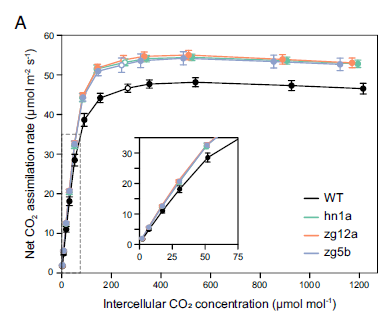
Boosting C4 photosynthesis and productivity by elevating Rubisco levels in sorghum and sugarcane
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe United Nations projects that by 2050, global food production must increase by 60% to meet growing demand, a goal that must be met under the pressures of global climate change and without further agricultural land expansion. With rising atmospheric CO₂ levels, Rubisco has emerged as the primary…
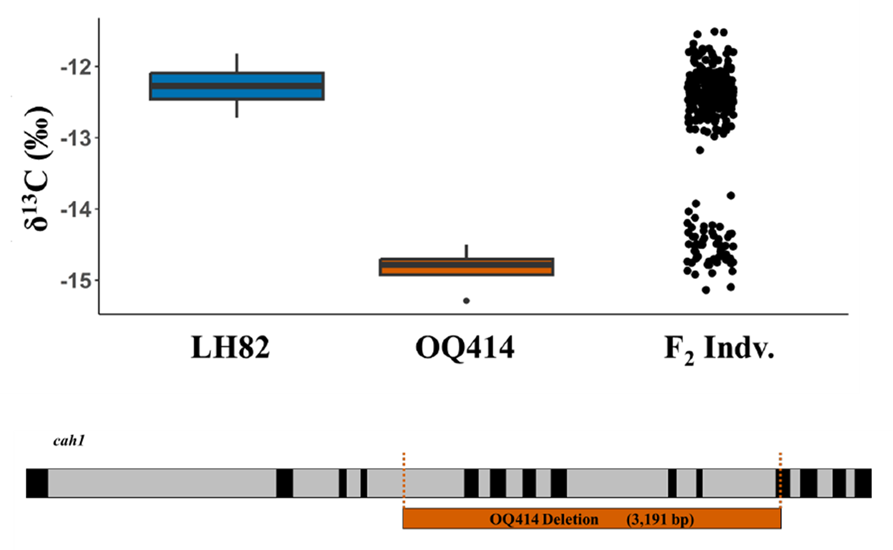
CA-nundrum: How a spontaneous mutation in carbonic anhydrase uncouples leaf δ13C, WUE and C4 photosynthesis
Plant Science Research WeeklyWith climate change, drought is expected to happen more frequently, making supplemental irrigation increasingly necessary to sustain crop productivity. One target trait to improve climate resilience is water use efficiency (WUE), defined by the ratio of carbon assimilation to water used by the plant.…
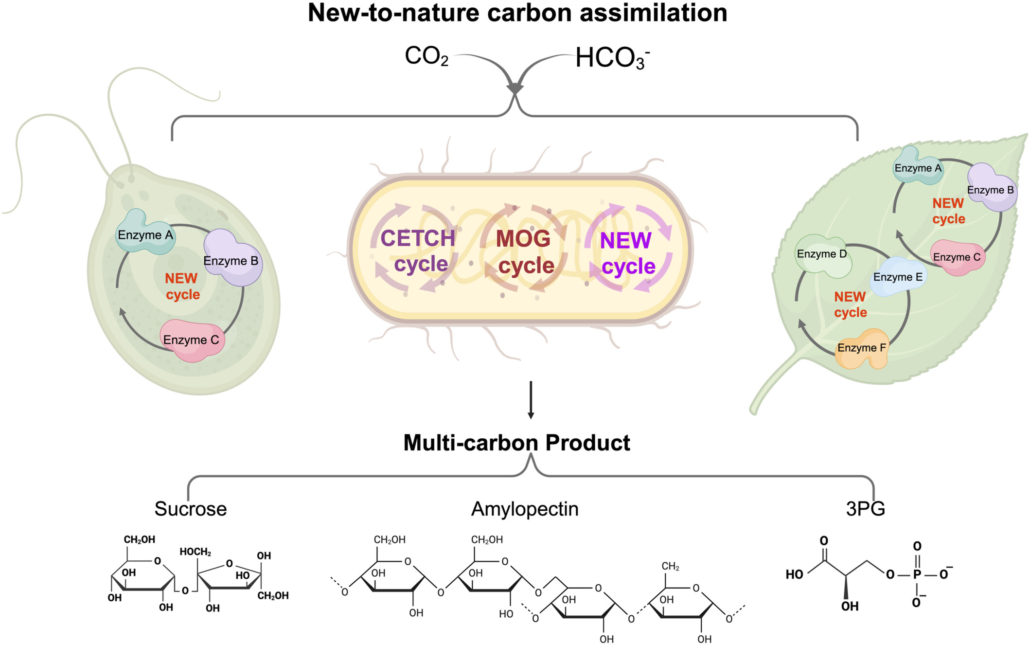
