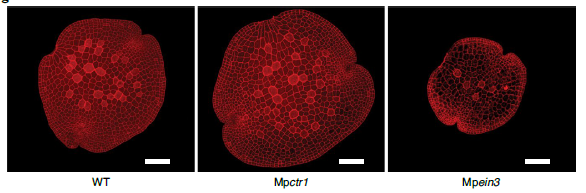
Ethylene independent functions of ACC in Marchantia polymorpha (Nature Plants)
Ethylene is synthesized from 1-Aminocyclopropane carboxylic acid (ACC), and ACC has long been used as a substitute to induce ethylene responses. In a new study, Li and colleagues show that ACC functions as a stand-alone signaling molecule in the liverwort Marchantia. While treatment with ethylene…
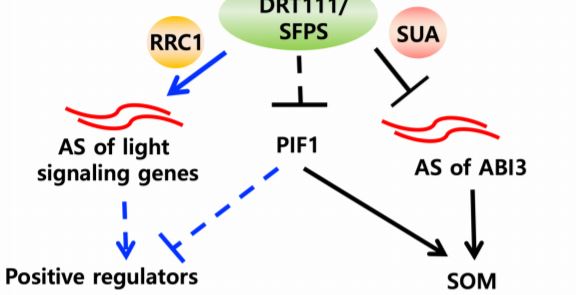
SPLICEd in the Seeds: Integration of ABA and Light Signaling in Arabidopsis
Dhineshkumar Thiruppathi 1,2
ORCID ID: 0000-0002-2018-3356
Donald Danforth Plant Science Center,
Saint Louis, Missouri 63132
1Author for contact: dthiruppathi@danforthcenter.org
2Lead author
Plant development and adjustment to the environment require not only tight regulation of core…
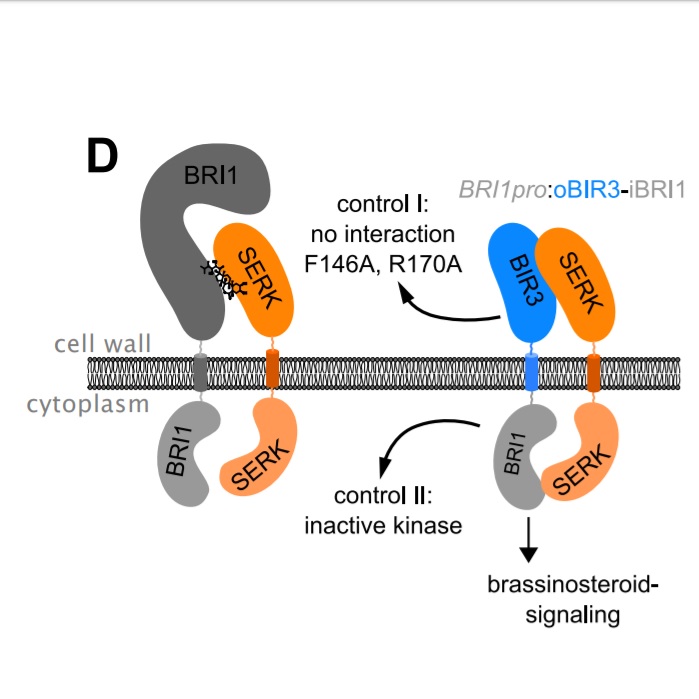
A protein engineering approach for elucidating receptor protein signaling function (Plant Cell)
Plant cells express an array of membrane-bound receptor proteins that recognize and respond to extracellular cues. However, their varied structure/specificity and methods of activation pose challenges in assessing their function. Focusing on Leucine-Rich Repeat Receptor Kinases (LRR-RKs), Hohmann et…
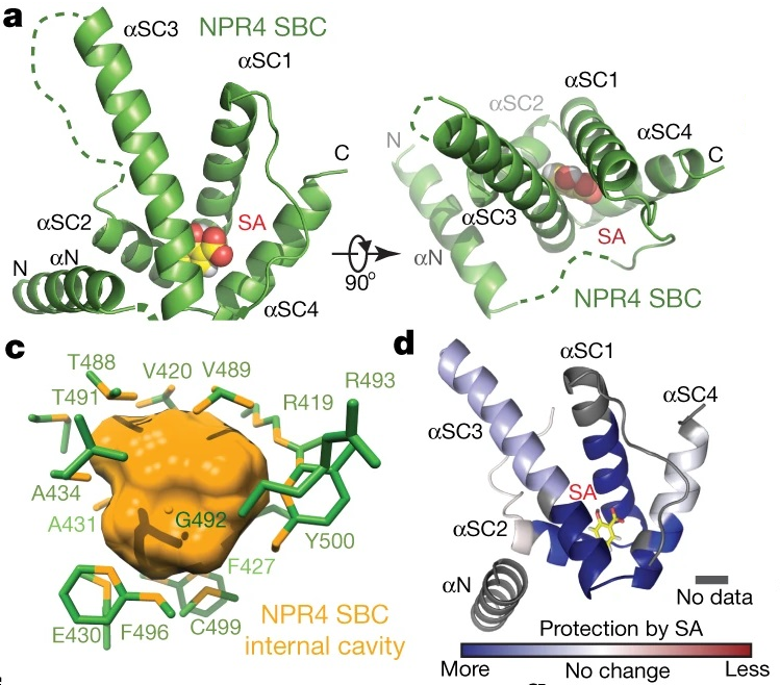
