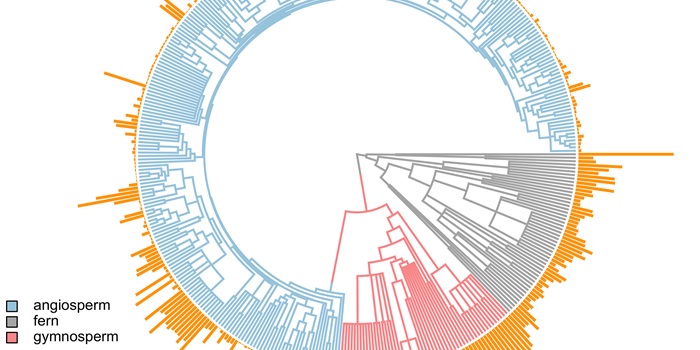
Genome downsizing, physiological novelty, and the global dominance of flowering plants
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPLOS Biol. Guard cell size is, in general, inversely related to stomatal density. It is advantageous for plants to maximize their photosynthetic capabilities by generating higher rates of gas exchange, thereby incorporating more CO2 to help drive this pathway. However, the number of cells that can occupy…

HOW TO BUILD A SEAWEED
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellGodfroy et al investigate basal cell fate determination in the brown alga Ectocarpus https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00440
BACKGROUND: Brown algae are multicellular photosynthetic marine organisms living on rocky shores across the globe and representing one of the most developmentally complex groups…
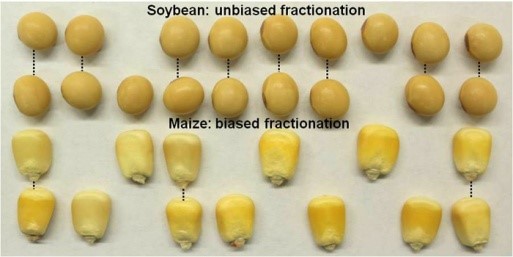
Duplicate Genomes Evolved Differently in Maize and Soybean
Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZhao et al. demonstrate that duplicated genomes in maize and soybean followed distinct trajectories over millions of years https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00595
By Meixia Zhao, Biao Zhang, Damon Lisch, and Jianxin Ma
Background: Over evolutionary time, many organisms, particularly plants, have periodically…
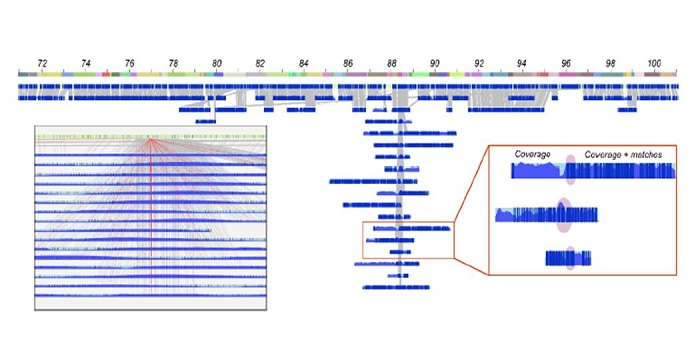
Commentary: Is it ordered correctly? Validating genome assemblies by optical mapping
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogOne of the hardest parts of any sequencing project is putting the pieces together. Physical sequence alignments can be cross checked against genetic linkage maps when they are available, but what about for species without genetic linkage data? Udall and Dawe describe the use of optical mapping, using…
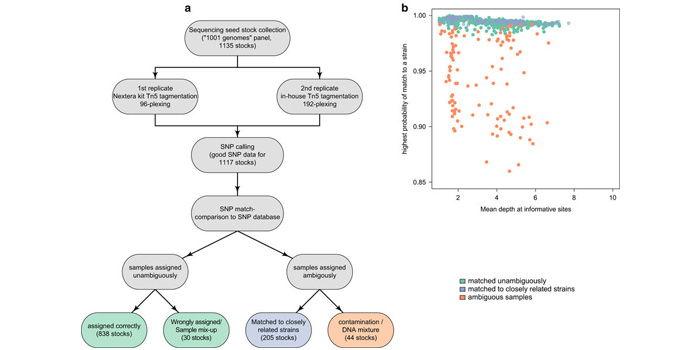
Verification of Arabidopsis stock collections using SNPmatch, a tool for genotyping high-plexed samples
