
Survival of the kleptoplasts (Front. Ecol. Evol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyHow chloroplasts remain viable inside of herbivorous sea slugs is a long-standing curiosity. Unlike corals, which host intact photosynthetic algae, sea slugs retain naked chloroplasts (which are then called kleptoplasts – stolen plastids), some of which remain viable for seveal weeks. Christa et al.…
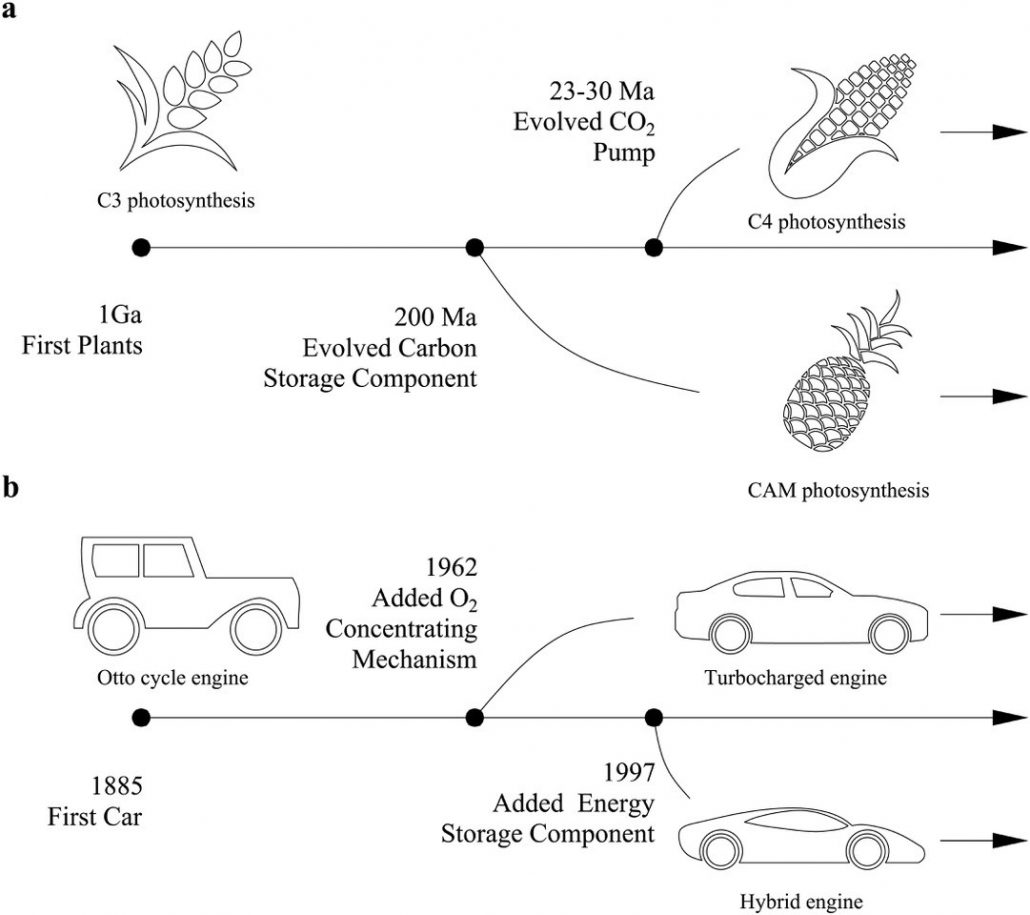
Review: What do cars and plants have in common? (PLOS One)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants and cars need energy and are powered by a process that has changed depending on the environment: photosynthesis, in the case of plants and an engine in the case of cars. Hartzell and coworkers make an analogy in the evolution of the original C3 pathway and the evolution of the internal combustion…
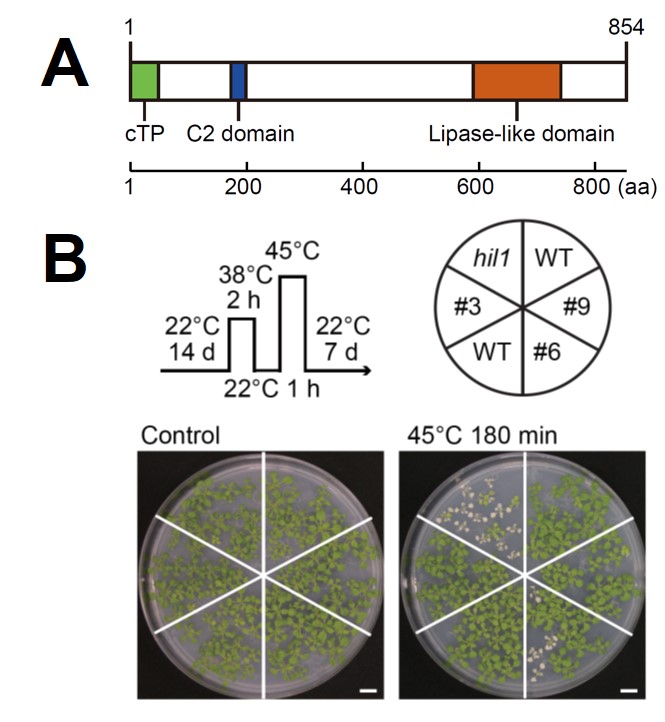
Heat Trims the Fat: HIL1 Functions in Lipid Homeostasis
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefGlobal climate change is one of the most pressing issues facing our world today. The impact of increasing temperatures can be felt in diverse areas, including human health and disease, natural ecosystems, and food security. In the agricultural sector, deciphering how plants respond to changing environmental…

