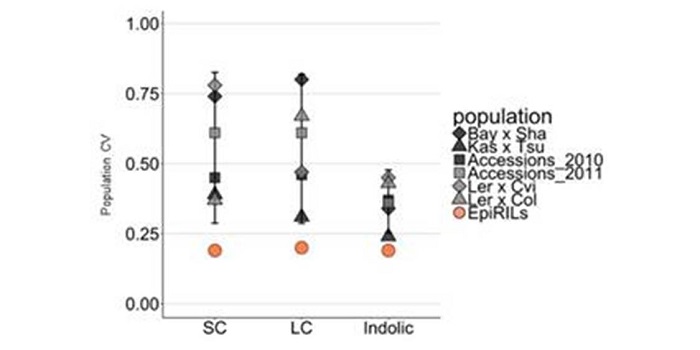
Comparison of the relative potential for epigenetic and genetic variation to contribute to trait stability
Plant Science Research WeeklyEpigenetic variation, both natural and induced, can influence heritable phenotypic variation of complex traits. Understanding the effect of epigenetic changes on trait variation is complicated by the confounding effects of DNA sequence polymorphisms. To overcome this complication, epigenetic recombinant…

Similarity between soybean and Arabidopsis seed methylomes and loss of non-CG methylation does not affect seed development
Plant Science Research WeeklyDifferent parts of the seed have distinct genetic origins and functions. The seed coat is maternally derived from ovule integuments, whereas the embryo descends from the fertilized egg and the endosperm from the central cell. Lin et al. profiled the methylome landscape during seed development and germination…
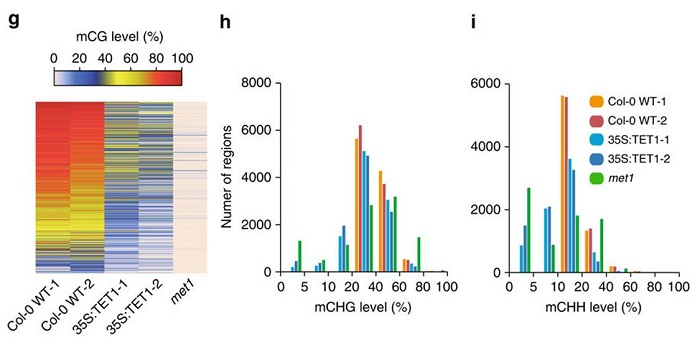
TET-mediated epimutagenesis of the Arabidopsis thaliana methylome
Plant Science Research WeeklyNatural and induced DNA methylation variations are known to alter gene expression changes that may ultimately be important for agronomically important traits. Epigenetically manipulating plant methylomes to create heritable changes can be invaluable in crop improvement programs. Ji et al. describe the…

Loss of mCHH islands in maize chromomethylase and DDM1-type nucleosome remodeler mutants
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant DNA methylation in different sequence contexts is catalyzed by distinct types of methyltransferases. METHYLTRANSFERASE 1 (MET1) is responsible for CG methylation, CHROMOMETHYLASE (CMT1, 2, and 3) methylates CHG and CHH, while DOMAINS REARRANGED METHYLTRANSFERASE (DRM1 and 2) methylates in all three…
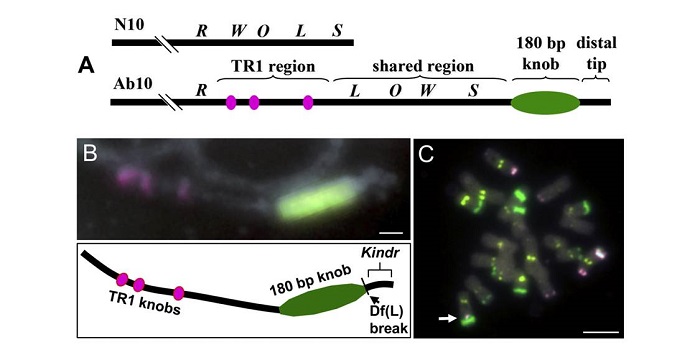
What We're Reading: April 20th
BlogThis week’s issue of What We’re Reading is guest edited by Sunil Kumar Kenchanmane Raju, a postdoc in Chad Niederhuth's lab at Michigan State University. He is interested in understanding the epigenetic and epigenomic diversity across land plants. Sunil is a postdoc ambassador of ASPB and social…