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogExperiments using large germplasm collections are prone to contamination. With dropping sequencing costs, it becomes easier to validate the genotype using minimal sequencing coverage. Pisupati and colleagues developed an open-source python pipeline, called SNPmatch, allowing identification of 930 Arabidopsis…
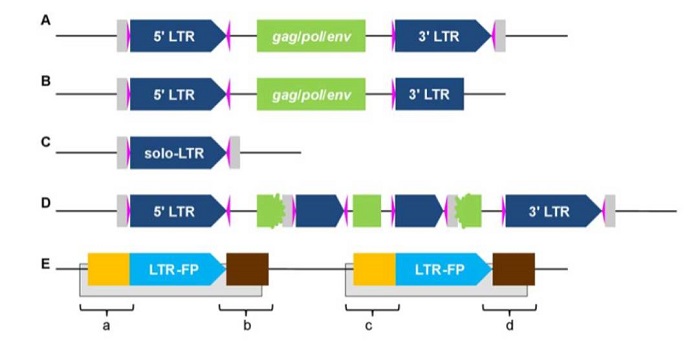
LTR_retriever: a highly accurate and sensitive program for identification of long terminal-repeat retrotransposons
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogTransposable elements are a major part of plant genomes. Long-terminal repeat retrotransposons (LTR (LTR-RTs) alone make up 78% of the maize genome (retrotransposons use a “copy and paste” transposition method meaning that a single source element can generate numerous clones of itself, leading to…
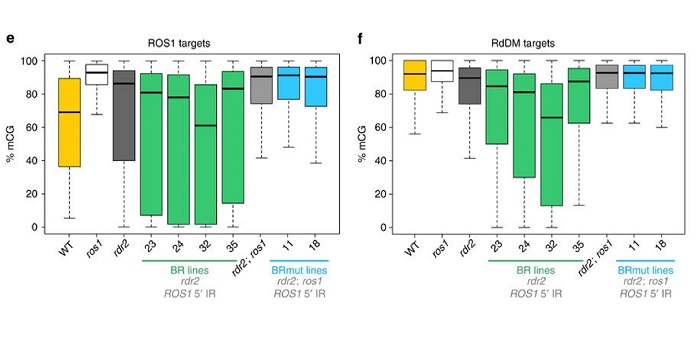
Methylome robustness in plants is conferred by a methylation-sensitive system.
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogDNA methylation is instrumental in promoting transcriptional silencing at repetitive elements, inhibiting illegitimate recombination and establishing genomic imprinting. In plants, DNA methylation profiles are stably inherited over generations through the activities of cytosine DNA methyltransferases…
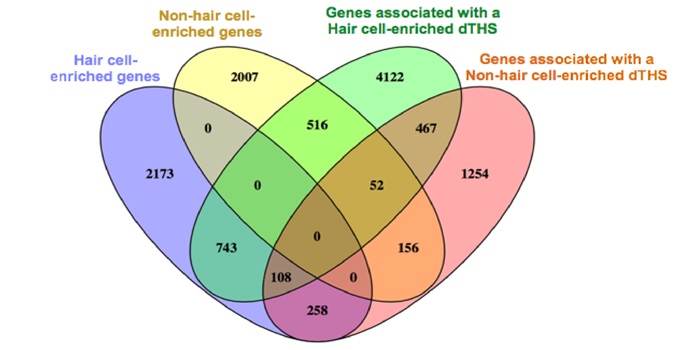
Chromatin region accessibility: cross-species comparisons and cell type distinctions
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogCis-regulatory elements direct transcriptional output during cell differentiation and coordinate adaptive responses to environmental stress. DNA becomes open and accessible when nucleosomes are displaced by DNA-binding proteins, indicating a correlation between open chromatin regions and transcriptional…
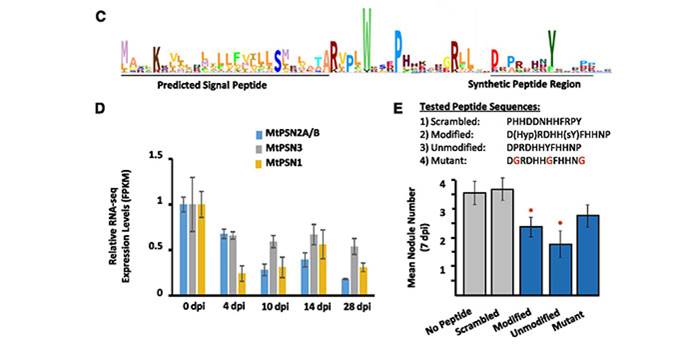
Genome-wide identification of Medicago peptides involved in macronutrient responses and nodulation
Blog, Plant Science Research Weekly, Research, Research BlogPlants are highly plastic and can modulate their growth and development to better respond to abiotic and biotic surroundings. Among the molecules involved in the adaptation to the environment, a crucial role is played by small secreted peptides (SSPs). In their paper, integrating 144 transcriptomic experiments,…

