
Transdisciplinary Plant Phenomics and Phenotyping for Maize Crop Improvement
Blog, Plantae Webinars, Research0 Comments
/
Transdisciplinary Plant Phenomics and Phenotyping for Maize Crop Improvement
Recorded Tuesday, January 21, 2020
About This Webinar
Emerging tools in plant phenomics and high-throughput field phenotyping are redefining possibilities for decisions in plant breeding and agronomy…
Simulation modeling platform provides a powerful tool for identifying optimal traits and management practices for wheat production
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: News and Views, ResearchAuthor: Robert P Skelton1
[email protected]
Affiliation: Dept. of Integrative Biology, University of California Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, 94720, USA
Global demand for food security places an emphasis on a need to improve crop yield. The complexity of plant development and its interaction…

Functional Phenomics: Studying Root Physiology Using Affordable Open Source Tools
Blog, Plantae Webinars, Research Skills, WebinarsFunctional Phenomics: Studying Root Physiology Using Affordable Open Source Tools
Recorded December 17, 2019
About This Webinar
Functional phenomics is an emerging discipline that utilizes phenotyping, physiology, multivariate statistics, and simulation modeling to generate and test new…
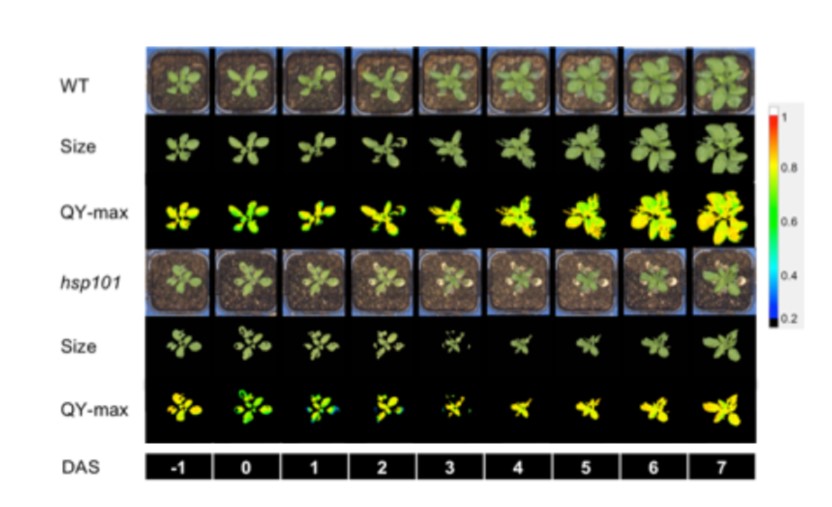
