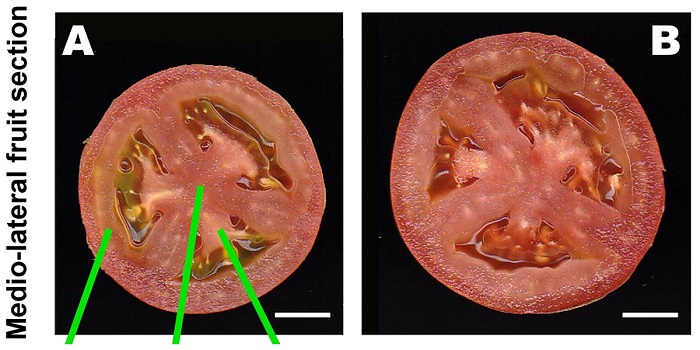
Tomato fruit weight controlled by Cell Size Regulator
Mu et al. mapped a QTL previously shown to control fruit weight in tomato, and named the responsible gene Cell Size Regulator (CSR). They found that CSR-D, the derived allele, increases cell size and is widespread in Solanum lycopersicum var. lycopersicum, but not in ancestral tomatoes with smaller fruit.…
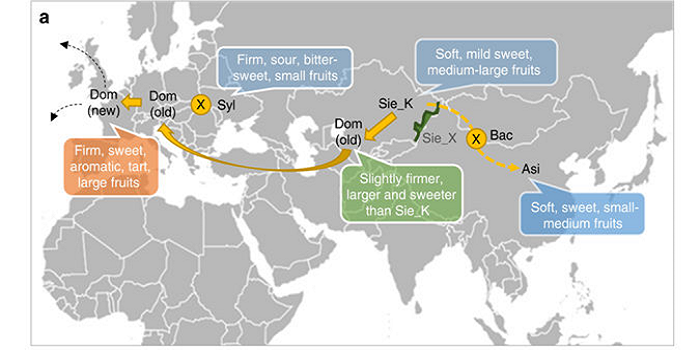
Genome re-sequencing reveals the history of apple and supports a two-stage model for fruit enlargement
Cultivated apples (Malus domestica) trace their roots to Kazakhstan 4000 – 10,000 years ago, and since then have been propagated, transported, hybridized to other Malus species, and domesticated. Duan et al. sequenced more than 100 diverse accessions to trace apple's history and identify loci subjected…
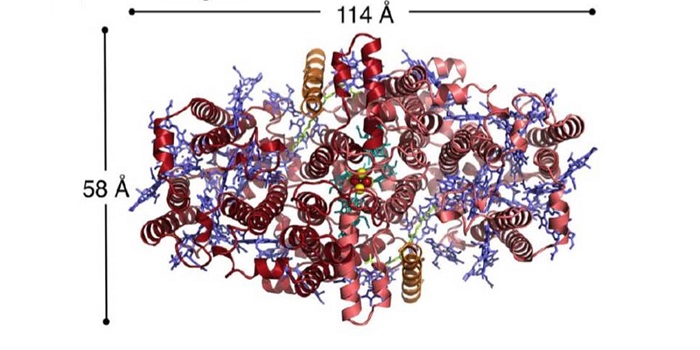
Structure of a symmetric photosynthetic reaction center–photosystem ($)
Plants, green algae and cyanobacteria carry out oxygenic photosynthesis through the coordination of two photosystems, PSI and PSII. Many other photosynthetic prokaryotes use a single reaction center to carry out anoxygenic photosynthesis. Gisriel et al. describe the structure of a photosynthetic reaction…
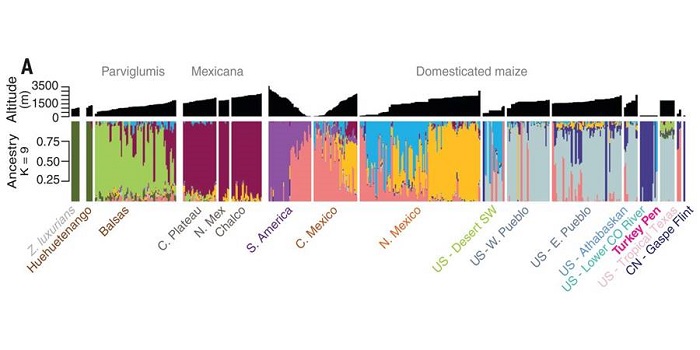
Genomic estimation of complex traits reveals ancient maize adaptation to temperate North America
Maize (corn), an important staple of the diet in ancient and modern times, was cultivated at higher altitudes in the southwestern United States, around 2,000 years after its introduction to the lowland US regions. In order to better understand how maize later adapted to high altitudes, authors sequenced…
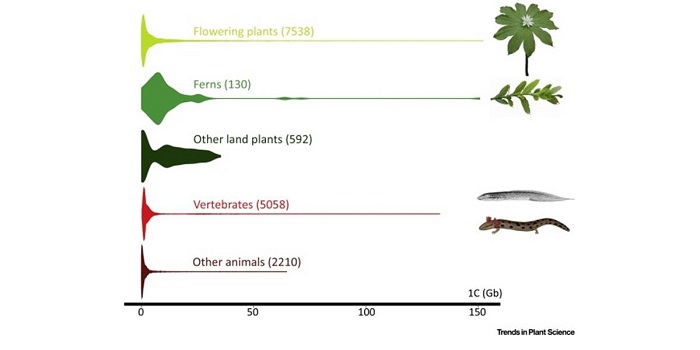
Opinion: Is there an upper limit to genome size? ($)
There are only ten organisms known to have genomes larger than 100 Gb in size and six of those are plants. Both Numbers 1 and 2 on the list are plants with genomes that are nearly 50x the size of the human genome (which is 3 Gb), and over 1000x that of Arabidopsis: the 148.8 Gb-genome Paris japonica…
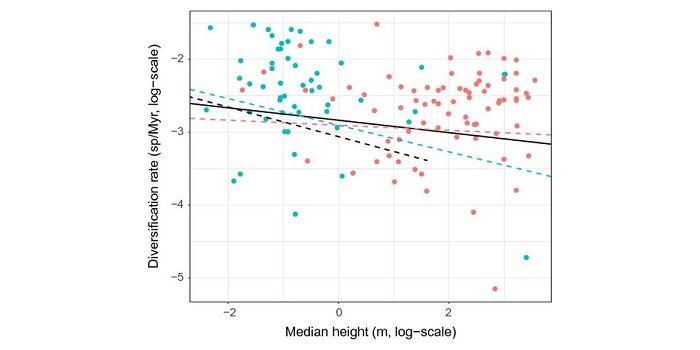
Plant size: a key determinant of diversification
Diversification in plants is driven by many factors, but one trait, plant size, has been systematically overlooked, in contrast with the zoological field where the influence of body size on diversification has long been recognized. In this Viewpoint paper, Boucher et al. try to convince us why we…

Live online chat discussion with featured community member Anne Sternberger
Mark your calendars for the first Plantae.org live online chat discussion with featured community member Anne Sternberger!
Support your peers | Discuss plant science topics | Learn about how others work
Tuesday, June 27th at 5pm EST / 11am HST | Join: www.plantae.org/annes
Anne is…