Structural basis of salicylic acid perception by Arabidopsis NPR proteins (Nature) ($)
Salicylic acid (SA) is a critical hormone in plant-pathogen responses. The main receptors of this hormonal signal are a small family of NPR proteins (NONEXPRESSOR OF PATHOGENESIS-RELATED GENES). Although NPR1 is a positive regulator of defense signaling, NPR3 and NPR4 serve as negative regulators; they…
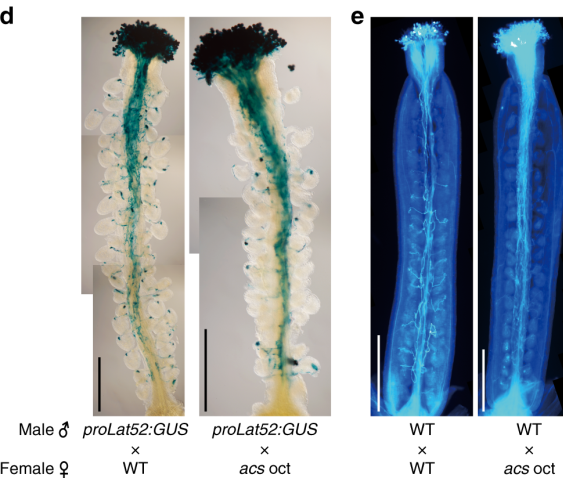
Going my own way: Ethylene-independent ACC signaling in pollen tube attraction (Nature Comms.)
1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) is the precursor of the phytohormone ethylene. Here, Mou and co-workers show ACC to act independent of ethylene in the ovule to attract growing pollen tubes. Mutants impaired in ACC biosynthesis had less fertilization and seed setting events. Fertilization…
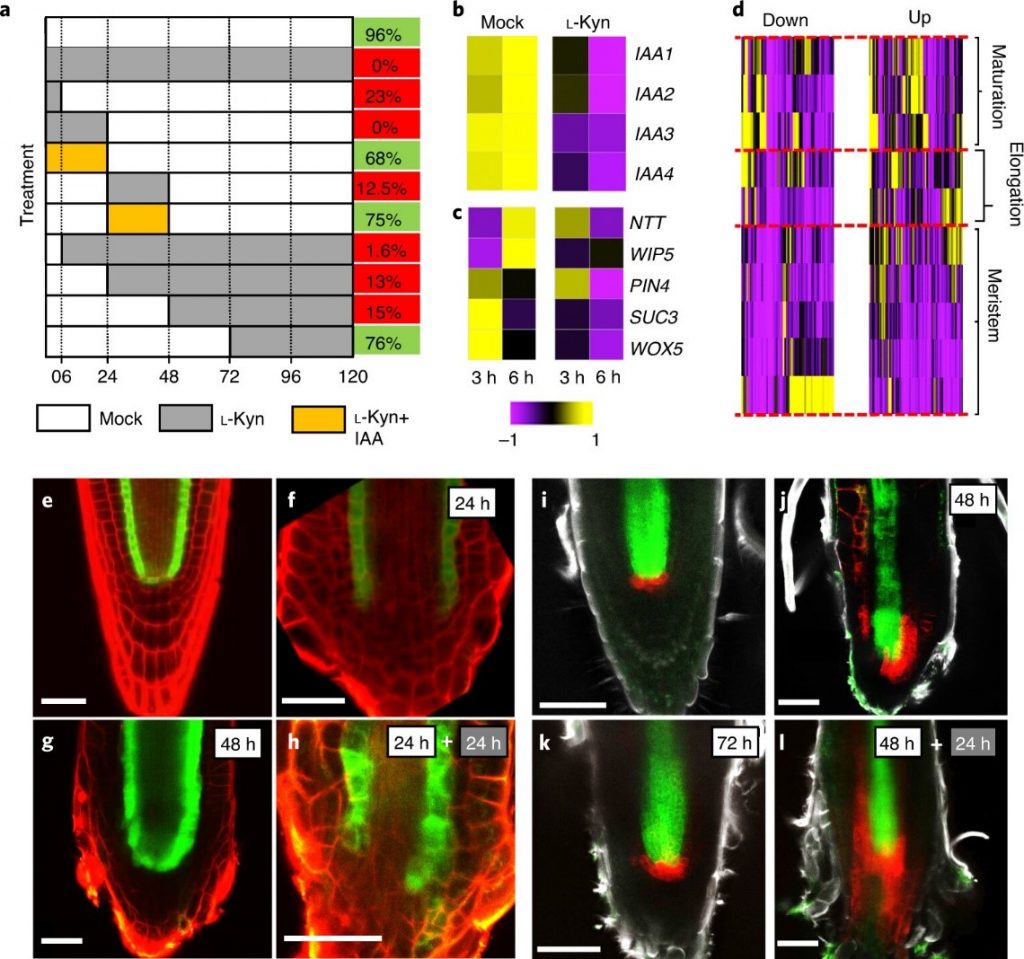
Local auxin biosynthesis is required for root regeneration after wounding (Nature Plants)
During root development, auxin accumulates at the stem cell niche (SCN) located at the root meristem. Both polar auxin transport and local auxin biosynthesis contribute to the auxin accumulation. During root regeneration after wounding, the source of auxin accumulation is still a question. To address…

