
Variation in xylem resistance to cavitation explains why some leaves within a canopy are more likely to die under water stress
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchMeisha Holloway-Phillips
Department of Environmental Sciences, University of Basel, Switzerland
[email protected]
When trees are subjected to soil water deficits, some leaves and branches show signs of stress or die before others in the canopy. Why is that? Here I highlight recent…
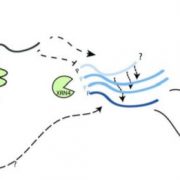
Rapid changes: ABA-independent SnRK2s target mRNA decay
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchMagda Julkowska
[email protected]
In response to stress, secondary messengers and rapid and reversible protein phosphorylation contribute to signaling cascades that generate unique signatures indicating stress type and severity. Activation of stress-induced signaling cascades…

Adapting to high light: At a different time and place?
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchWhen rays of light enter a plant cell, they find their way to the chlorophyll pigments located in the chloroplast. Chlorophyll molecules are embedded in the light reaction complexes photosystem I (PSI) and photosystem II (PSII), which capture and store the energy needed for carbon fixation in the Calvin…

Enhanced Metabolic Degradation: The Last Evolved Glyphosate Resistance Mechanism of Weeds?
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchFor the past two decades, glyphosate has been the most used herbicide worldwide, resulting in prolonged, extreme selection pressure for glyphosate-resistant (GR) weeds. Glyphosate’s only target as a herbicide is 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS), an enzyme of the shikimate pathway. …
A novel upstream regulator of trichome development inhibitors
Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchMuch like the spikes that deter birds from sitting on fences, trichomes — hair like projections on the leaf surface — are the epidermis’ first line of defence, discouraging insects and other pests (Levin, 1973). In addition to their role protecting the plant, trichomes are an excellent marker to…
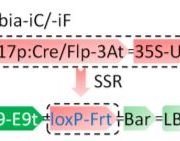
Restriction Release: improved maize transformation efficiency
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchMagdalena M. Julkowska
[email protected]
Improvement of crops using traditional breeding is too slow to ensure food production able to sustain the growing human population, especially in the face of climate change (Hickey et al., 2019). Transformation methods for monocot crops depend…
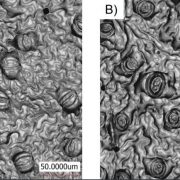
Keep it steamy: improved quantification of the humidity within the leaf
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchMagdalena M. Julkowska
[email protected]
Stomata are the gatekeepers of plant water status, regulating the balance between plant CO2 uptake and water loss. Stomatal conductance (gs) can be estimated by microscopy of wax or plastic leaf surface imprints, but this technique is time…
How To Identify Autophagy Modulators
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchAuthor: Masanori Izumi
Affiliation: RIKEN Center for Sustainable Resource Science, Wako 351-0198, Japan
[email protected]
Autophagy is the ubiquitous process in eukaryotes leading to the degradation of intracellular components, during which a portion of the cytoplasm, including organelles,…
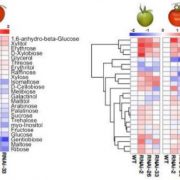
NTRC: a key regulatory hub in carbon metabolism and redox balance in developing tomato fruits
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchMaria Grazia Annunziata
Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology, 14476 Potsdam-Golm, Germany.
ORCID ID: 0000-0001-8593-1741
By acting as redox regulatory factor, NADPH-dependent thioredoxin reductase C (NTRC) is involved in many metabolic processes as well as plastid biogenesis. It…

