
Trust but Verify: A Lesson in Technology Limitations and Error Propagation
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefBy C. Robin Buell
Unlike molecular biology techniques that are routinely used in individual investigator labs, the high cost of infrastructure historically has resulted in genome sequencing being performed at genome centers in which quality control and quality assessments are a mainstay, and it is…

The Real Yield Deal? Nitrate Transporter Expression Boosts Yield and Accelerates Maturation
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefApproaches to improve final grain production must consider yield stability, that is ways to prevent yield losses. For example, flowering time affects yield and yield stability-- if grains mature late, they may be literally caught out in the cold, as late-season weather turns. Indeed, the application…
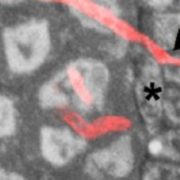
The Trojan Horse Approach to Protein Jockeying
Blog, Research Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIn the decades since Agrobacterium tumefaciens was first used as a vector to deliver genetic material into plants (Zambryski et al., 1983), this powerful tool has provided important insights into the biological functions of countless gene products. However, this approach has its shortcomings; in addition…
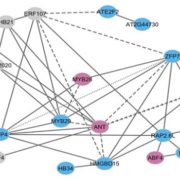
Symphony of the regulators: How do plants control complex responses to environmental signals?
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThere are several models we use to conceptualize how plants respond to environmental signals through transcriptional regulation. In perhaps the best-understood model, the perception of some environmental signal flows through one or several mechanisms to a master regulator, often a transcription factor…
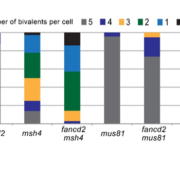
Hold Me Closer: Meiotic Crossover Formation and FANCD2
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefMeiosis takes a single, diploid cell and turns it into four haploid spores. The equal distribution of genetic material is critical for genome stability across generations, and relies heavily on proper pairing of chromosomes and their timely release. During the first meiotic division, crossovers (COs)…
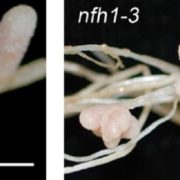
Goldilocks Principle: MtNFH1 Ensures Optimal Nod Factor Activity
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPartner selection is a critical step that must occur early during establishment of Root Nodule Symbiosis (RNS). RNS refers to the mutualistic interaction between legumes and some non-legumes with soil bacteria that help convert atmospheric nitrogen into plant usable ammonia. In legumes such as Medicago…
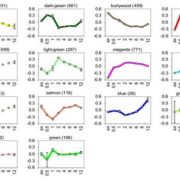
The Shifting Transcriptional Response of Corn Smut Fungus
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefAs a biotrophic fungus, Ustilago maydis (corn smut fungus) relies on living plant tissues for sustenance. Once U. maydis cells of compatible mating types fuse on a leaf surface, they produce a dikaryotic filament with a specialized infection structure—the appressorium—that penetrates epidermal cells.…
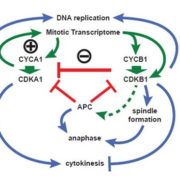
Cell Cycle Regulation by Chlamydomonas Cyclin-Dependent Protein Kinases
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefCyclins and cyclin-dependent protein kinases (CDKs) are critical regulators of cell cycle progression. Although CDK1 is essential for mitosis in animals and fungi, CDKA, the plant and algal ortholog of CDK1, is not essential for cell division in Arabidopsis (Nowack et al., 2012). By contrast, CDKB is…
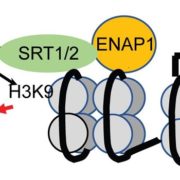
Ethylene Represses Gene Transcription via Histone Deacetylases
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefApproximately half of all ethylene-responsive genes are downregulated in the presence in ethylene (Chang et al, 2013), but this repression has received relatively little attention compared to the ethylene-mediated activation of expression. The known positive regulators of ethylene signaling include ETHYLENE…