Review: Genetic engineering for carbon assimilation in plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyRubisco (Ribulose‐1,5‐bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) is the central enzyme for photosynthesis, This enzyme poorly discriminates between CO2 and O2, which limits its efficiency. To work around this and make carbon assimilation more efficient, scientists have been employing different engineering…
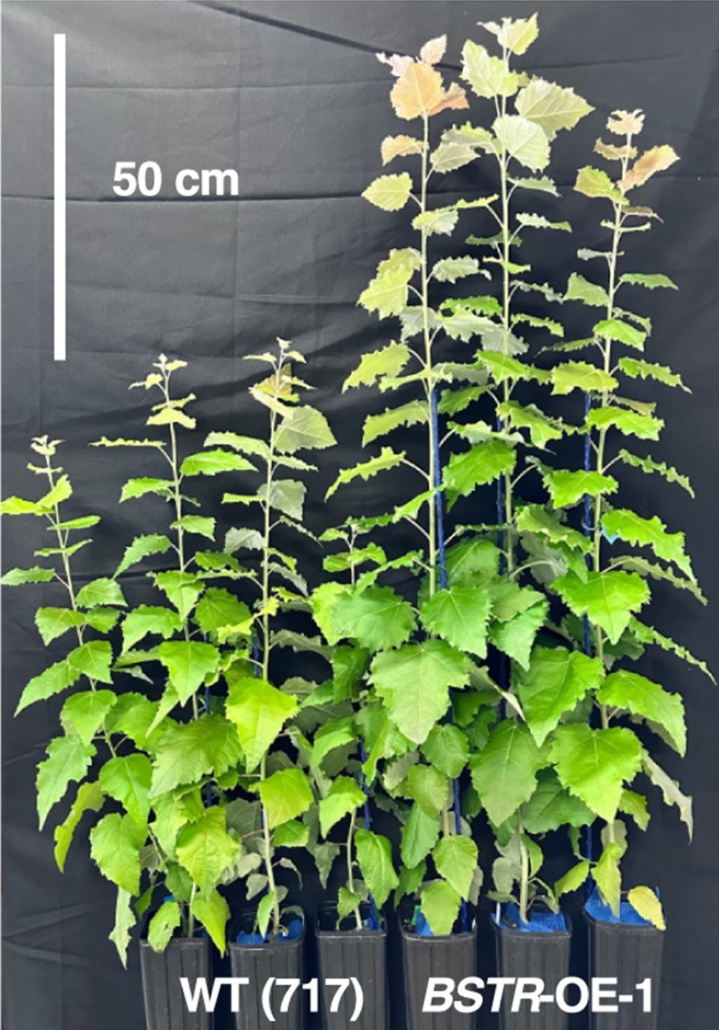

BOOSTER: Unlocking photosynthetic efficiency for enhanced plant productivity
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotosynthesis is a fundamental biological process for carbon fixation and capturing light energy to drive plant growth. However, excessive sunlight can cause photodamage, which is detrimental to plant health. To protect the photosynthetic machinery from over-excitation and subsequent damage, plant cells…
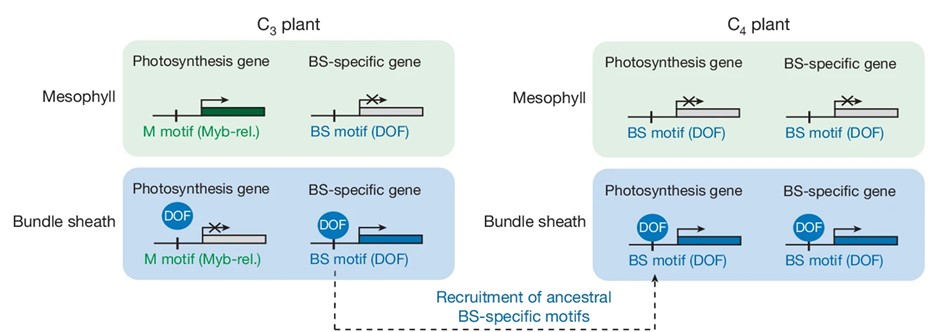
Changes in regulatory regions shape C3 to C4 evolution
