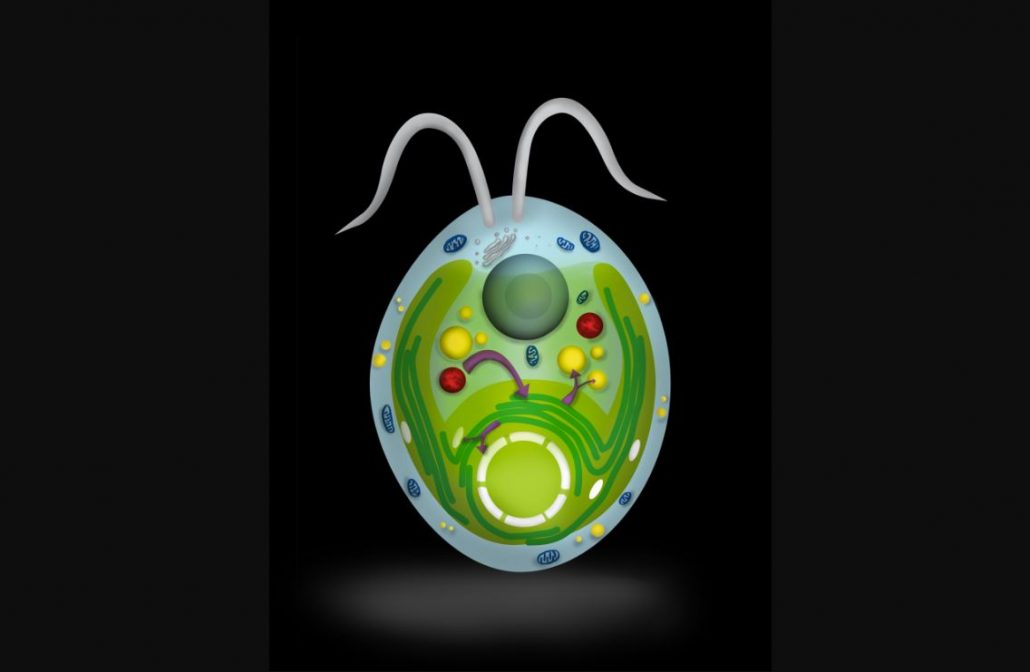
How Peroxisomes Modulate Chloroplast Activity in a Microalga
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellBackground: Chloroplasts are the major powerhouse of plant and algal cells, where photosynthesis—the conversion of carbon dioxide into organic compounds using sunlight energy—occurs. Chloroplasts are also where important cell components (such as membrane lipids and pigments) and energy-rich compounds…
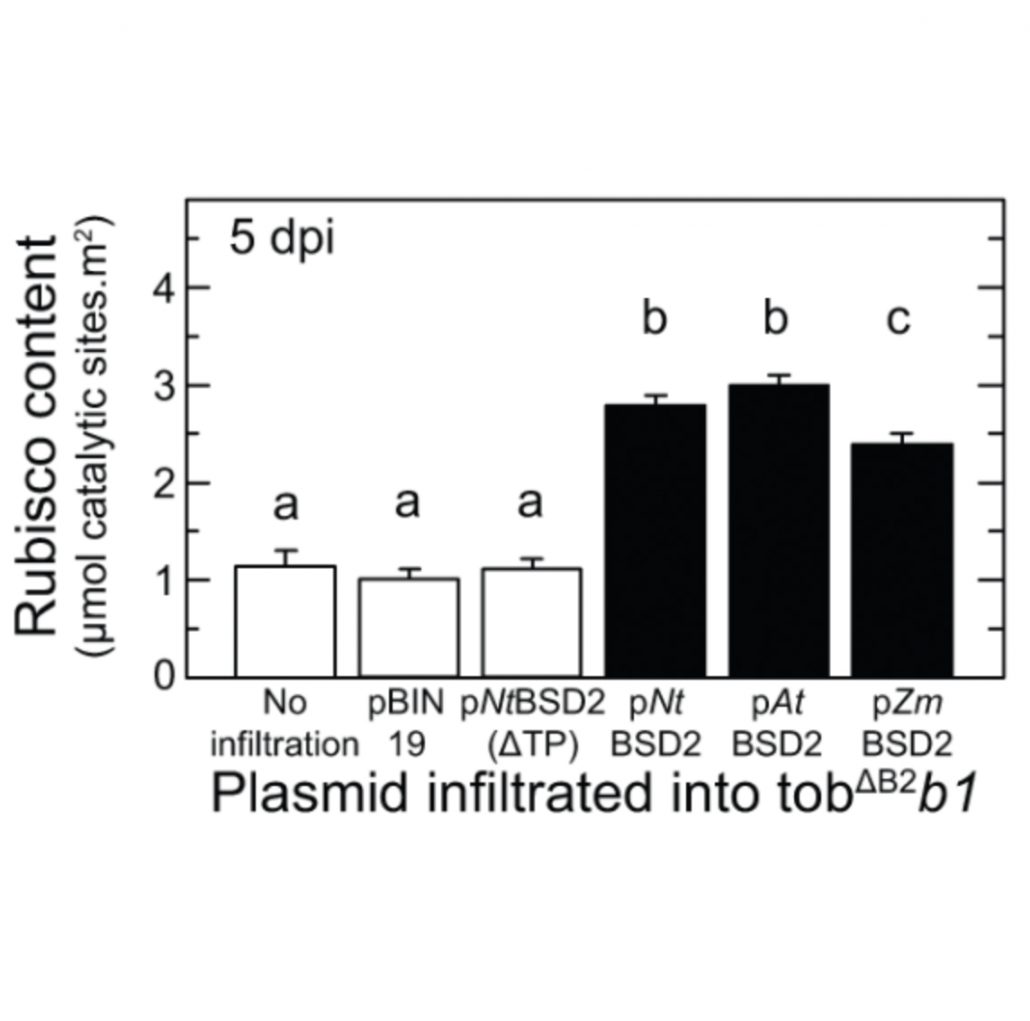
BSD2 is a Rubisco specific assembly chaperone, forms intermediary hetero‐oligomeric complexes and is non‐limiting to growth in tobacco (Plant Cell Environ)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe rubisco holoenzyme is