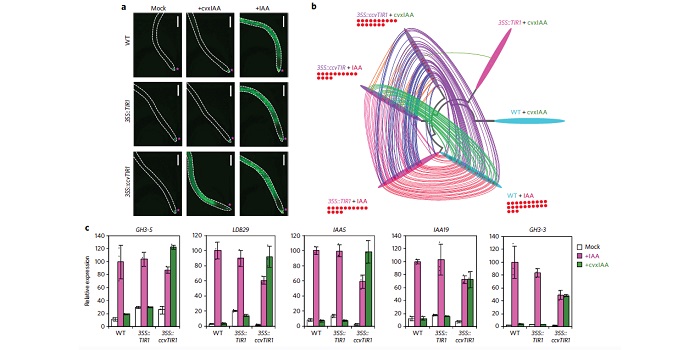
Chemical hijacking of auxin signaling with an engineered auxin–TIR1 pair ($) (Nature Chemical Biology)
Gene redundancy and/or developmental defects of higher order mutants make it hard to study the role of individual components of auxin signaling. Structural biology approach can provide a detour that circumvents endogenous auxin signaling. Removing of the phenyl moiety of F79 in the auxin receptor…
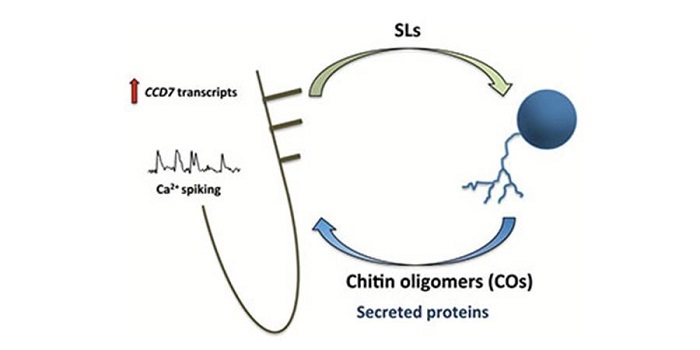
Review: Strigolactones and symbiosis across the kingdoms (plants, fungi, and bacteria) (J. Experimental Botany)
Strigolactones (SLs) are plant hormones with pivotal roles in plant growth. Being conserved among all plant species, they’ve been recruited by plant-associated microbes as plant-derived molecules allowing microbes to detect plants, exchange signals and establish interactions with them. In this review,…

Nutrient modulation of Arabidopsis shoot apical meristem dynamics (PNAS)
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. The shoot apical meristem (SAM) is essential for the adaptation of aerial plant tissue architecture to changes in the environment. This paper by Landrein and colleagues connects changes in the plant environment (soil type, soil fertility, nitrate concentration) to changes…
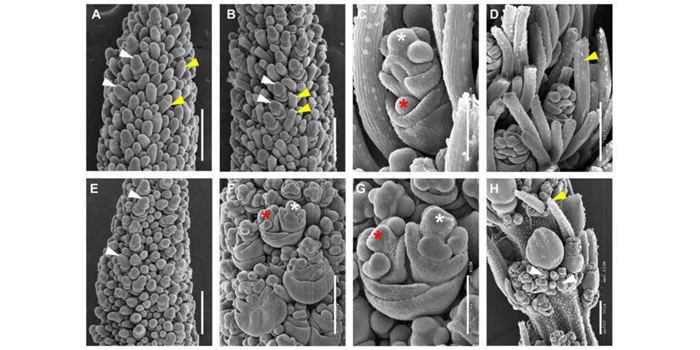
Brassinosteroids modulate meristem fate and differentiation of unique inflorescence morphology in Setaria viridis
Plant Cell. The yield potential of crops is strongly influenced by floral architecture, a trait determined by the fate of stem cells in meristematic tissue. Meristems themselves are influenced by several factors, including phytohormones such as brassinosteroids (BRs) and gibberellic acid (GA). BRs…
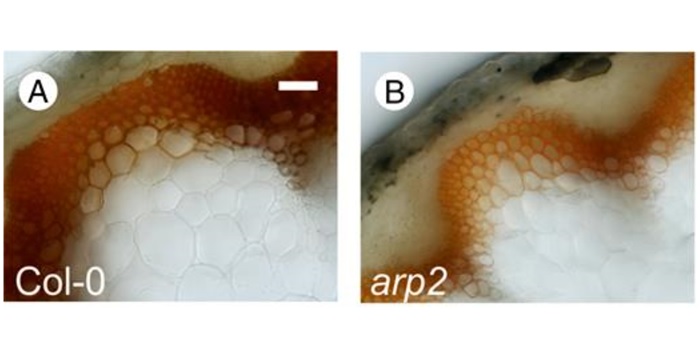
Arabidopsis thaliana plants lacking the ARP2/3 complex show defects in cell wall assembly and auxin distribution