Diffusion of CO2 across the mesophyll-bundle sheath cell interface in a C4 plant with genetically reduced PEP carboxylase activity (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyC4 photosynthesis relies on the transport of carbon (in the form of C4 acids) from the mesophyll into bundle sheath cells (BSCs). Subsequent decarboxylation of these C4 acids generates a high concentration of CO2 in the vicinity of Rubisco, helping to improve the catalytic efficiency of this enzyme. …

Assembling a Nanomolecular Power Station
The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefThe ATP synthase complex of chloroplasts is an elegant example of the union of structure and function at the molecular level (Junge and Nelson, 2015). This enzyme complex consists of an integral membrane CFo component that transports protons and an extrinsic CF1 component that synthesizes ATP (Hahn et…

Review: Applying synthetic biology and genetic engineering to photosynthesis
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotosynthesis is a complex process that has the potential to be greatly improved through human modifications. However, these modifications have been limited by two main factors: the high degree of conservation of the components, and the multiprotein complexes that require specifically modified proteins…
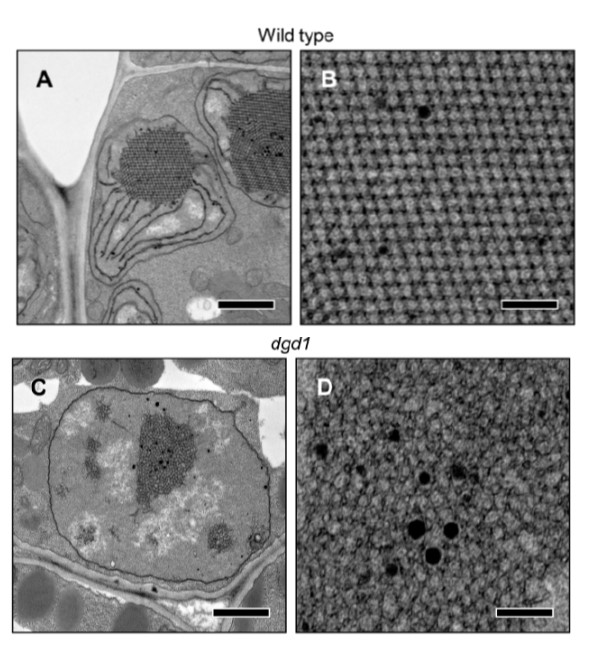
Etioplasts: The Role of Digalactosyldiacylglycerol
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideIn dark-grown plants, the plastids of cotyledon cells develop as etioplasts. Etioplasts contain unique internal lattice membrane structures called prolamellar bodies (PLBs) and lamellar prothylakoids (PTs). PLBs accumulate protochlorophyllide (Pchlide), a chlorophyll intermediate, in a complex with NADPH…
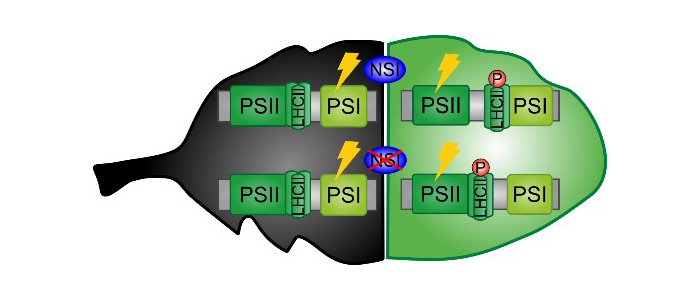
Regulation of Photosynthesis: Shedding Light on Protein Acetylation
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellKoskela and Brünje et al. identified a chloroplast protein acetyltransferase, which is required for the regulation of light harvesting in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell (2018) https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00155.
by Minna M. Koskela, Annika Brünje, Iris Finkemeier, Paula Mulo
Background: Plants…

New discovery on photosynthesis discovered
Blog, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: News9:07:18 | Editor: Marc Platthaus From Neue Erkenntnis zur Fotosynthese entdeckt Translated by Google.
The conversion of carbon dioxide and sunlight into energy (or biomass) and oxygen: hardly any process is as crucial to life on earth as photosynthesis. Although the process has been studied extensively…