Peptide-Receptor Signaling Pumps the Brakes on Auxin Biosynthesis and Ethylene Signaling to Harmonize Root Growth and Nodulation
Nitrogen (N) is the most abundant element in Earth’s atmosphere. However, plants must capture this essential element from soil through their roots. To do this, legume roots forge symbioses with rhizobia to initiate nodule development. Root nodules provide rhizobia an environment suitable for converting…
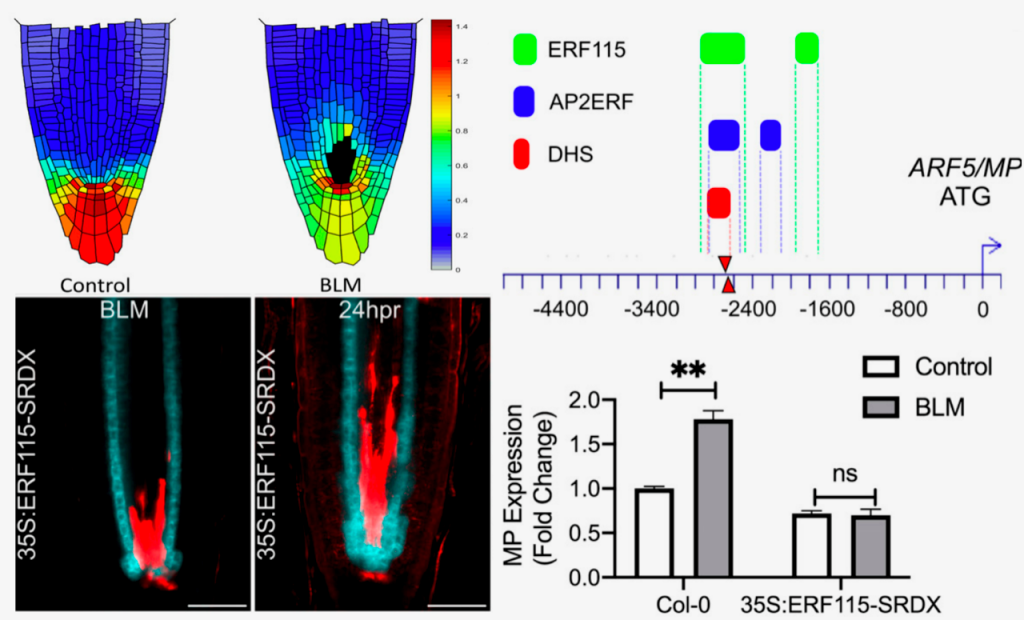
Rocks in the auxin stream: Wound-induced auxin accumulation and ERF115 expression synergistically drive stem cell regeneration (PNAS)
Plants have evolved exquisite regenerative capacities to repair wounds or even reform complete organs thanks to the proliferative activity of stem cell niches residing in meristems. Different types of injuries elicit different developmental and regenerative responses. However, a key player seems to be…

Fluctuating auxin response gradients determine pavement cell-shape acquisition (PNAS)
The leaf epidermis is composed primarily of undulated pavement cells arranged in a jigsaw puzzle-like architecture, with neighboring cells flawlessly interlacing with one another thanks to synchronized growth, thus making it an ideal model to study morphogenesis regulation. Seeking to better understand…

