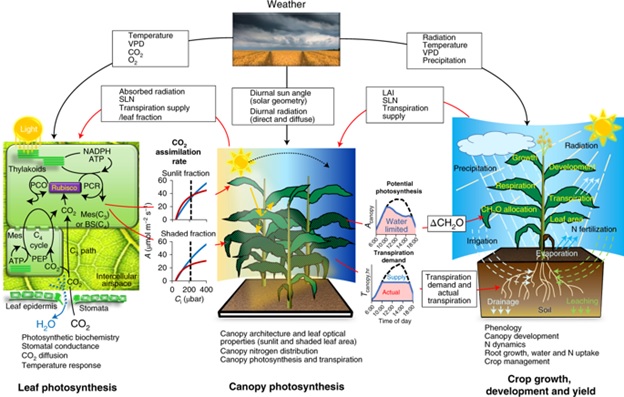
Modeling crop yield changes due to increased photosynthetic capabilities ($) (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWith the need to feed the growing population and the threat of global climate change, there is an imminent need to increase crop yields. One commonly accepted method of accomplishing this is by enhancing the photosynthetic capability of major crop plants, which may result in an increased yield. A recent…
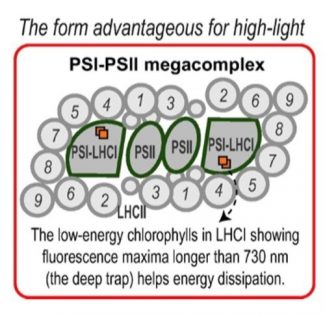
A direct connection between PSI & PSII systems in green plants (Plant Cell Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants often optimize their development according to the prevailing environmental conditions, of which light is one of the most important. Arabidopsis uses a PSI-PSII megacomplex as the photosystem reaction center, to transfer the excessive energy from PSII to PSI rapidly. Recently, Yokono et al. proposed…
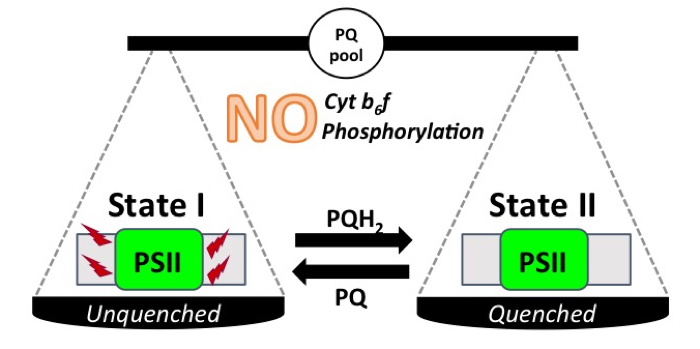
Balancing photosystem activities: different mechanisms in plants and cyanobacteria
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellCalzadilla et al. investigate the mechanism underlying state transitions in cyanobacteria. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00159
By Pablo I. Calzadilla and Diana Kirilovsky, Institute for Integrative Biology of the Cell, CEA, CNRS, Université Paris-Sud, Université Paris-Saclay, Gif sur…
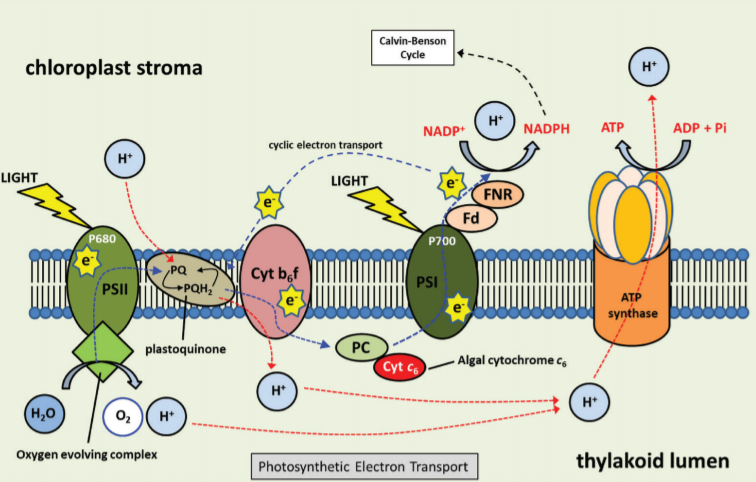
Review. Feeding the world: improving photosynthetic efficiency for sustainable crop production (J Exp Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe global population is estimated to rise by 2 billion by 2050 placing strains on major food crops. To sustainably feed future populations and reduce the environmental damage of intensive agriculture, crop yields must be improved without increasing the amount of cultivatable land. In this review, Simkin…
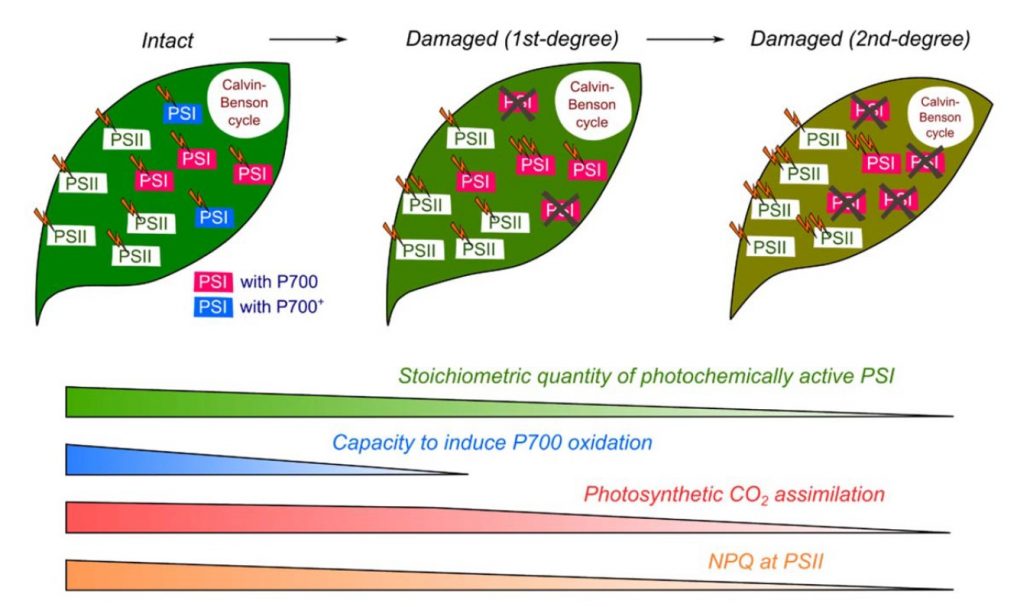
What quantity of photosystem I is optimum for safe photosynthesis? ($) (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhotosynthesis is one of the most vital and complex processes carried out by plants. During photosynthesis, Photosystem I and II (PSI and PSII) undergo photo-excitation. Excessive photo-excitation can damage and deactivate the PSI by generating reactive oxygen species (ROS). This kind of photoinhibition…

