
Regulation of postembryonic root organogenesis from Arabidopsis leaf tissue (Plant Physiol)
Organogenesis is an essential process in embryonic development. Additionally, plants can generate new organs, such as roots, from postembryonic tissues utilizing postembryonic pathways. Bustillo-Avendaño and colleagues investigated de novo root formation from Arabidopsis thaliana leaf tissue. They…

Review: The pivotal role of ethylene in plant growth (Trends Plant Sci)
Phytohormones, their ratios and gradients, regulate plant development to allow them to adapt to environment changes. Ethylene, one such hormone, is produced in response to a multitude of stresses: biotic, osmotic, flooding, drought or even shading by neighbors. Dubois et al. report in this review how…

Ethylene receptors signal via a noncanonical pathway to regulate abscisic acid responses ($) (Plant Physiol.)
The two-carbon containing gaseous hydrocarbon, ethylene, is one of the most important phytohormones. It is perceived by a set of receptors (ETR1, ETR2, ERS, ERS2, EIN4). Bakshi et al. found that ETR1 (etr1-6) and ETR2 (etr2-3) mutants have opposite effects on seed germination in the presence of NaCl,…
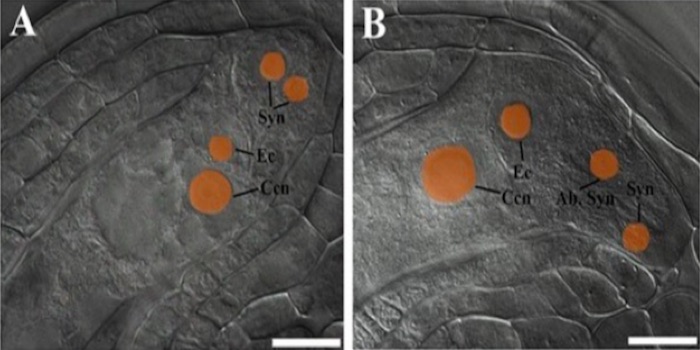
ARF2 – ARF4 and ARF5 are essential for female and male gametophyte development in Arabidopsis (Plant Cell Physiol.)
Auxin is considered a master molecule for plant growth and development; in a whimsical way, IAA (Indole – 3 – Acetic Acid) has been defined as "Induce Almost Anything"! Auxin-mediated gene expression is regulated by Auxin Responsive Factor (ARFs). The model plant Arabidopsis thaliana contains 23…
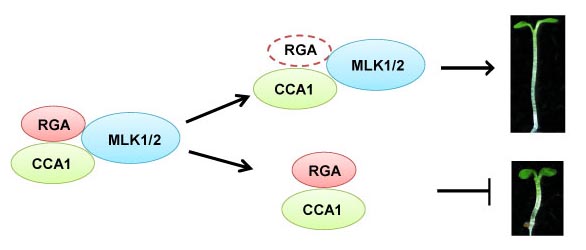
Combining Forces for Hypocotyl Elongation: Histone Modifications, GA, and the Circadian Clock
Zheng et al. discover proteins that mediate interactions between gibberellins and the circadian clock https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00830
By Han Zheng and Yong Ding
Background: Hypocotyl elongation helps the shoot emerge from the soil surface. The gibberellin (GA) signaling protein RGA inhibits…
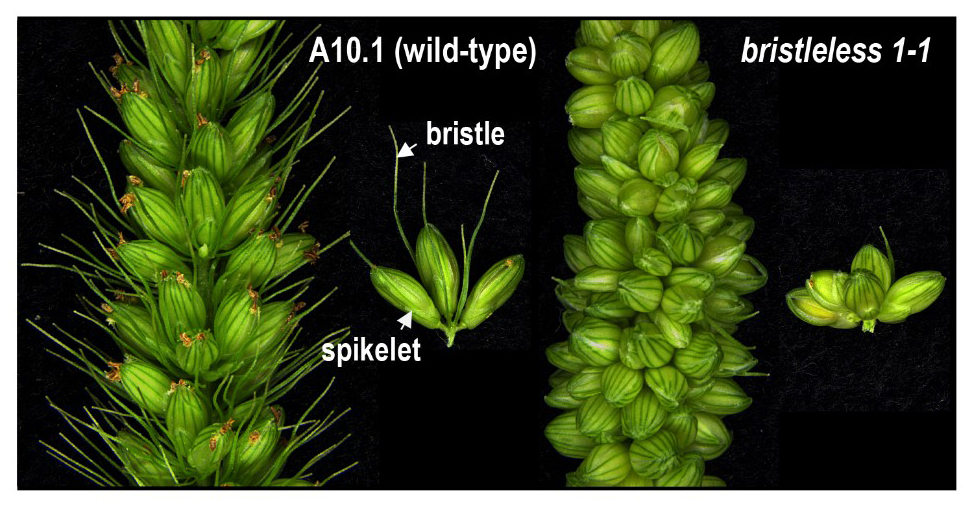
Changing Fates: Brassinosteroids Underlying Yield Potential in Millet
Yang et al. reveal a role for brassinosteroids in spikelet and floral meristem fate in Setaria viridis. The Plant Cell (2017) https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00816
By Jiani Yang and Andrea L. Eveland
Background: Grass inflorescences show extensive morphological diversity between species, due…

The Phytohormone Ethylene and Transcriptional Repression
Zhang et al. investigate histone deacetylase in the ethylene response. Plant Cell (2017). https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00671
By Fan Zhang
Background: Ethylene is the only gaseous hormone in plants, and is a key hormone controlling plant growth and resistance to stress. Epigenetic mechanisms are…

Auxin synthesis contributes to virulence of Pseudomonas syringae (PLOS Pathogens)
Plant pathogens have developed a large range of strategies to allow them to have successful interactions with their plant host, including physiological manipulation. For example, Pseudomonas syringae, the cause of speck disease in many plant systems, manipulates the auxin phytohormone physiology in its…

Cytokinin regulation in the endoplasmic reticulum (Plant Physiology)
Cytokinin is a phytohormone involved in many plant processes such as cell proliferation, apical dominance, leaf senescence, tissue patterning, organ initiation, environmental responses… To allow for effective control of all these processes, cytokinin concentrations need to be continuously adjusted.…

