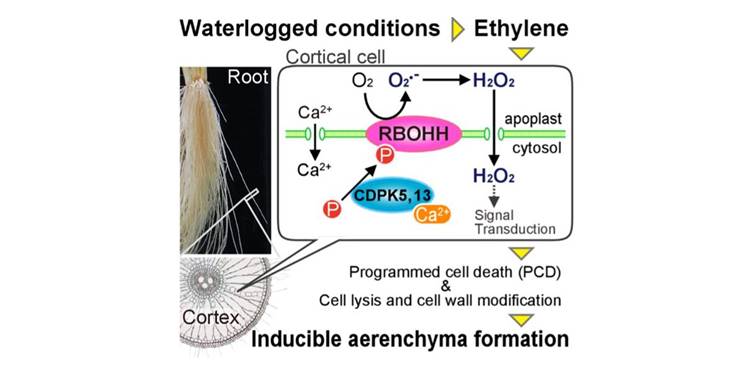
Better understanding how plant roots breathe under water ($)
0 Comments
/
Waterlogging, a process by which water saturates soil, results in oxygen-deficient soil conditions and can result in massive crop loss. In order for plants to survive in waterlogged soil, shoots transport oxygen to roots through lysigenous aerenchyma, a specialized tissue type formed by ethylene-induced…
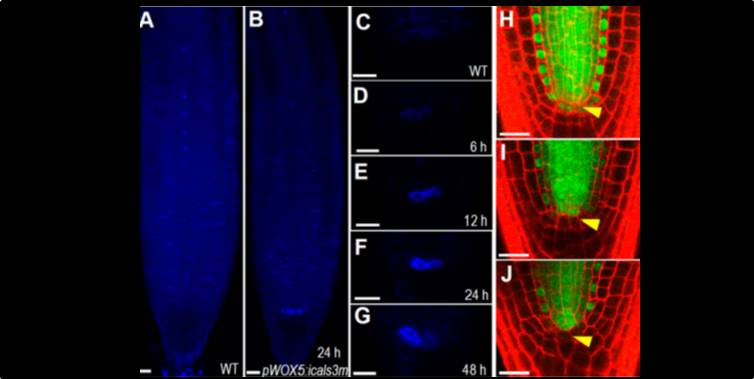
Symplastic communication spatially directs local auxin biosynthesis to maintain root stem cell niche in Arabidopsis ($)
Although plant cells are surrounded by walls, cytoplasmic strands connect adjacent cells through junctions called plasmodesmata. Liu et al. investigated the contributions of plasmodesmata to signaling between root quiescent center (QC) cells and the cells that surround the QC by expression of an inducible…
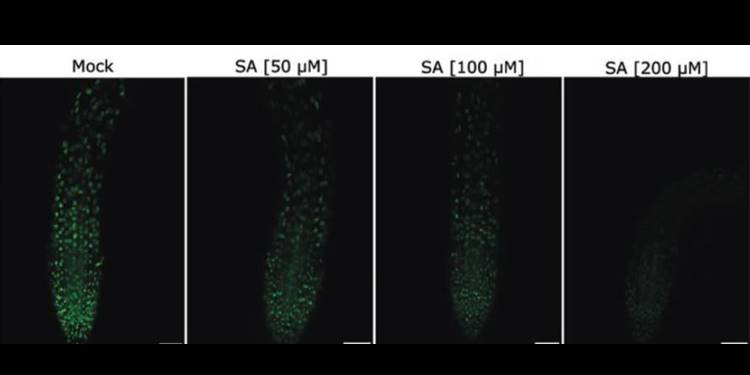
Salicylic acid interferes with GFP fluorescence in vivo
Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) is a widely-used reporter with which to analyze protein localization and expression levels. De Jonge et al. report that GFP fluorescence is greatly diminished in the presence of the hormone salicylic acid (SA), as is the fluorescence of the reporters RFP and VENUS. The…
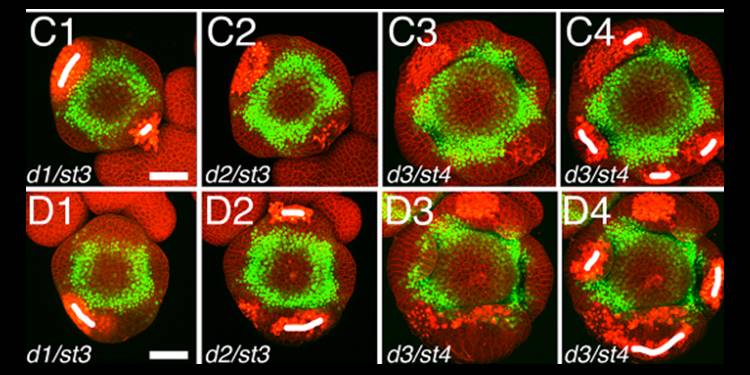
Live Confocal Imaging of Developing Arabidopsis Flowers
Monitoring cells and their activities in real time provides exceptional insights into their mechanisms and strategies of growth. Prunet has used live confocal imaging of Arabidopsis flowers to study the placement of floral organs and the dynamics of floral stem cells. Here, he presents a detailed protocol…
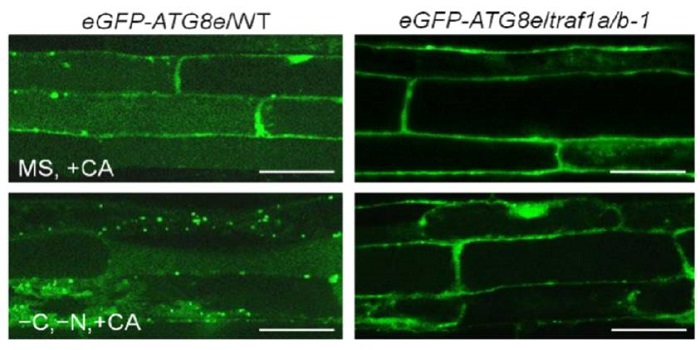
Family Chores: TRAF-Family Proteins Help Recycle Cellular Rubbish by Regulating Autophagy Dynamics
