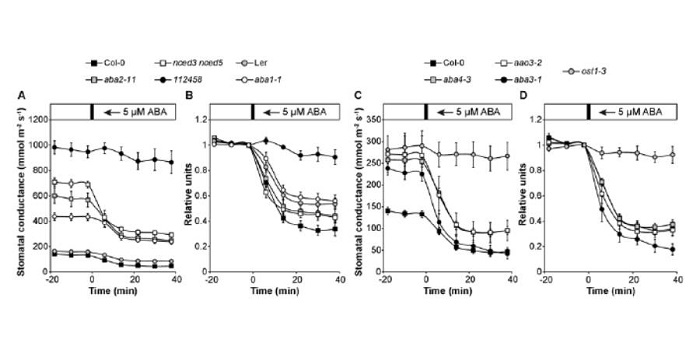
Origin and Role of ABA in Stomatal Regulation
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogWhen the vapor pressure difference (VPD) between a leaf and the atmosphere increases (i.e., when air humidity decreases), guard cells lose turgor, thereby leading to stomatal closure. The evolution of this mechanism was an important step in the colonization of land by plants, since it enabled plants…
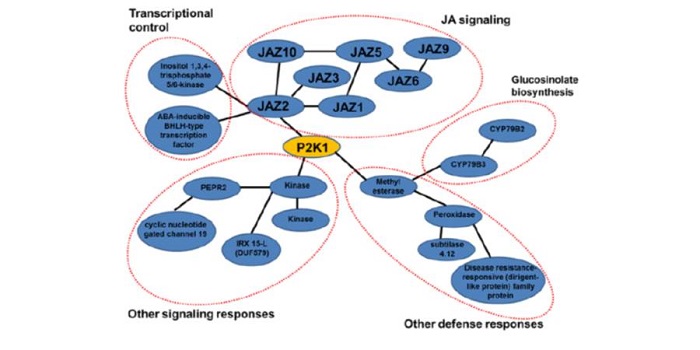
Extracellular ATP Boosts Plant Immunity Via Jasmonate Signaling
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogDamage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) are endogenous chemicals that are released from damaged cells and which play a role as “danger signals.”
Adenosine 5’-triphosphate (ATP) becomes a DAMP signal after release into the extracellular milieu following cellular damage. Extracellular ATP…
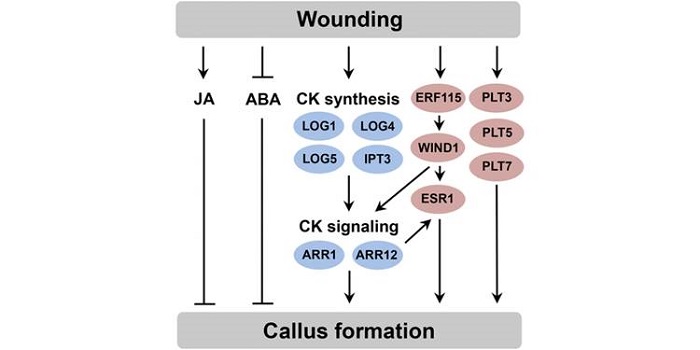
New Insights into Wound-Induced Callus Formation
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogPlants repair wound sites through the formation of unorganized cell masses called calli, which can also serve as progenitors of new organs. Callus formation and organ regeneration often entail cell cycle re-entry of quiescent cells, which is achieved through the re-activation of core cell cycle regulators…

The tomato DELLA protein PROCERA acts in guard cells to promote stomatal closure
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research Blog, The Plant CellNuclear accumulation of DELLA proteins induces transcriptional reprogramming and is well known to suppress the gibberellin (GA) pathway. While DELLAs can negatively regulate GA, increased GA levels can also signal DELLA degradation. GA is a growth-regulating hormone that is also involved in inhibiting…
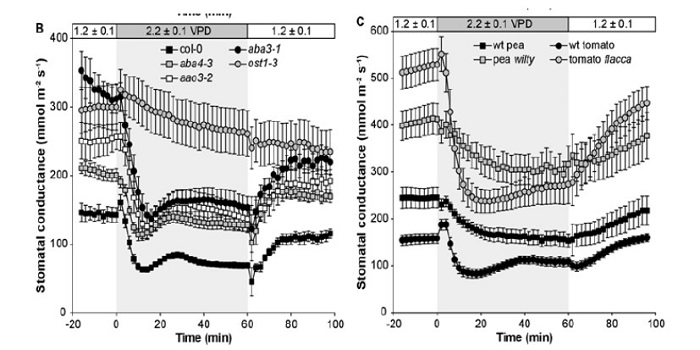
Origin and Role of ABA in Stomatal Regulation
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogWhen the vapor pressure difference (VPD) between a leaf and the atmosphere increases (i.e., when air humidity decreases), guard cells lose turgor, thereby leading to stomatal closure. The evolution of this mechanism was an important step in the colonization of land by plants, since it enabled plants…
