
A Rubisco-binding protein is required for normal pyrenoid number and starch sheath morphology in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn most eukaryotic algae, carbon fixation takes place in an organelle within an organelle, the pyrenoid inside of the chloroplast. Besides being functionally very important, pyrenoids are interesting because they are what is called a phase-separated structure, that is they are not membrane enclosed;…
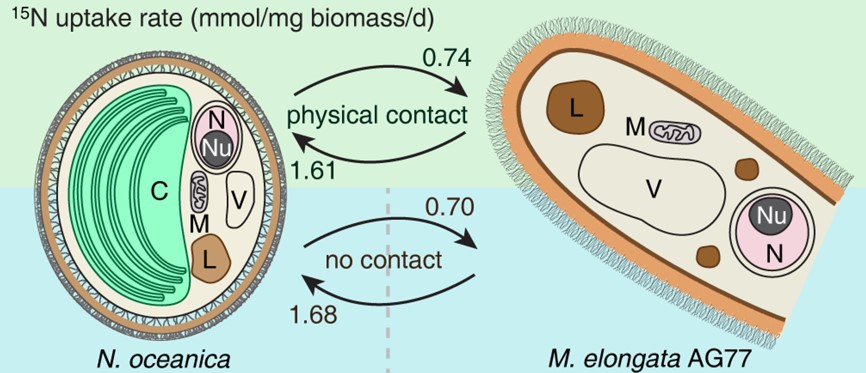
Algal-fungal symbiosis may account for the origin of basal land plant species (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyLight serves as the source of energy as well as an information signal for photosynthetic plants. During evolution, plants have acquired the ability to monitor environmental light radiation and adjust their developmental patterns to optimally utilize light energy for photosynthesis. However how the early-diverging…
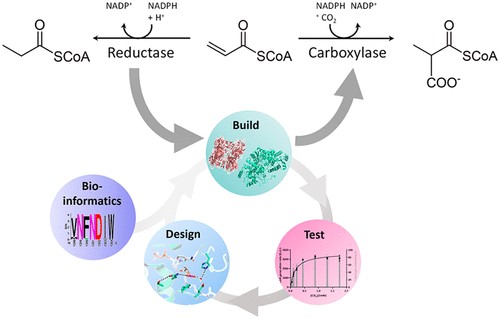
Awaking the sleeping carboxylase ($) (JACS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyOne of the things I like most about synthetic biology is the “why not” attitude. This article by Bernhardsgrütter et al. is intriguing because rather than taking the standard “let’s fix Rubisco approach,” the authors started with a non-CO2 fixing enzyme and engineered it towards having carboxylase…
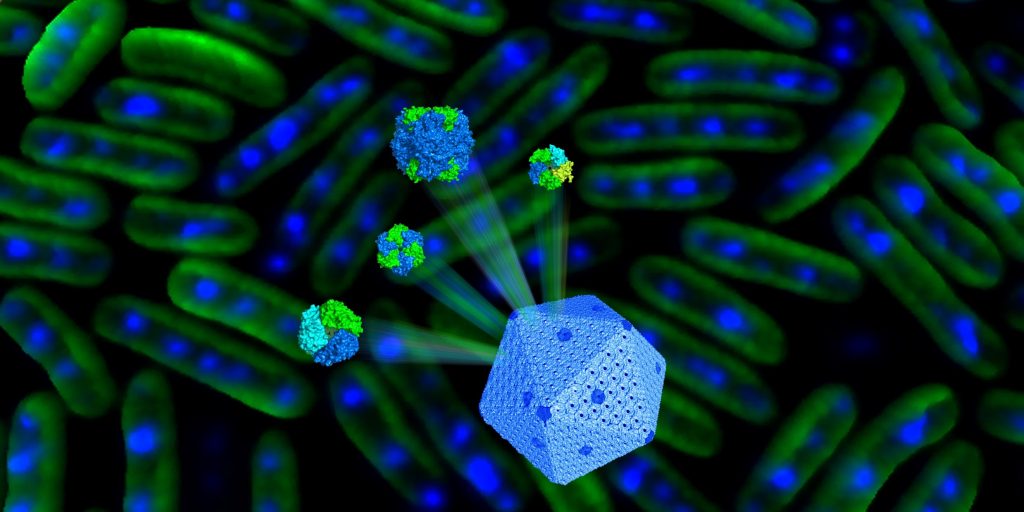
Self-assembling organelles for CO2 fixation: stoichiometry and structural plasticity
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellSun et al. investigate how carboxysomes are constructed and regulated in cyanobacteria. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00787
By Luning Liu
Background: All cells are composed of well-defined compartments to encase enzymes and reactions to increase the efficiency of biological processes.…
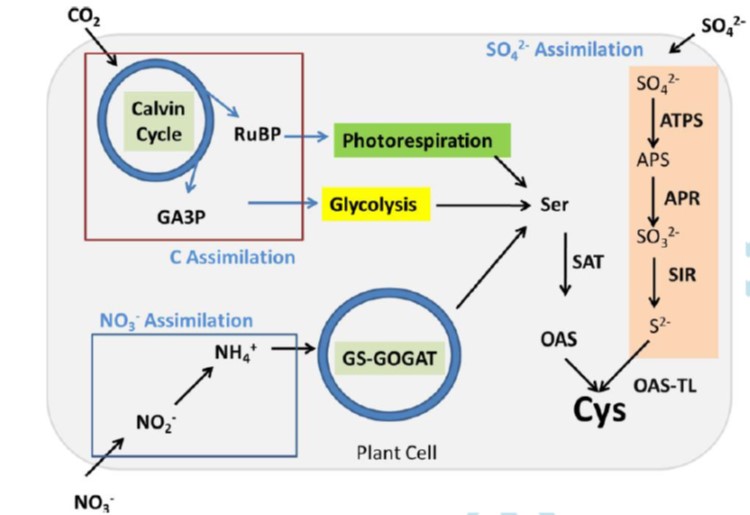
Review: Integration of sulfate assimilation with C and N metabolism in transition from C3 to C4 photosynthesis (J Exp Bot)