Rubisco condensate formation by CcmM in β-carboxysome biogenesis (Nature) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCyanobacterial carbon-dioxide concentrating mechanisms elevate intracellular inorganic carbon as bicarbonate, and then concentrate it as carbon-dioxide around the enzyme Rubisco in specialized protein micro-compartments called carboxysomes. The formation of B-carboxysomes involves an aggregation between…

Synthetic glycolate metabolism pathways stimulate crop growth and productivity in the field ($) (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRubisco uses CO2 from the air to carboxylate its substrate RuBP, resulting in an increase in fixed carbon. However, rubisco can also oxygenate RuBP and this leads to the production of glycolate. Plants must invest energy in recycling this toxic by-product in a process called photorespiration, resulting…

New Insights into Carboxysomes
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideDespite its essential role in photosynthetic carbon fixation, ribulose 1,5 bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) is a relatively inefficient enzyme, due in part to its inability to discriminate between CO2 and O2 as substrates. To suppress the oxygenase reaction and enhance the carboxylase activity…
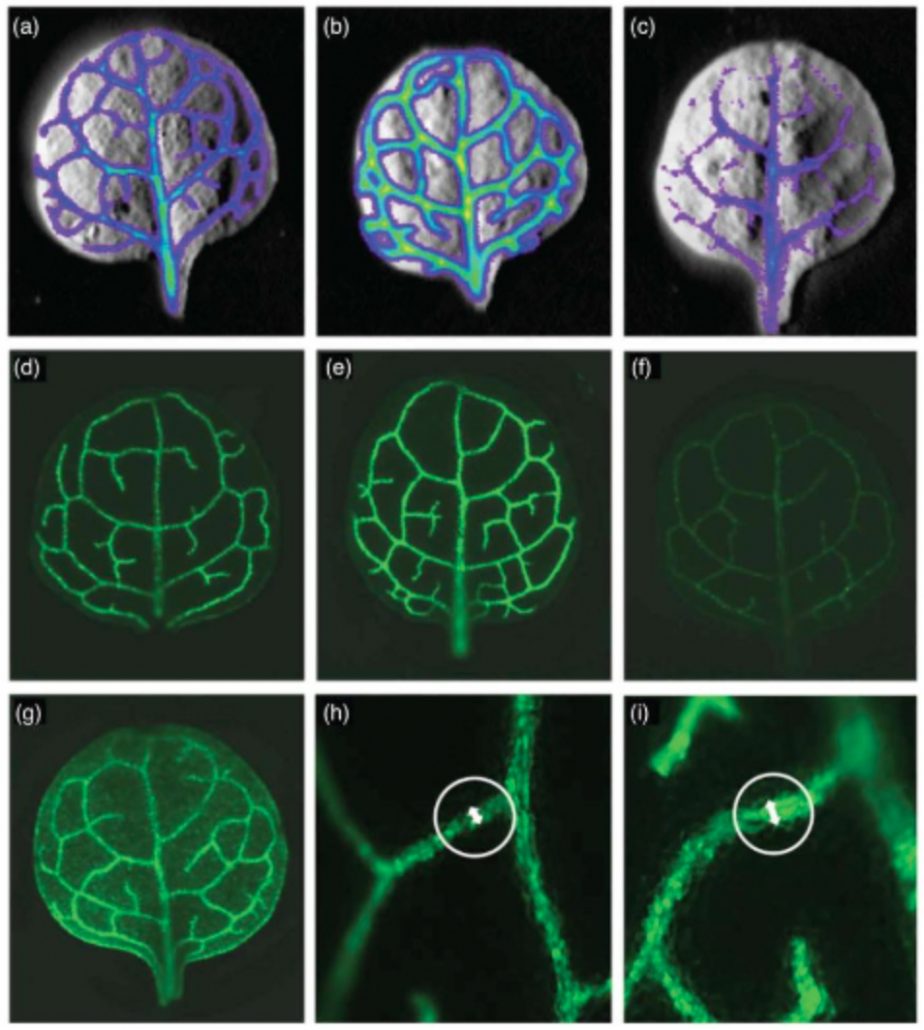
Reporter‐based screen to identify bundle sheath anatomy mutants ($) (Plant J)
Plant Science Research WeeklyInstallation of C4 photosynthesis into C3 crops appears a realistic way to boost crop yields. A key aspect of C4 photosynthesis is an enlarged bundle sheath volume and an increase in bundle sheath chloroplast number. To identify the regulators of this phenotype, Döring et al. subjected Arabidopsis…