The plant cytoskeleton determines cell shape and integrity by delivering cellulose microfibrils and other cell wall components to the plasma membrane and cell wall. Auxin is involved in establishing the polarity of cell expansion and auxin distribution is partly regulated by actin. Sahi et al. examine…
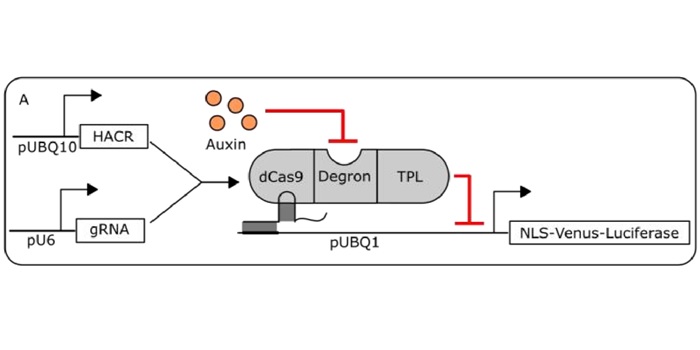
Synthetic hormone-responsive transcription factors can monitor an reprogram plant development
Development is driven by the activities of hormones which control expression of various traits. Modeling hormone pathways is complicated by extensive cross-talk, redundancy, and feedback loops. Khakhar et al. investigate the use of a technique known as Hormone Activated Cas9-based Repressors (HACRs)…
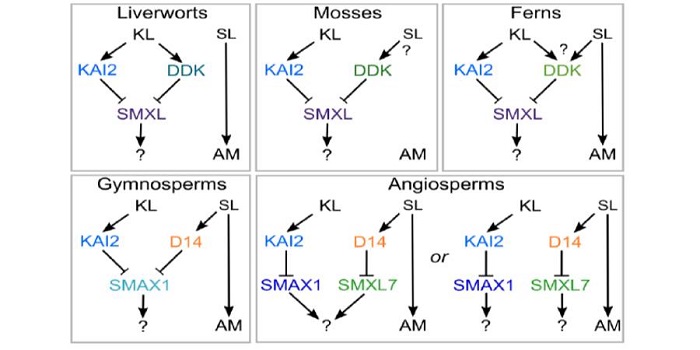
Reassessing the evolution of strigolactone synthesis and signaling
Much of our understanding of strigolactones (SLs) as developmental hormones and rhizosphere signals comes from studies of angiosperms. Understanding the ancestral role for strigolactones is complicated by the fact that some of the SL-related genes are closely related to those responsive to karrikins…
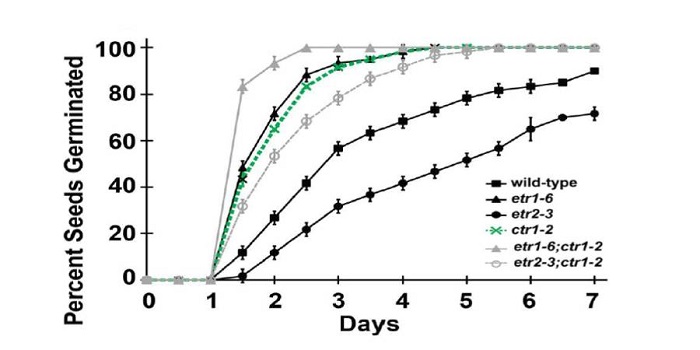
Non-Canonical Signaling of Ethylene Receptors
Ethylene is a gaseous plant hormone that affects the growth and development of plants and mediates plant stress responses. Ethylene is perceived by a family of five receptors in Arabidopsis thaliana including ETHYLENE RESPONSE1 (ETR1) and ETR2. Surprisingly, there are cases where the different ethylene…
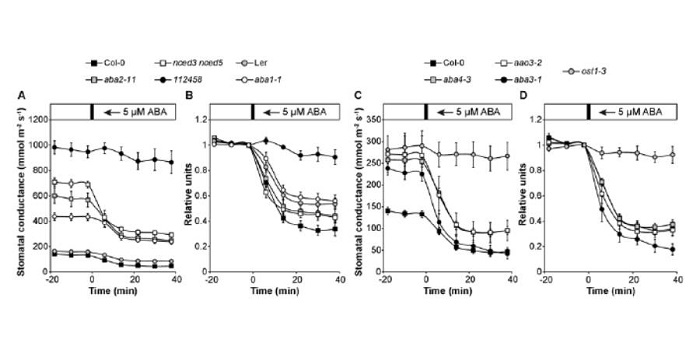
Origin and Role of ABA in Stomatal Regulation
When the vapor pressure difference (VPD) between a leaf and the atmosphere increases (i.e., when air humidity decreases), guard cells lose turgor, thereby leading to stomatal closure. The evolution of this mechanism was an important step in the colonization of land by plants, since it enabled plants…

