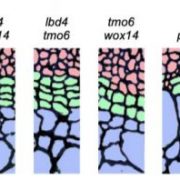
The Shape of Rings to Come: Systems Approach to Xylem and Phloem Formation in Arabidopsis
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPlants have veins too. As in animals, the plant vasculature facilitates the circulation of water and nutrients across tissues and organs. Unlike animals, it originates from a self-renewing population of meristematic cells forming the (pro)cambium ring within stems and tree trunks and roots. Local signals…
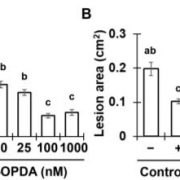
Xylem-mobile Oxylipins are Critical Regulators of Induced Systemic Resistance in Maize
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIn addition to promoting plant growth and development, the colonization of roots by beneficial microorganisms often provides aboveground tissues with enhanced resistance to pathogen attack. This form of resistance, referred to as ‘induced systemic resistance’ (ISR), relies on the long-distance movement…
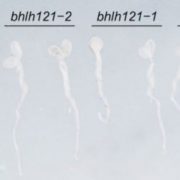
Personal Trainer: bHLH121 Functions Upstream of a Transcriptional Network of Heavy Lifters Involved in Balancing Iron Levels
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefIron is a cofactor of numerous plant proteins that function in processes ranging from redox reactions during photosynthesis to respiration. Typical soils contain approximately 1–5% iron, but much of this iron is not readily accessible to plants due to low solubility. Nongraminaceous plants help solubilize…
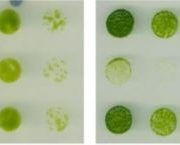
Phosphorus Sensing by LST8 Acts as a TOR Guide for Cell Growth in Chlamydomonas
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefPlant cell growth is often limited by the availability of two key nutrients, phosphorus (P) and nitrogen (N). As in mammals and yeast, a kinase known as TOR (target of rapamycin) is a key nutrient-responsive regulator of primary metabolism and cell growth in plants (Gonzalez and Hall, 2017; Dobrenel…

Stiffening stems: identification of the stiff1 gene involved in maize stalk strength
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefStalk lodging, a structural failure in which crop stalks break prior to harvest, can result in high grain moisture, reduce grain quality, and cause harvesting difficulties. For the popular high-yielding cereal maize (Zea mays), lodging may result in global annual yield reductions of approximately 5-20%…
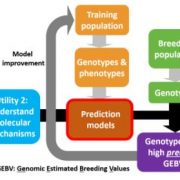
Predicting adult complex traits from early development transcript data in maize
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefAn enduring goal of biologists is to link variation in the genome to phenotype. The discovery of easily measurable genetic markers in the recent past has led to the identification of variants controlling different traits through linkage analysis. Subsequently, advances in high-throughput sequencing have…
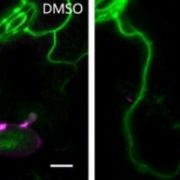
Lipid Rafts to the Rescue! Plants under Fungal Attack Recruit Phospholipase Dδ
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefWhen your fort is under attack during battle, and the wall is breached, you can choose to fight, flee, or forgo. Plants, on the other hand, are left with little choice: they must fight. Winning any battle, though, depends on a multitude of factors, most notably your available arsenal, soldiers, and importantly,…
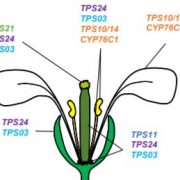
Attract or Defend: The CYP-associated Versatility of Terpenoids
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefFloral scent, a blend of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), is a communication signal central to plant interactions. For example, VOCs attract pollinators when flowers are opened (Muhleman et al., 2015).
However, some plants do not cross-pollinate and depend less on VOCs. Flowers are fragile structures…
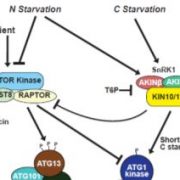
You Are What You Eat: An ATG1-Independent Path to Autophagy
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefFixed carbon derived from photosynthates serves critical roles as both a chemical energy reservoir and a building block for anabolic processes. Environmental constraints that place limitations on a plant’s fixed-carbon economy, such as prolonged darkness and photosynthetic stress, can therefore be…

