
Hijacking the ER membrane – lessons from Turnip mosaic virus
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsBy Lynn GL Richardson
Positive-strand (+)RNA viruses account for the majority of plant viruses. Apart from their significant impact on worldwide agriculture, they also inform our understanding of basic virus biology (Scholthof et al., 2011). Upon entry into the cells of their host, (+)RNA viruses…
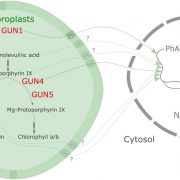
Another gun Dismantled: ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE4 Is Not a Target of Retrograde Signaling
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsBy Amna Mhamdi and Charlotte M.M. Gommers
The nuclear genome encodes the majority of chloroplast-localized proteins and, in return, chloroplasts exert some control over nuclear gene expression via so-called retrograde signals. These signals derive from developing chloroplasts (referred to as biogenic…

Moonlighting Enzymes: How Often Are We Missing Secondary Functions?
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsWe think of enzymes as highly specific catalysts that carry out one reaction and show nearly absolute substrate specificity. However, absolute specificity is the exception, not the rule, as most enzymes accept several structurally similar substrates. Moreover, many enzymes catalyze alternative reactions…

Plant Cell Wall Composition: Does Ploidy Matter?
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsMost of the carbon dioxide sequestered by plants during photosynthesis is converted into sugars and stored into polysaccharide-enriched cells walls that constitute the majority of the plant biomass. While plants have long been considered a valuable resource of biomaterials for the chemical and textile…
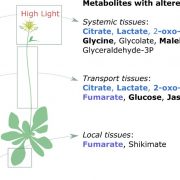
Highlighting the fast signals that establish remote metabolite profiles
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsBy Amna Mhamdi and Scott Hayes
They say you can get too much of a good thing, and for plants that is certainly true. Light is essential for growth, but excessive light causes an overloading of the plant’s photosynthetic machinery. This excess energy can spill out and, through formation of reactive…

Spot the Difference: Distinct Cargo-Specific Functionality of Two Closely Related SNAREs
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsExocytosis is a form of an active transport in which vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane. This vesicle transport secretes soluble cargo proteins and polysaccharides into the apoplast, but also delivers membrane lipids and transmembrane proteins to the plasma membrane. Vesicle trafficking is initiated…
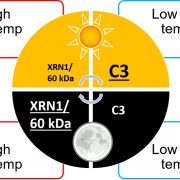
Alternative Splice Variant Sheds Light on Temperature Acclimation in Algae
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsClimate change is a potent environmental force that all living organisms must contend with. This is especially true for photosynthetic, microalgae that are forced to acclimate to ever changing water temperatures and coordinate changes in their physiology and growth rates (Singh and Singh, 2015). These…
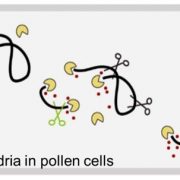
Discovery of mitochondrial endonucleases
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsProkaryotic endosymbiont-derived organelles (i.e. mitochondria and chloroplasts), contain their own genomes and the copy number of organelle genomes per cell is high; indeed, a previous study calculated that in Arabidopsis thaliana, each cell has 1000 to 1700 copies of the chloroplast genome (Zoschke…

Setting and Diffusing the Cyanide Bomb in Plant Defense
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and ViewsHydrogen cyanide (HCN) is a potent inhibitor of cytochrome c oxidase, a conserved component of the respiratory electron transport chain in all aerobic life. Thus, HCN is well suited to serve as a broad-spectrum chemical defense, and indeed it plays such a role in many interactions between plants and…

