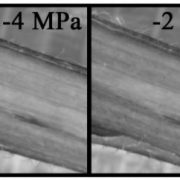
Stem diameter fluctuations provide a new window into plant water status and function
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchAuthor: Robert Skelton
[email protected]
Affiliation: South African Environmental Observation Network, Private Bag X7, Claremont, 7735, South Africa
Knowledge of the spatio-temporal dynamics of water storage in plant stems is fundamental to understanding plant physiological function under…
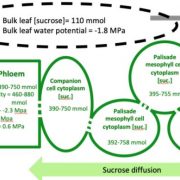
Gaining sugars while sweating, how do leaves regulate their osmolarity?
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchGuillaume Charrier
Université Clermont Auvergne, INRAE, PIAF, F-63000 Clermont-Ferrand, France.
[email protected]
Leaves are specialized for the photosynthetic assimilation of atmospheric carbon, but they also are responsible for the transpiration of water into the atmosphere, as…
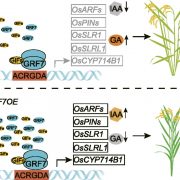
A Molecular Determinant of Rice Plant Architecture
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsidePlant architecture is a major determinant of rice (Oryza sativa) productivity. Rice plant architecture is mainly defined by plant height, the spatial pattern of leaves, and tiller and inflorescence branching patterns. Plant height and tiller branching determine the biomass and harvest index, while the…
Sphingolipids and Plasmodesmata
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsidePlasmodesmata are cytoplasmic channels that physically connect the cytoplasm and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of adjoining plant cells. These intercellular channels play important roles during plant development by allowing the molecular exchange of signaling molecules such as transcription factors, RNAs,…

The Regulation of Cuticle Biosynthesis
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe outer surface of the aerial parts of land plants is covered by the cuticle, a waxy layer that provides a barrier against damage caused by environmental factors as well as protection against non-stomatal water loss. Castorina et al. (10.1104/pp.20.00322) now show that both cuticle deposition and…
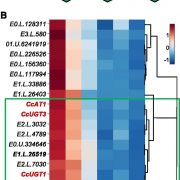
Biosynthesis of Montbretin, an Anti-Diabetes Drug
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideDiabetes and obesity are major health challenges. Diabetes alone affects over 422 million people worldwide and is among the top ten leading causes of death. Type-2 diabetes (T2D) is characterized by the body’s inefficient use of insulin, which leads to elevated blood Glc levels with detrimental effects…

Villin and GLABRA2 Regulate Root Hair Growth
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe enhanced elongation of root hairs in response to mild water deficiency permits more effective water and nutrition uptake. The growth of root hairs is regulated in part by actin dynamics. Thick actin-filament bundles (“thick bundles”) in the apical and subapical area of root hairs, for example,…
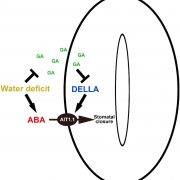
A Novel Form of Crosstalk Between Gibberellic Acid and Abscisic Acid
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe negative interaction between gibberellic acid (GA) and the stress hormone abscisic acid (ABA) has been studied for many years in numerous plant species. These studies suggest that GA and ABA negatively affect each other’s biosynthesis and signaling. The nuclear DELLA proteins suppress almost all…
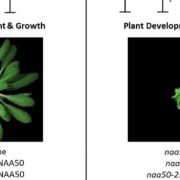
The Meaning of an End: N-terminal Acetyltransferase NAA50 Controls Plant Growth and Stress Responses
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchAuthor: Sjon Hartman
ORCID: 0000-0002-6709-6436
Plant Ecophysiology, Institute of Environmental Biology, Utrecht University, Padualaan 8, 3584 CH, Utrecht, The Netherlands
At least 80% of eukaryotic proteins are estimated to undergo N-terminal acetylation (NTA), making it likely that your…