The use of high throughput phenotyping for assessment of heat stress-induced changes in Arabidopsis (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWith global temperatures rising, tolerance to heat is becoming increasingly important as a breeding target for crop plants, but it is a highly complex response that includes processes including plant cooling capacity, growth recovery, and maintenance of photosynthesis. Using Arabidopsis, Gao et al. developed…
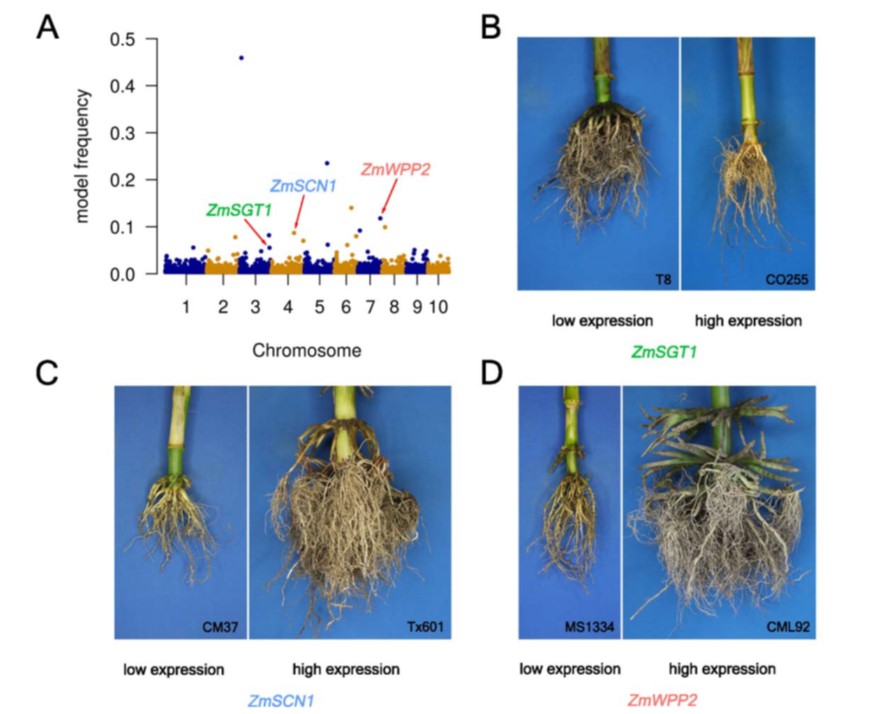
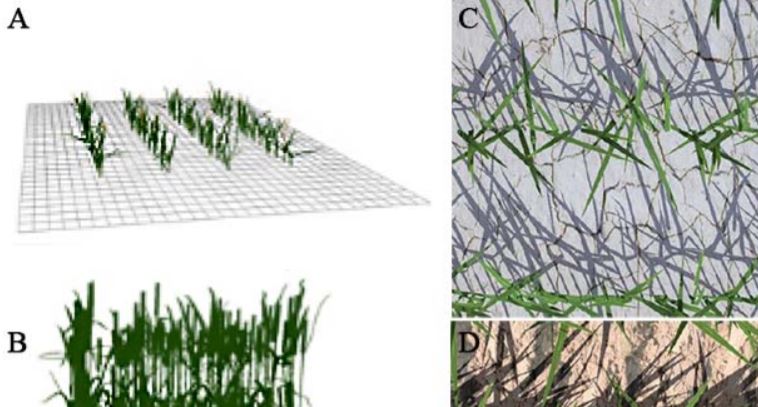
Shared genetic control of root system architecture between Zea mays and Sorghum bicolor (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoot research got a boost from Arabidopsis grown on Petri plants, but what do you do if you study something bigger, or want to see how roots grow in soil? Zheng et al. developed a new set of tools they call CREAMD-COFE [Core Root Excavation using Compressed-air (to extract the roots from soil), and Core…
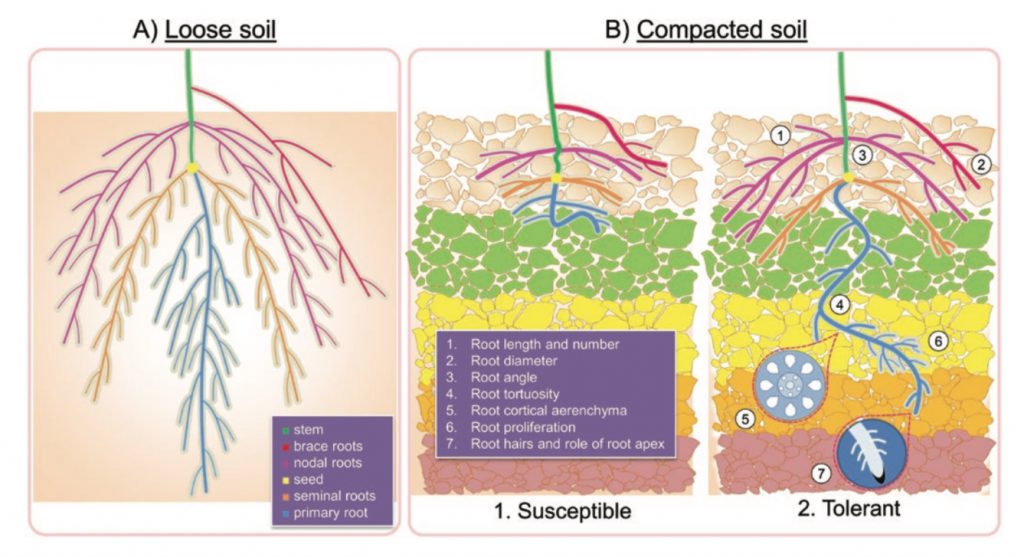
Review: Soil compaction and the architectural plasticity of root systems (J Exp Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoot system architecture (RSA) describes the spatial arrangement of root components within the soil. RSA is useful to understand the exploration of the plant to get nutrients and water through the soil space. In a new review, Correa et al. discuss RSA plasticity in response to soil compaction, which…
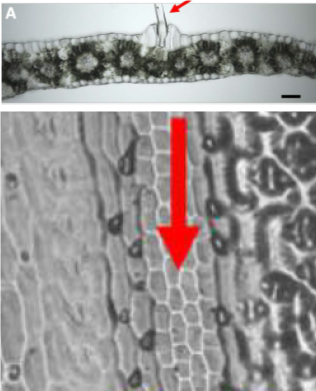
