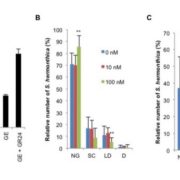
Strigolactone-Gibberellin Cross Talk
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research0 Comments
/
Strigolactones Root parasitic weeds, such as broomrape (Orobanche spp.) and witchers weed (Striga spp.), are harmful plants in sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, and Asia that maintain seed dormancy in the absence of host plant. Both parasitic plant species require germination stimulants released from…

Freeze-Thaw-Induced Embolism and Ultrasonic Emissions in Angiosperms
Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchAll organisms including plants share the tetrapyrrole biosynthesis pathway that is critical for the production of compounds such as heme and chlorophyll. During tetrapyrrole biosynthesis, coproporphyrinogen III oxidase (CPO) catalyzes the conversion of coproporphyrinogen III into protoporphyrinogen IX.…
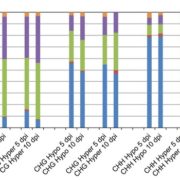
Nematode Cysts and DNA Methylation
Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchPlant-parasitic cyst nematodes (Heterodera species) are among the most devastating pathogens of plant roots. These obligate parasites initiate a long period of biotic interactions with their host plants where formation of an operative feeding structure, the syncytium, is vital for nematode survival and…

Thapisgargin Formation in Thapsia
Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchThe Mediterranean plant Thapsia garganica (Apiaceae), also known as deadly carrot, produces the highly toxic compound thapsigargin. This compound is a potent inhibitor of the sarcoplasmic-endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase calcium pump in mammals and is of industrial importance as the active moiety of…
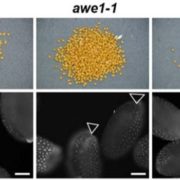
Suberin and Seed Dormancy
Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchEnvironmental signals during seed production are important determinants of seed properties, including seed dormancy and seed longevity. The mother plant plays an important role in this signaling process, collecting signals throughout her life history and modulating dormancy by providing hormones to maturing…
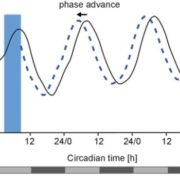
Blue Light Photoreception by Chlamydomonas
Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchCryptochromes are flavin-binding proteins that act as blue light receptors in bacteria, fungi, plants and insects and are components of the circadian oscillator in mammals. Animal and plant cryptochromes are evolutionarily divergent, although the unicellular alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii has both an…

A Controller of Leaf Angle in Soybean
Plant Physiology: On The Inside, ResearchSoybean (Glycine max) is one of the most important oilseed crops that provides edible oil for humans and is a major renewable feedstock for biodiesel production around the world. As such, increasing soybean yield potential has become a long-term breeding objective. Soybean leaf petiole angle is an important…

Insights into Salicylic Acid and Mitochondria
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogWithin the mitochondrial electron transport chain, complex II (succinate dehydrogenase [SDH]) oxidizes succinate to fumarate by transferring electrons to ubiquinone (UQ), which is reduced to ubiquinol. The enzyme is formed by four subunits: a flavoprotein (SDH1), which contains the FAD cofactor, an iron…
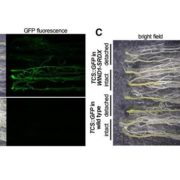
The Root Greening Response in Arabidopsis
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogBased on various developmental, environmental, and hormonal cues, proplastids can be converted into different types of plastids within cells. In Arabidopsis, chloroplast development is repressed in roots via auxin signaling. When roots are detached from the shoot, and its supply of auxin, roots develop…