Plant Science Research Weekly“Cysteine (HO2CCH(NH2)CH2SH) synthesis is the converging point of the three major pathways of primary metabolism: carbon, nitrate, and sulfate assimilation.” It’s hard enough to coordinate two pathways, let alone three; but these metabolic connections are revealed in that a deficiency in one nutrient…
A Reversible Switch for Algal Photosynthesis
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellRoth et al. investigate how a green alga turns photosynthesis off and on when glucose is added and then removed from the culture medium. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00742
By Melissa Roth and Krishna Niyogi, University of California-Berkeley
Background: Photosynthesis is the life-sustaining…

Shared expression of crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) genes pre-dates the origin of CAM in the genus Yucca (J Exp Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyCrassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) is a carbon fixation pathway that reduces photorespiration and increases water use efficiency, enabling CAM plants to survive in inhospitable environments. The evolution of CAM on 35 independent occasions across angiosperms makes it a notable case study of convergent…

A Glucose Transporter Promotes Stomatal Conductance and Photosynthesis
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellHai Wang et al. identify a regulator of stomatal movement and photosynthesis. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00736
By Hai Wang, Biotechnology Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences
Background: Fixation of atmospheric CO2 through photosynthesis is crucial for the…
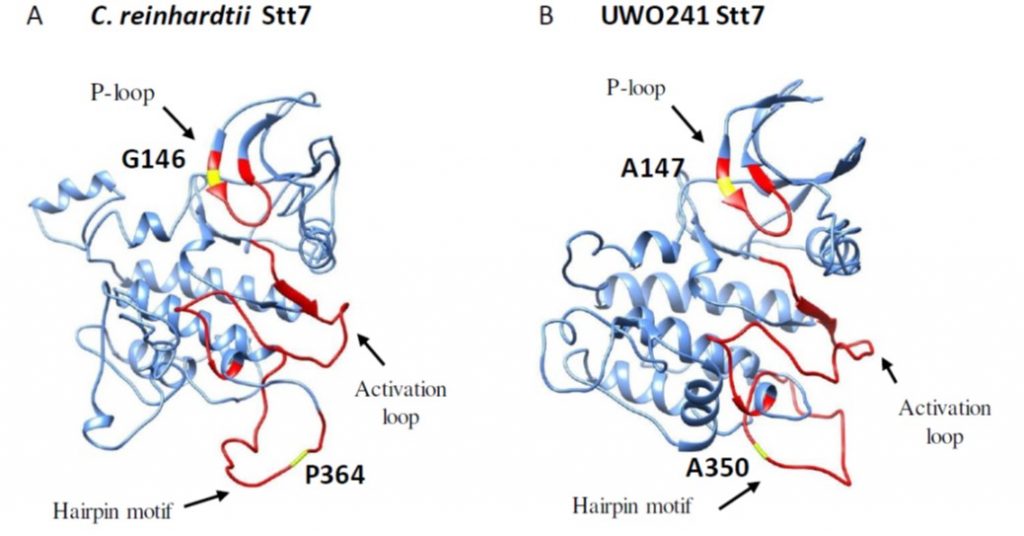
Cold-adapted protein kinases and thylakoid remodeling impact energy distribution in an Antarctic psychrophile (Plant Phys)
Plant Science Research Weekly“Earth is a cold place with 80% of its biosphere permanently below 5°C,” begins this study of an Antarctic psychrophile (“cold-lover”). As Szyszka-Mroz et al. indicate, the permanently cold-adapted inhabitants of permanently frozen lakes are highly vulnerable to the effects of climate change,…