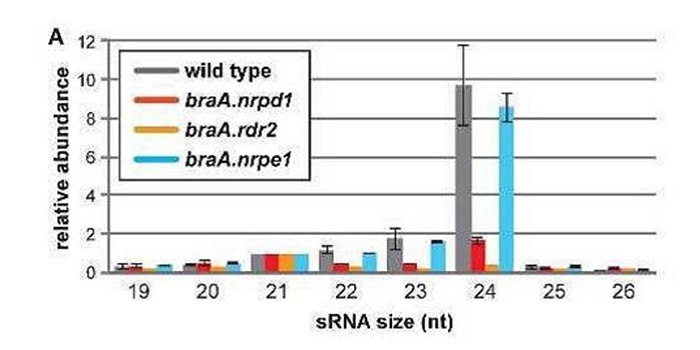
Maternal components of RdDM are required for seed development in Brassica rapa
Plant Science Research WeeklyRNA directed DNA methylation (RdDM) is an epigenetic process in which plant double-strand RNAs are processed into small RNAs (sRNA) that add repressive DNA methylation to homologous DNA sequences. RdDM primarily acts on repetitive DNA and transposable elements (TEs). Despite its important biological…
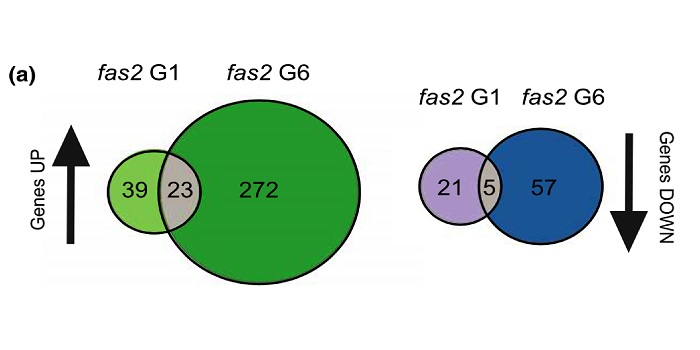
An epigenetic origin behind the transgenerational fitness decline in chromatin assembly impaired plants (New Phytol) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPackaging of nuclear DNA in chromatin is critical for the maintenance of genome integrity as well as fundamental cellular processes such as DNA replication and transcription. Chromatin assembly is mediated by histone chaperones, such as Chromatin Assembly Factor 1 (CAF-1). CAF-1 ensures faithful replication-coupled…
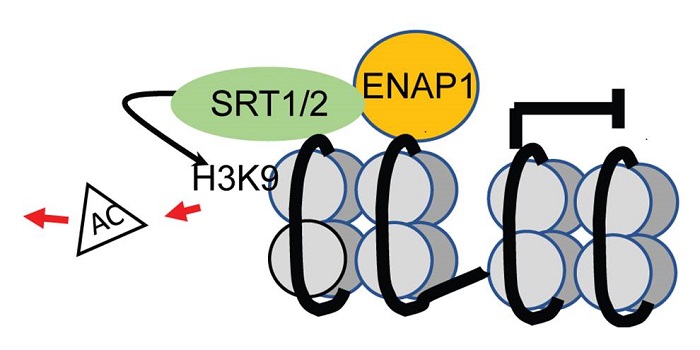
Ethylene Represses Gene Transcription via Histone Deacetylases
Blog, Research, The Plant Cell, The Plant Cell: In BriefApproximately half of all ethylene-responsive genes are downregulated in the presence in ethylene (Chang et al, 2013), but this repression has received relatively little attention compared to the ethylene-mediated activation of expression. The known positive regulators of ethylene signaling include ETHYLENE…
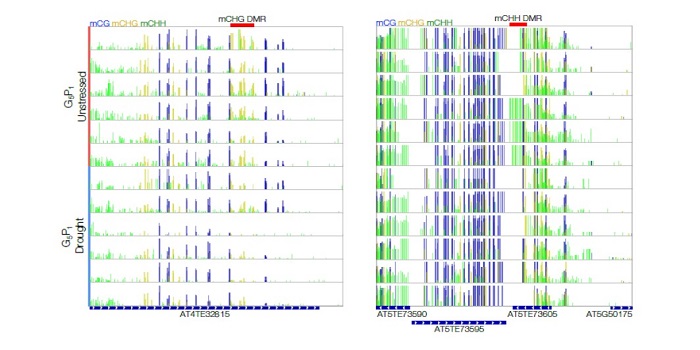
Arabidopsis DNA Methylome Stability under Stress
Blog, Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The Inside, Research, Research BlogIt has been speculated that DNA methylation could complement genetic variation, as a mode for transferring heritable information, to contribute to phenotypic variation. Indeed, DNA methylation states can be maintained faithfully over both mitotic and meiotic cell division. According to this view, any…