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn most land plants, carbon fixation into a three-carbon compound by the enzyme Rubisco takes place in the leaf mesophyll cells; these are called C3 plants. However, a different and more efficient pathway has evolved independently many times, in which a four-carbon metabolite is first produced in the…
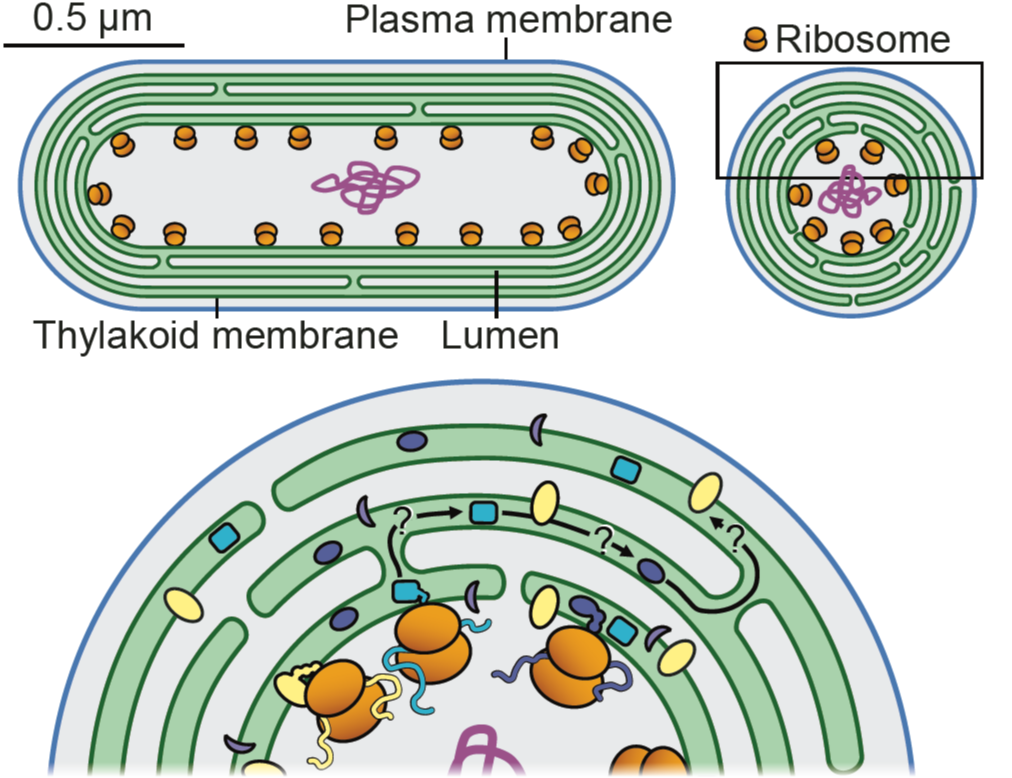
Review. Lighting the way: Compelling open questions in photosynthesis research
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotosynthesis is fundamental to life on Earth and a topic that all plant biologists should have a good understanding of, but it is also an incredibly complex set of processes, reactions and structures spanning great temporal and spatial distances. In this new Commentary by Eckardt et al., several experts…
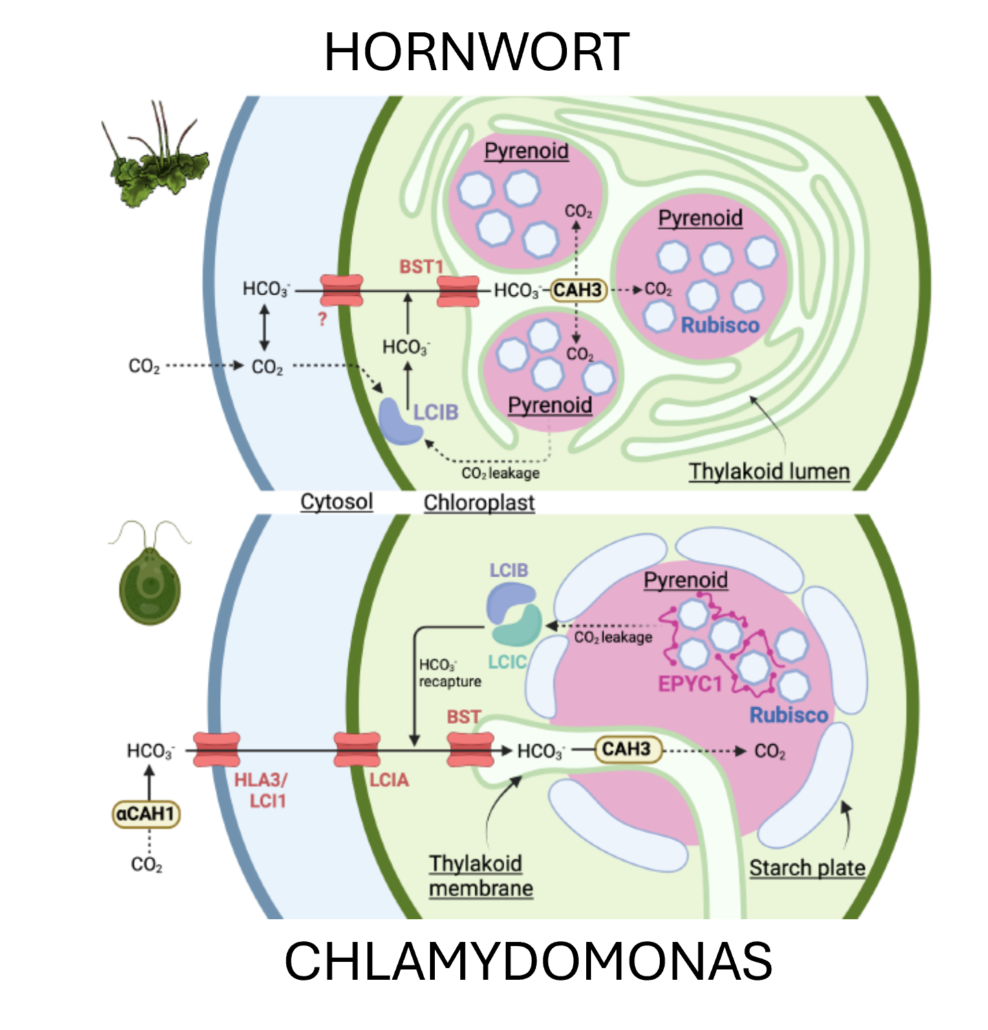
Characterization of pyrenoid-based CO2-concentrating mechanism in hornworts
Plant Science Research WeeklyPyrenoids are structures that concentrate carbon dioxide around Rubisco, most commonly studied in green algae such as Chlamydomonas. However, hornworts, one of the three types of bryophytes (along with liverworts and mosses) also have a pyrenoid-based CO2-concentrating mechanism (pCCM), unique among…

