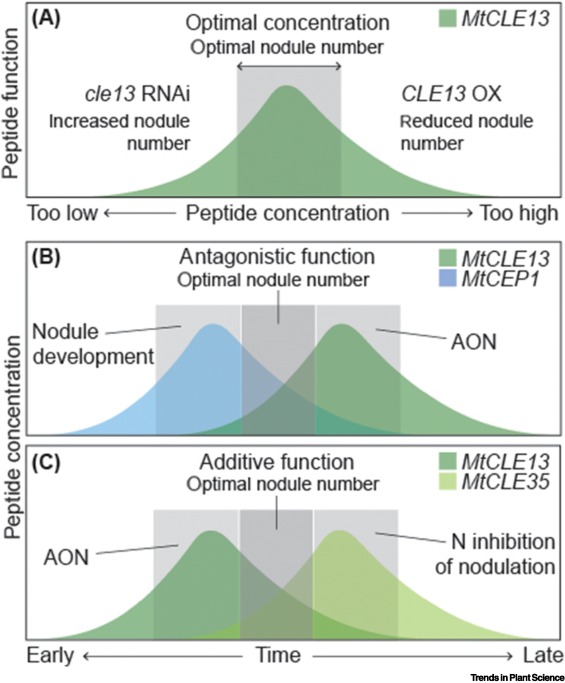
Review: A rulebook for peptide control of legume–microbe endosymbiosis (Trends in Plant Sci)
Symbiotic associations with bacterial or fungal partners enhance nutrient uptake for most plants, and recent years have uncovered the very sophisticated means by which these associations are established and controlled. Peptides have emerged as key regulators of many facets of mycorrhizal and rhizobial…
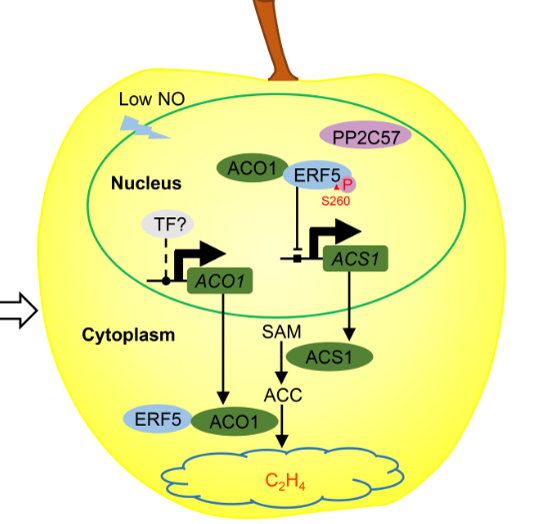
Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 5 mediated by nitric oxide suppresses ethylene biosynthesis in apple fruit (New Phytol.)
Mechanisms of phytohormone modulation and their interface with other regulatory molecules are still being uncovered. Nitric oxide (NO) is a regulatory molecule which has been shown to affect ethylene biosynthesis through the action of ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 5 (ERF5) in apple fruit. New work by Ji et…
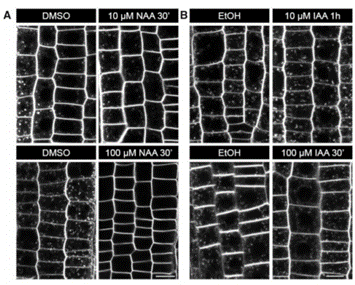
Trapped in traffic – redefining cellular responses to auxin pharmacology (Plant Physiol.)
Understanding cellular responses to the phytohormone auxin has always been a challenge and decades of work has constantly renewed our knowledge of the same. Here, Narasimhan and colleagues attempted to revisit and resolve the basis of differential action of naturally occurring auxin indole-3-acetic acid…
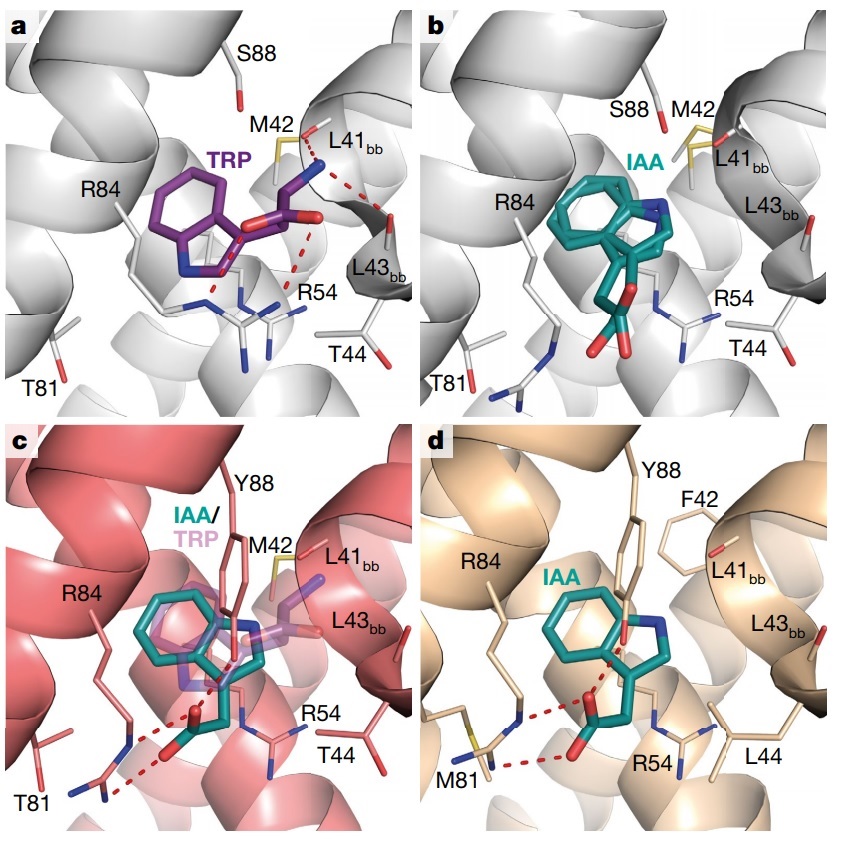
A biosensor for the direct visualization of auxin (Nature)
Auxin is an omnipresent, tryptophan-derived phytohormone that plays roles in innumerable physiological processes, so it is imperative to understand its distribution. Currently the best tools to do so employ the use of indirect sensors, such as the synthetic auxin-responsive promoter DR5. While invaluable,…
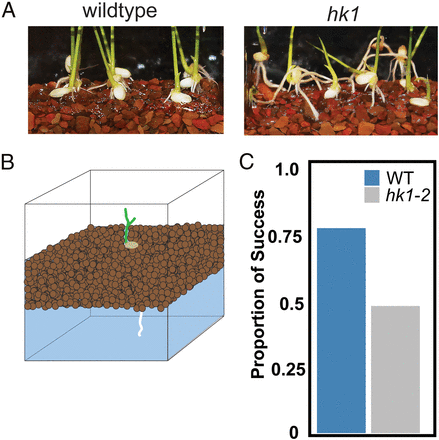
Mechanism and function of root circumnutation (PNAS)
