
Recognizing Plant Physiology first authors: Nikolay Manavski
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: Author ProfilesNikolay Manavski, first author of CHLOROPLAST RIBOSOME ASSOCIATED supports translation under stress and interacts with the ribosomal 30S subunit
Current Position: Postdoc at IBMP-CNRS, Strasbourg, France
Education: Diploma and PhD in Molecular Biology, Department of Molecular Plant Biology, University…

Plant Cell Editor Profile: Blake Meyers
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: Editor ProfilesBy Alex Harkess and Margaret Frank
While working on very small RNA molecules, Blake Meyers tackles some of the biggest problems in plant biology. Blake has spent much of his academic career generating and sifting through billions of sequence reads to ask a deceptively simple question: what do small…
Introducing the journal Plant Physiology, featuring EIC Mike Blatt
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: EditorialsEditor-in-Chief Mike Blatt talks about the journal Plant Physiology, how online communication accelerates the pace of scholarly publishing, and the need to express key research findings in an accessible way.
"What I often encourage authors to do when they prepare manuscripts is to think about the sound…

Critical plant gene takes unexpected detour that could boost biofuel yields
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: News
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., June 15, 2018 - For decades, biologists have believed a key enzyme in plants had one function--produce amino acids, which are vital to plant survival and also essential to human diets.
But for Wellington Muchero, Meng Xie and their colleagues, this enzyme does more than advertised.…
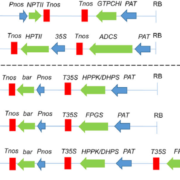
P-HYDROXYPHENYLPYRUVATE DIOXYGENASE from Medicago sativa Is Involved in Vitamin E Biosynthesis and Abscisic Acid-Mediated Seed Germination (OA)
Plant Science Research WeeklySci. Rep. Vitamin E has been shown to scavenge singlet oxygen, reduce lipid oxidation by-products and inhibit lipid peroxidation, thereby helping plant defenses against various stresses.
In this study, the authors identified MsHPPD as a key gene for vitamin E biosynthesis in alfalfa – an important…

What We're Reading: June 15th Edition
WWR Full PostPlant Vitamins and Cofactors Special Issue
This week’s “What We’re Reading” summarizes recent findings on plant vitamin and cofactor biosynthesis and their role in plant defense responses. This selection includes two reviews and nine research papers. The first review focuses on biofortification…
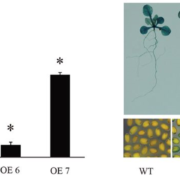
Aldehyde Dehydrogenases Function in the Homeostasis of Pyridine Nucleotides in Arabidopsis thaliana (OA)
Plant Science Research WeeklySci. Rep. Aldehyde dehydrogenase enzymes (ALDHs) are very common proteins involved in the oxidation of aliphatic and aromatic aldehydes to their corresponding carboxylic acids, using NAD and NADP as electron acceptors.
In this paper the authors explore the hypothesis that ALDHs are also important…

A Lectin Receptor Kinase as a Potential Sensor for Extracellular Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide in Arabidopsis thaliana (OA)
Plant Science Research WeeklyeLife Besides its role as an enzyme cofactor, NAD is also a plant signaling molecule. In particular, it leaks from wounded areas and activates defense pathways in the neighboring tissue, an effect that can be mimicked by application of extracellular NAD.
The presence of a sensing mechanism for extracellular…

Folate Biofortification of Potato by Tuber-Specific Expression of Four Folate Biosynthesis Genes ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMol. Plant Deficiency in Vitamin B9 (folate) is one of the major causes of birth defects and maternal deaths. As potato is a staple crop for several populations worldwide, one strategy to reduce the risks of folate deficiency is the biofortification of potato. This would be extremely useful, as the…