comprised of eight large subunits and eight small subunits (L8S8). Several auxiliary proteins are required to correctly assemble the functional protein. In this manuscript, Conlan et al investigate the chaperone function of one of these proteins, BSD2, in tobacco. The authors…
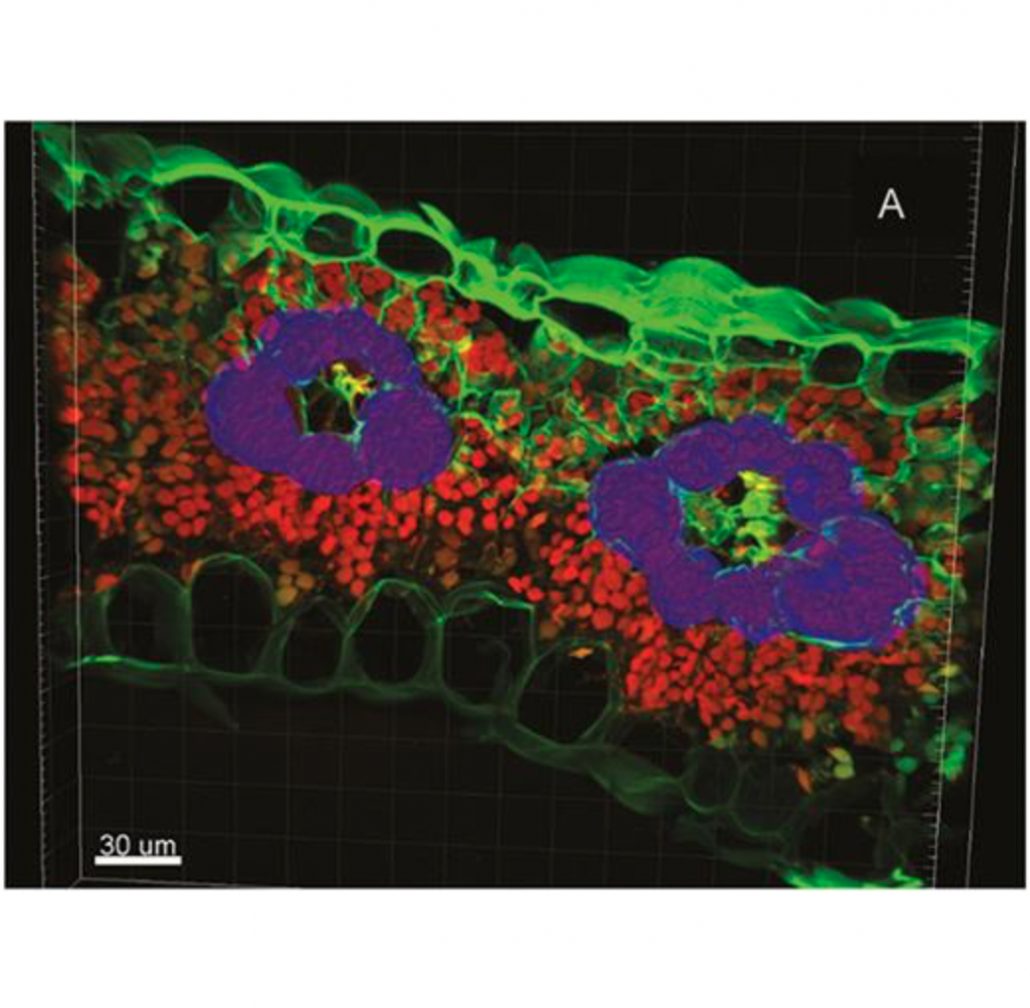
Bundle sheath chloroplast volume can house sufficient Rubisco to avoid limiting C4 photosynthesis during chilling (J Exp Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIt has long been thought that C4 species generally perform less well than C3 species in cold environments as a consequence of a physical space restriction. C3 species tend to accumulate more rubisco under chilling stress to avoid limiting photosynthesis, but there is less capacity for this in C4 species…