This is an engrossing paper. The authors start off with a simple mutant screen for abnormal root growth in rice seedlings, through which they identified three “long root” mutant alleles of a rice mutant in a gene encoding a histidine kinase, HK1. Careful analysis showed that the mutant roots fail…
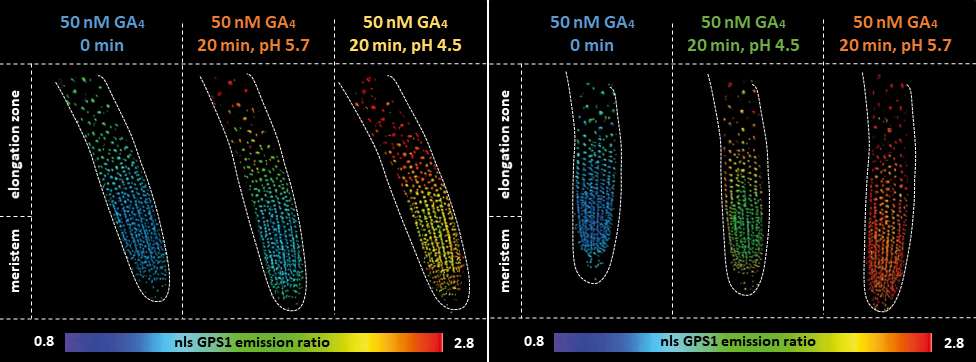
Differential biosynthesis and cellular permeability explain longitudinal gibberellin gradients in growing roots (PNAS)
Gibberellin (GA) controls multiple developmental processes throughout the plant life cycle, from seed germination to flowering. In Arabidopsis, GA also regulates division of meristematic cells at the tip of the root and cell elongation in the growing zone. Despite its importance, little is known about…

Microbiota-root-shoot axis modulation by MYC2 favors Arabidopsis growth over defense under suboptimal light (bioRxiv)
Microbiota-root-shoot axis modulation by MYC2 favors Arabidopsis growth over defense under suboptimal light
Below- and aboveground plant organs experience distinct biotic and abiotic environments. Thus, coordination between root and shoot responses are likely crucial for plant survival. Given that…
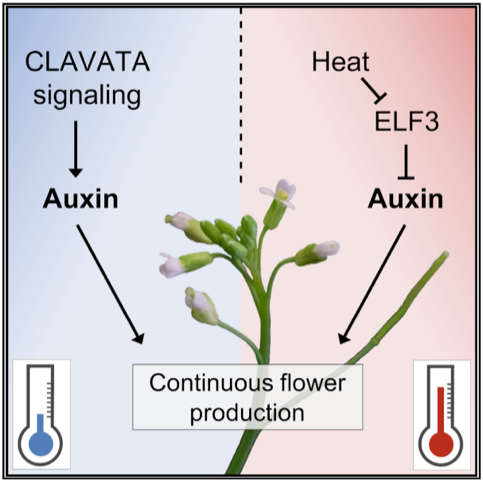
CLAVATA signaling ensures reproductive development in plants across thermal environments (Curr. Biol.)
Plant reproduction and development requires robust signaling pathways that integrate environmental queues such as temperature. In Arabidopsis, the formation of flower primordia from the inflorescence meristem (IM) depends on the proliferation/ differentiation balance and is regulated by auxin and the…

CAMEL in the canal: Regulation of PIN proteins during canalization (Science)
Auxin transport during development or wound regeneration is known to require auxin-induced channel or ‘canal’ formation that includes polar localization of PIN auxin transport proteins. Hajný and colleagues have characterized a receptor-like kinase (RLK) complex involved in auxin-induced pattern…

