
A role for melatonin in the defence of sweet oranges against citrus greening disease
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchIf you regularly enjoy a cold glass of orange (Citrus × sinensis) juice, freshly squeezed or store-bought (who has time for the former, really?), then you should know that the future of this drink is at stake. Citrus greening disease or Huánglóngbìng (HLB) has been wreaking havoc on the citrus industry…

Got Rosettes? Phenotype Them Fast, Accurately, and Easily with ARADEEPOPSIS!
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In Brief“Deep learning” is a buzz term that seems to be cropping up in plant biology research these days. Originally reserved, perhaps, for computer nerds rather than us biology ones, deep learning is a type of machine learning used in the field of artificial intelligence. Modeled on the human brain, deep…
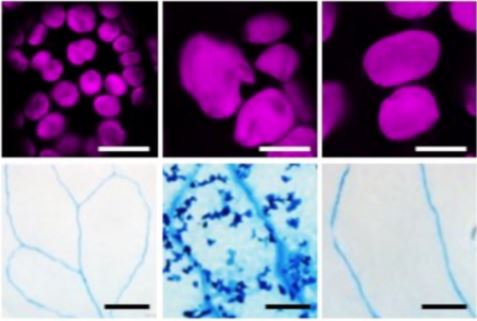
More Than Just a FAD(5): Unsaturated Fatty Acids in Chloroplasts Elicit Protective Autoimmunity
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefArabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) chloroplast-division mutants that have abnormally large chloroplasts have been around for quite some time, not only because they can be identified relatively easily through screening (Pyke & Leech 1991) and because their spectacular morphology sparks intrigue, but…
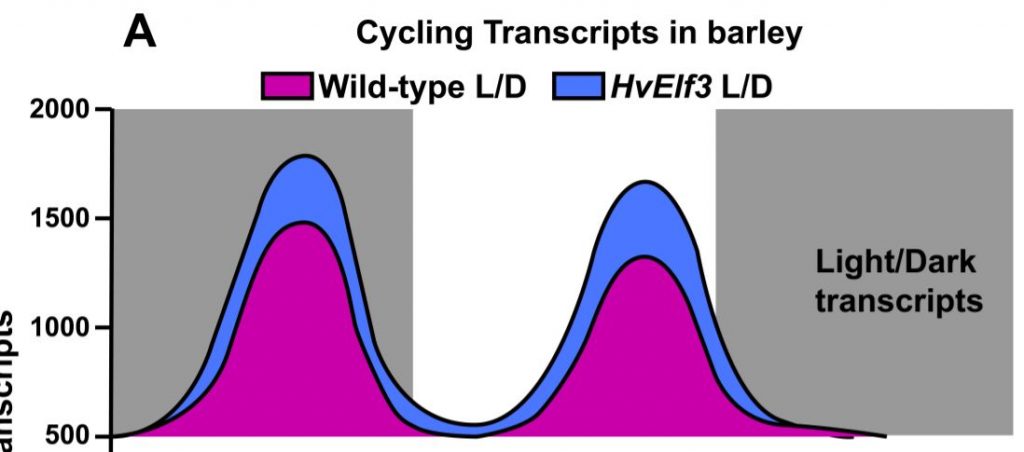
The rhythm of the light: how light and the clock drive cycling of transcript levels in barley
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchCircadian rhythms are ubiquitous among living things. A core set of so-called clock genes and their products assemble an oscillatory network that provides a rhythm to anticipate dawn and dusk (Hsu and Harmer, 2014). The circadian clock regulates the day/night rhythms of plants and light itself has many…

In the Transcripts: Long-read Transcriptomics Enables a Novel Type of Transposable Element Annotation in Plants
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefTransposable Elements (TEs) are mobile genetic elements and major constituents of eukaryotic chromosomes. TEs promote genetic and epigenetic variation within genomes and are a major source of evolutionary novelty and adaptation (Lisch, 2013). In plants, TEs represent from 20% of the genomic content in…

NLR-Annotator: a tool for de novo annotation of intracellular immune receptor repertoire
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchWei Zhang
ORCID: 0000-0002-5092-643X
Department of Plant Pathology, Kansas State University, 1712 Claflin Road, Throckmorton Hall, Manhattan, KS, 66506, USA
[email protected]
Nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat (NLR) proteins serve as intracellular immune receptors in plants to…

Comparative profiling examines roles of DNA regulatory sequences and accessible chromatin during cold stress response in grasses
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPhysical access to regulatory DNA, including cis-regulatory sequences found within proximal promoters and distal enhancer elements, is a vital property of chromatin. In turn, their access is determined by nucleosome occupancy and post-translational modification of histone proteins. A continuum of chromatin…
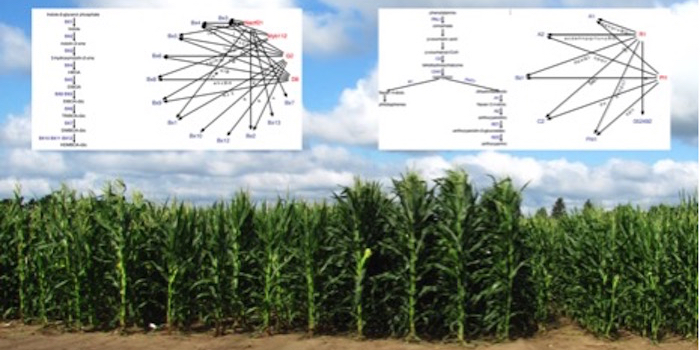
Predicting Gene Regulatory Networks
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZhou et al. develop and test potential gene regulatory networks in maize. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.20.00080
By Peng Zhou and Nathan Springer
Background: Transcription factors (TFs) play critical roles in regulating the expression of genes. A single TF can control the expression of…
Arabidopsis bioinformatics resources: Current state, challenges, and priorities for the future (Plant Direct)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFuture research success demands that data are reliable, accessible and shareable. This means that as types and magnitudes of data change, best practices for how data are collected and stored must be regularly updated. Following a focused workshop, the International Arabidopsis Informatics Consortium…