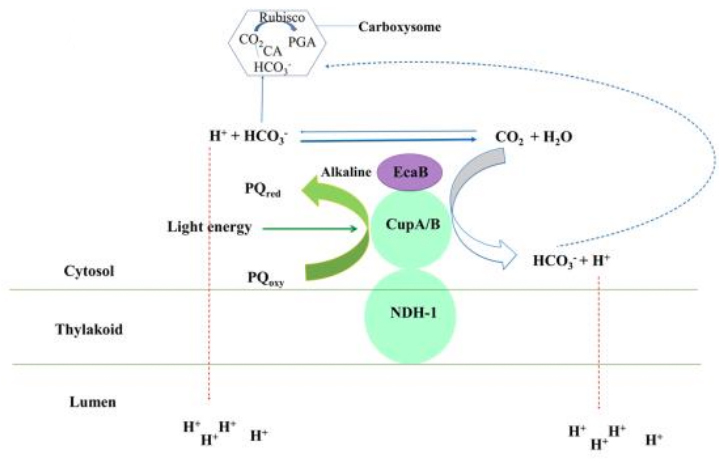
A thylakoid-located carbonic anhydrase regulates CO2 uptake in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe cyanobacterial CO2 concentrating mechanism (CCM) is dependent on a continuous supply of inorganic carbon (Ci) to rubisco inside carboxysomes in order to function optimally. CO2 uptake pathways are therefore of great importance for a full understanding of the cyanobacterial CCM. Sun et al demonstrate…
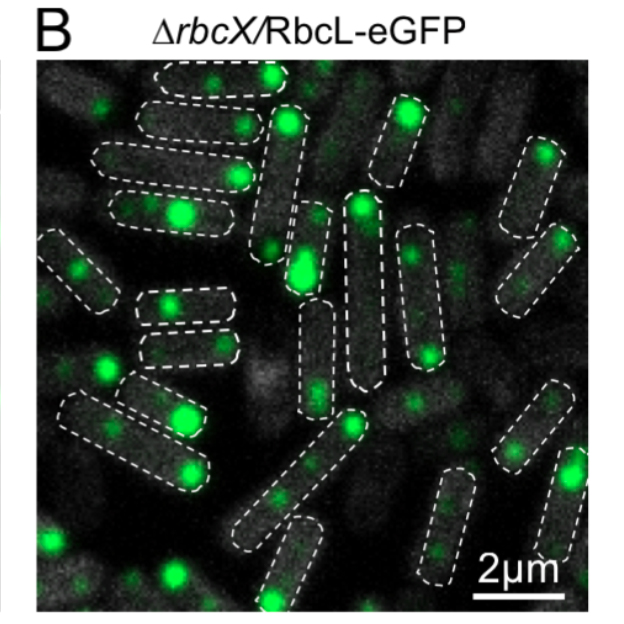
Roles of RbcX in carboxysome biosynthesis in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongates PCC 7942 (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIntroduction of the cyanobacterial carboxysome into C3 crops represents a viable strategy to increase photosynthetic conversion efficiency and boost crop yield. Key to this challenge is gaining a full understanding of the carboxysome system in cyanobacteria, including how these microcompartments assemble…
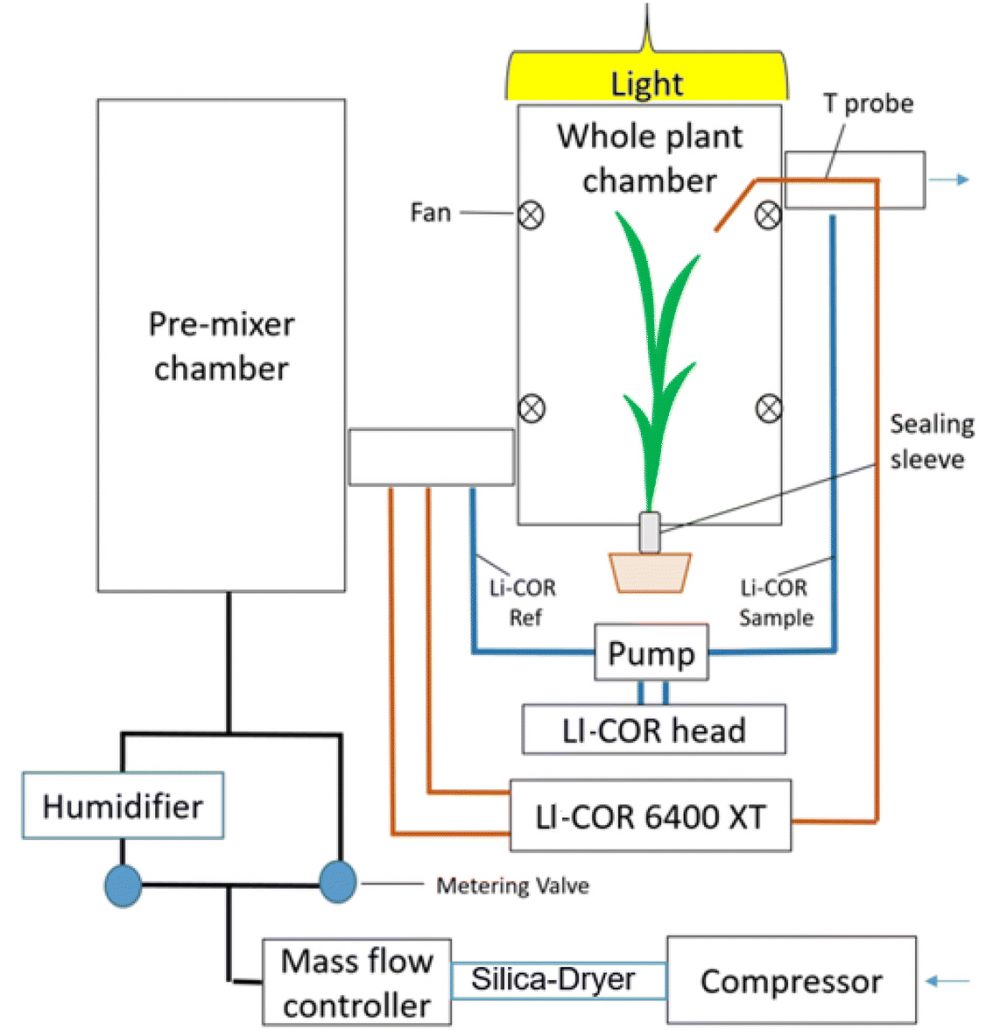
Whole plant chamber to examine sensitivity of cereal gas exchange to changes in evaporative demand (Plant Methods)
Plant Science Research WeeklyStomata represent the entry point into the leaf for CO2 that will be fixed by rubisco in photosynthesis and the exit point of water as it is lost to the atmosphere. As such, they are subject to tight regulation in response to the environment so that water loss is minimised and a supply of CO2 is…