Machine learning enables high-throughput phenotyping for analyses of the genetic architecture of bulliform cell patterning in maize (G3)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBulliform cells lie in rows along the upper (adaxial) surface of the maize leaf, and through changes in volume contribute to leaf-rolling, which is a response to water deficit. Several mutants have been identified that affect bulliform cell formation and function, but as yet their occurance in natural…
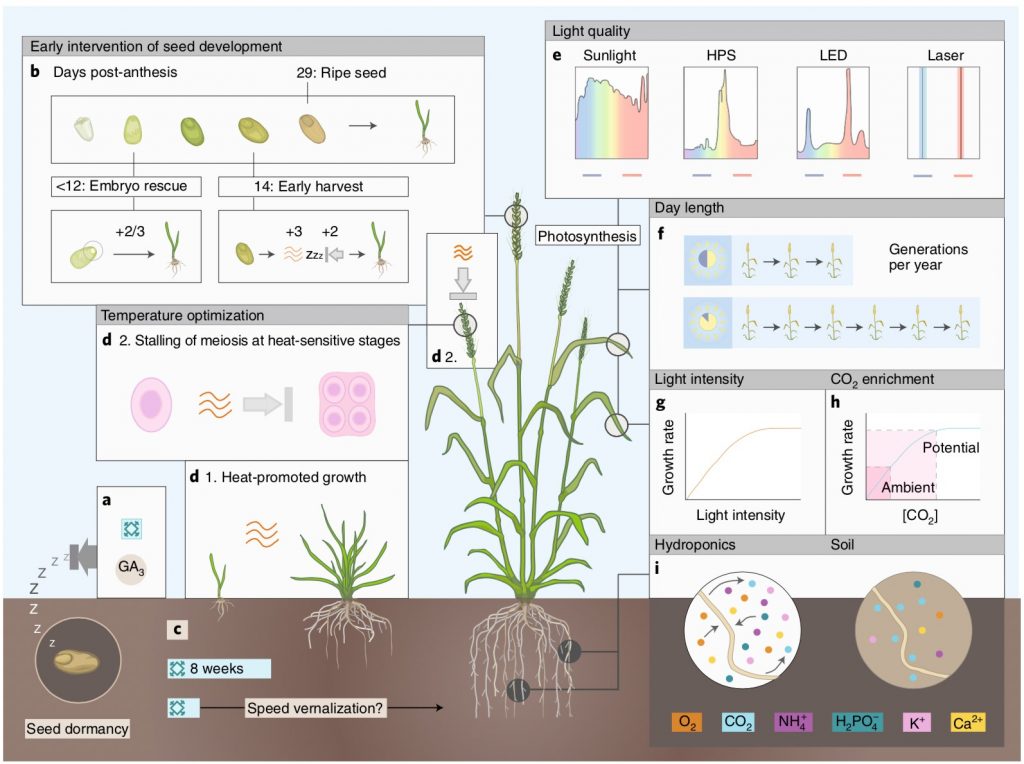
Review: Crop breeding technologies to feed the world (Nature Biotech)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe world demands food, plant scientists and breeders have the challenge of feeding a growing population. In a recent review Hickey et al. summarize the state-of-the-art technologies used for crop improvement. In use since 2003, ‘speed breeding’ is a set of improved methods for fast-tracking plant…
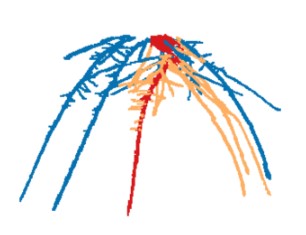
Three-dimensional time-lapse analysis of maize root system archictecture (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoot system architecture (RSA) profoundly affects plant nutritent uptake and response to drought, and is also famously extremely developmental plastic, which makes it difficult to identify genes that control root growth traits. Here, Jiang et al. analyzed 3D growth patterns over time of three maize lines…