Posttranslational regulation of photosynthetic activity via the TOR kinase in plants
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn the dazzling dance of plant cellular life, chloroplasts must groove in harmony with growth to sidestep the perils of photooxidative damage. This harmony between photosynthesis and photooxidative damage is orchestrated by the guanosine tetraphosphate (ppGpp) signalling pathway which traces its roots…
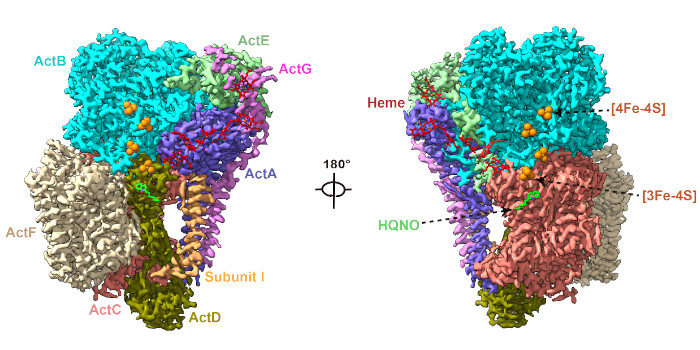
Alternative complex III: an ancient counterpart of the bc1/b6f complex
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellXin et al. determined the cryo-EM structure of HQNO-bound Alternative Complex III from the anoxygenic phototrophic bacterium Chloroflexus aurantiacus. The Plant Cell (2024)
https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koae029
By Xiaoling Xu at Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou, China
Background: Photosynthesis…