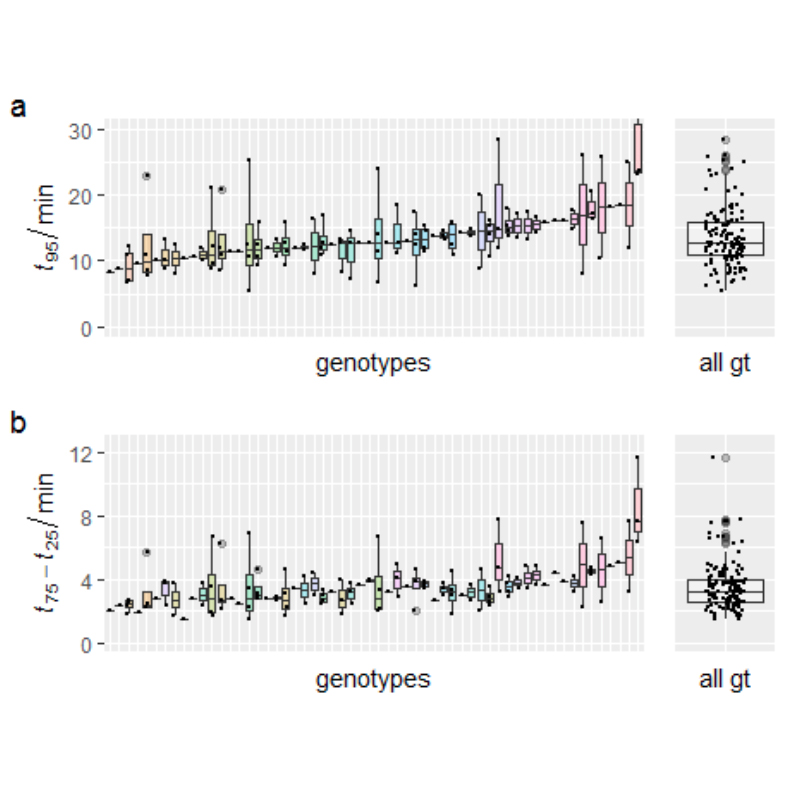
Rate of photosynthetic acclimation to fluctuating light varies widely among genotypes of wheat (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe speed at which photosynthesis is induced during shade-sun transitions, such as sun-flecks, contributes towards determining crop yield. The speed of induction can be limited by the dynamics of stomatal and mesophyll conductance, deactivation rates of photoprotective mechanisms, the acclimation rate…
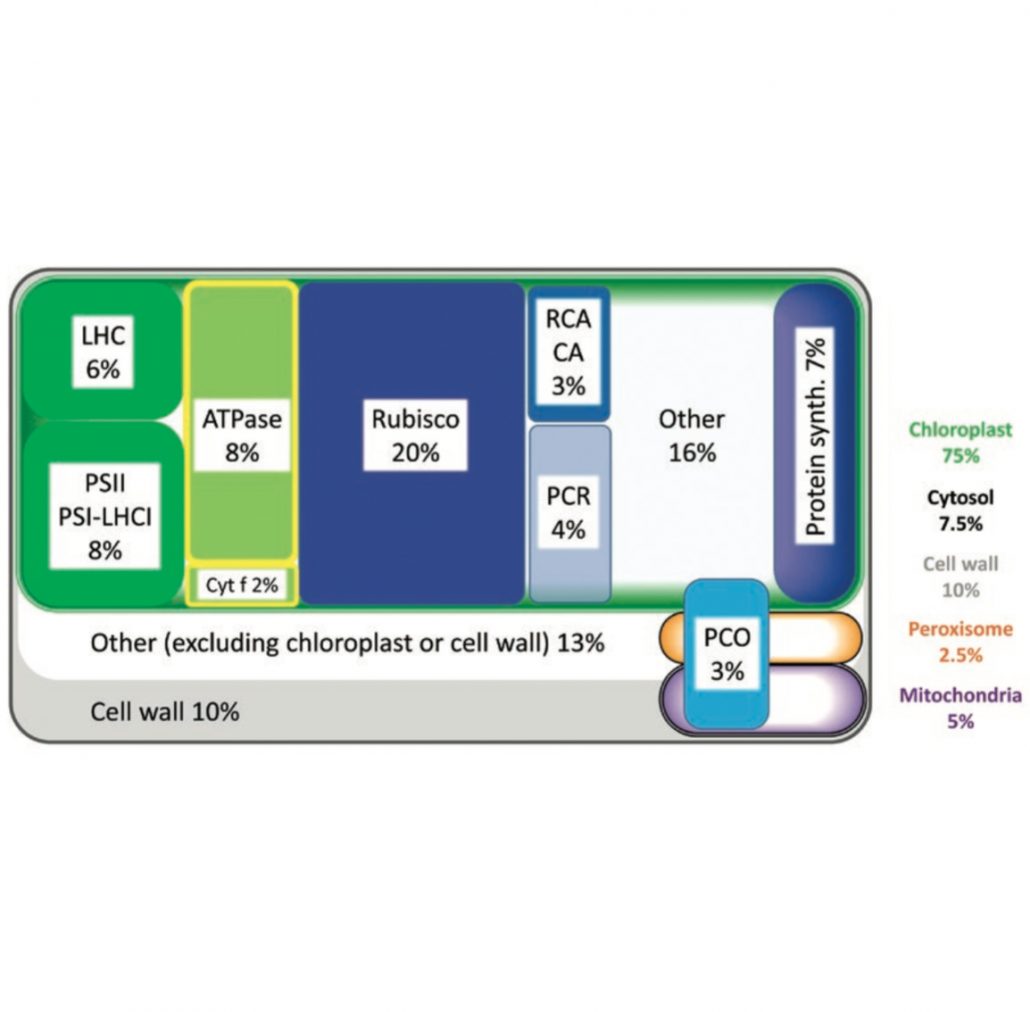
Expert View: The nitrogen cost of photosynthesis (J Exp Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyModern crop production is intimately