IN BRIEF by Jennifer Lockhart jlockhart@aspb.org
Plant cell components that are no longer needed are degraded in the vacuole, but they don’t get there by magic. Sack-like double-membrane structures called autophagosomes engulf this cellular rubbish and neatly transport it to the vacuole for degradation.…
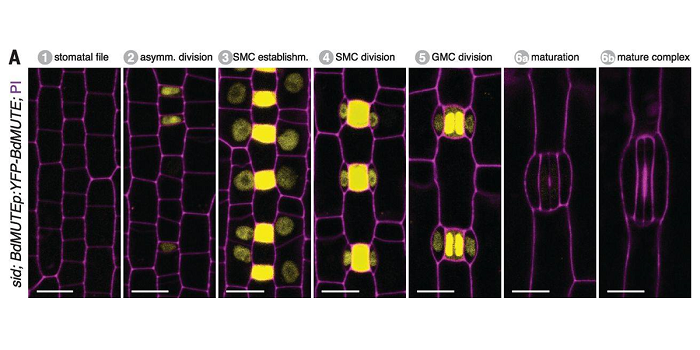
Mobile MUTE specifies subsidiary cells to build physiologically improved grass stomata ($)
Plants breathe through pores called stomata on leaf surfaces. Stomata are the point of contact with the outside world as they allow gas exchange (e.g., CO2 for photosynthesis) and transpiration. Grasses have evolved to form more efficient stomata in which the guard cells are flanked by additional subsidiary…
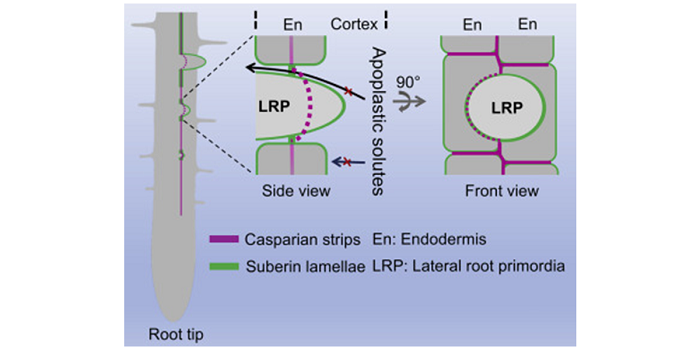
Role of LOTR1 in Nutrient Transport ($)
Casparian strips, named after the German botanist Robert Caspary who discovered them, are a cellular feature found in the roots of all higher plants. They are ring-like lignin polymers deposited in the middle of anticlinal cell walls (parallel to the root radius) between endodermal cells. Along with…

How a kernel of corn may yield answers into some cancers (by Kevin Folta)
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.
By Kevin M. Folta, University of Florida
Driving down a country highway in the Midwest can seem an endless ribbon flanked by green walls of corn, neatly planted in stately rows. But who would guess…

Review: Methods of cell-specific hormone analysis ($)
Plant hormones are active at very small quantities and often act differently in different cell types. Various methods, primarily involving mass spectrometry and sensors, have been developed to identify and quantify hormones with cellular-level precision. Novák et al. review these methods and discuss…