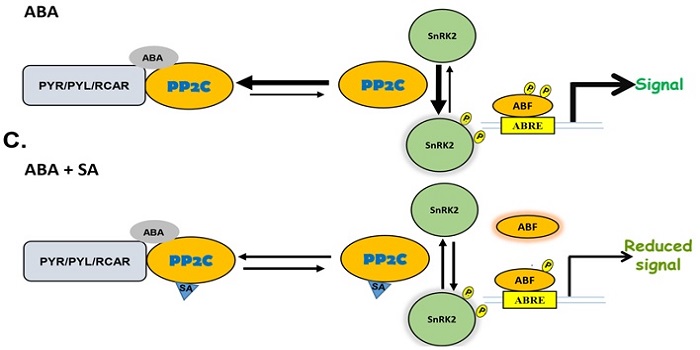
Members of the abscisic acid co-receptor PP2C protein family mediate salicylic acid-abscisic acid crosstalk
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogIf we know anything about how ABA regulates plant response to environmental stresses it is that the pathway if very complicated and anything but straightforward. The ‘core’ ABA pathway is activated by first inhibiting a specific class of protein phosphatases, PP2Cs. This inhibition of PP2Cs allows…
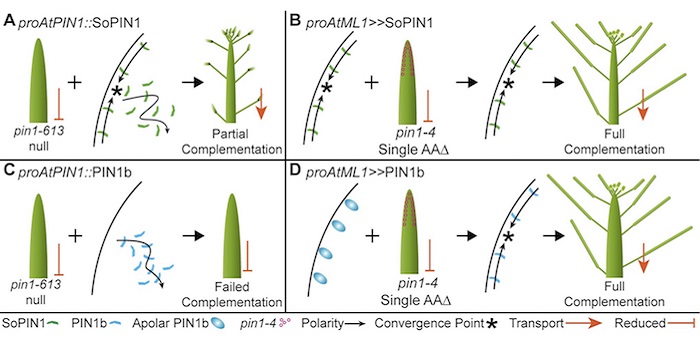
Cross-species functional diversity within the PIN auxin efflux protein family
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPolar localized PIN FORMED (PIN) efflux carriers proteins organize directional auxin flow and accumulation. Most flowering plants have another family of PIN proteins called Sister of PIN1 (SoPIN1), which Arabidopsis and members of the Brassicacea family do not have. The grass Brachypodium dystachion…
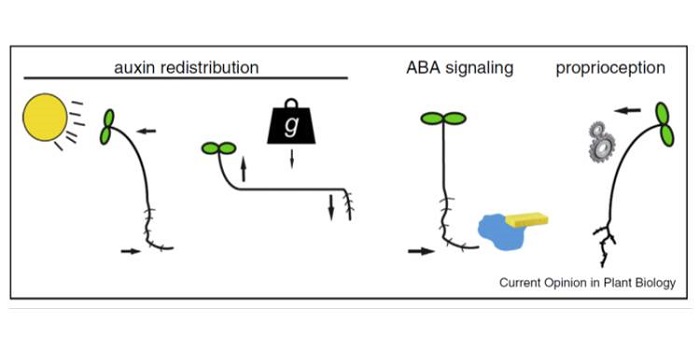
Review: Growth-mediated plant movements: hidden in plain sight ($)
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogTime-lapse imaging reveals the slow movements of plants, such as phototropism and gravitropism. Harmer and Brooks review the molecular bases for these growth-mediated movements. While auxin has long been known to be involved in photo- and gravitropisms, new results show that ABA is involved in the movement…
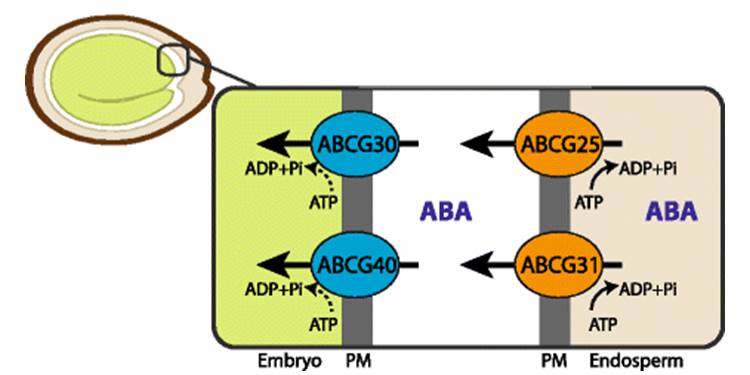
Review: Plant hormone transporters: what we know and what we would like to know
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogHormones are signaling molecules, and in most (but not all) cases part of their function is to convey information from one cell or tissue to another, sometimes from cell-to-cell and sometimes through vascular tissues. Park et al. review our current state of understanding of transporters for diverse…