linked to the availability of nitrogen. Photosynthetic proteins (including rubisco) account for most of the nitrogen in leaves, a significant amount of which is removed during harvesting and must be replenished primarily through the application of synthetic nitrogen…
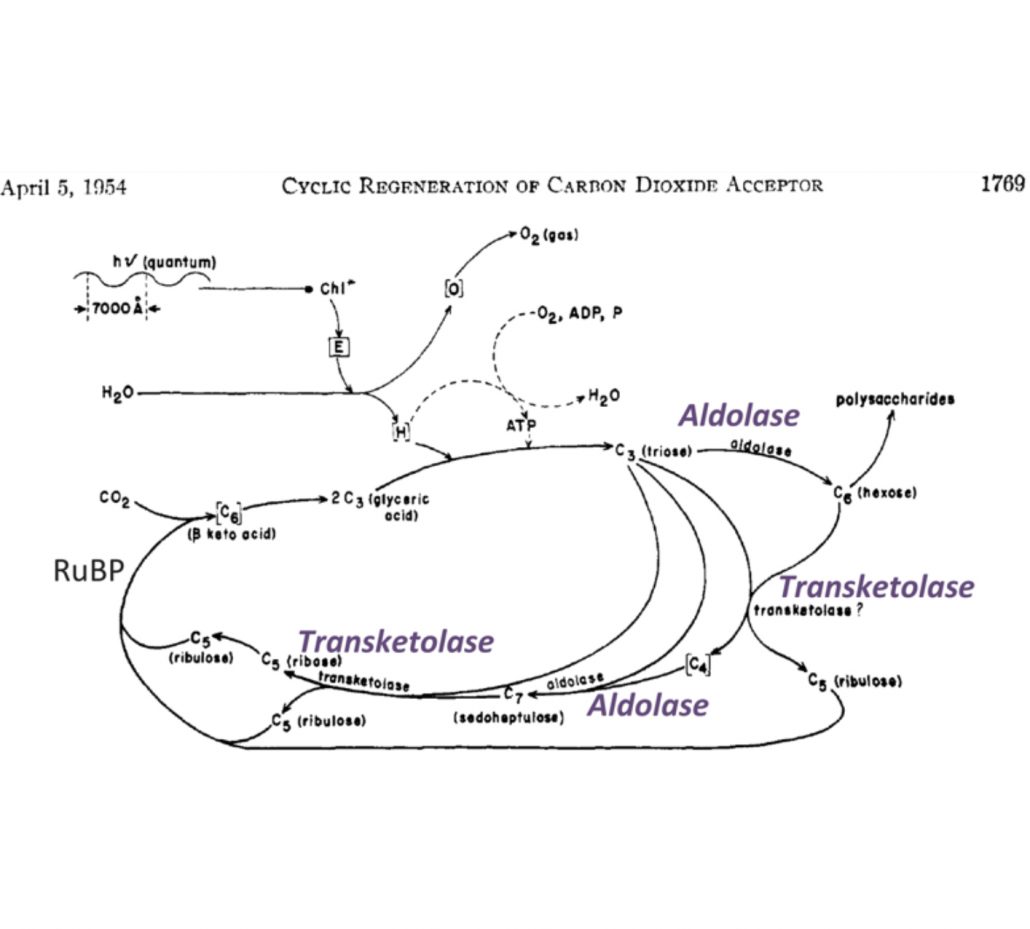
Review: Discovery of the canonical Calvin–Benson cycle (Photosynth Res)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIt has been over seventy years since Melvin Calvin and Andrew Benson first started on their journey to discovering the Calvin-Benson cycle – the series of biochemical reactions in which the Sun’s energy is converted to chemical energy stored inside the cells of plants, cyanobacteria and algae. …

