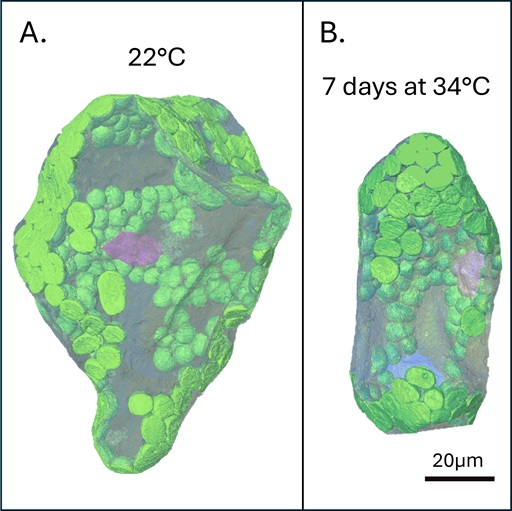
Sweet heat: Organelle-specific carbohydrate metabolism in heat stress
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant metabolism varies substantially between developmental stages, cell types, and intracellular environments. Similarly, biochemical responses to abiotic stress often deviate between neighboring cell types, but discerning what is changing where becomes more challenging in smaller and more fragile sub-compartments. …
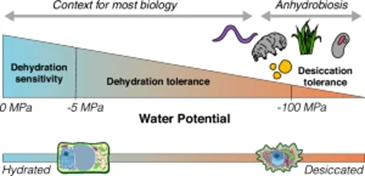
Perspective. The art of drying gracefully: The future for desiccation research
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn their perspective article, “Life on the dry side: a roadmap to understanding desiccation tolerance and accelerating translational applications,” Marks et al. outline the current state and future promise of desiccation tolerance research. They define desiccation tolerance as “the ability to dry…
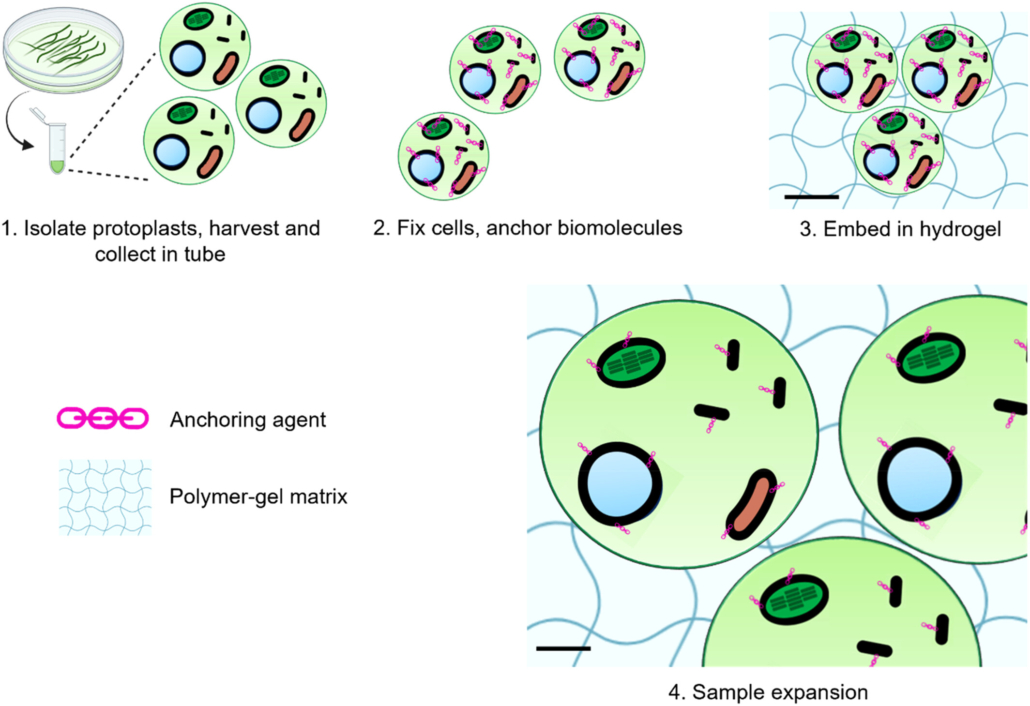
Cells are larger than life when ExPOSEd
Plant Science Research WeeklyCells are as small as life gets, but can be much larger than they appear if given room for expansion. This is possible with expansion microscopy, a technique that enables three dimensional cell imaging by physically expanding cellular components for visualization. Although expansion microscopy has been…
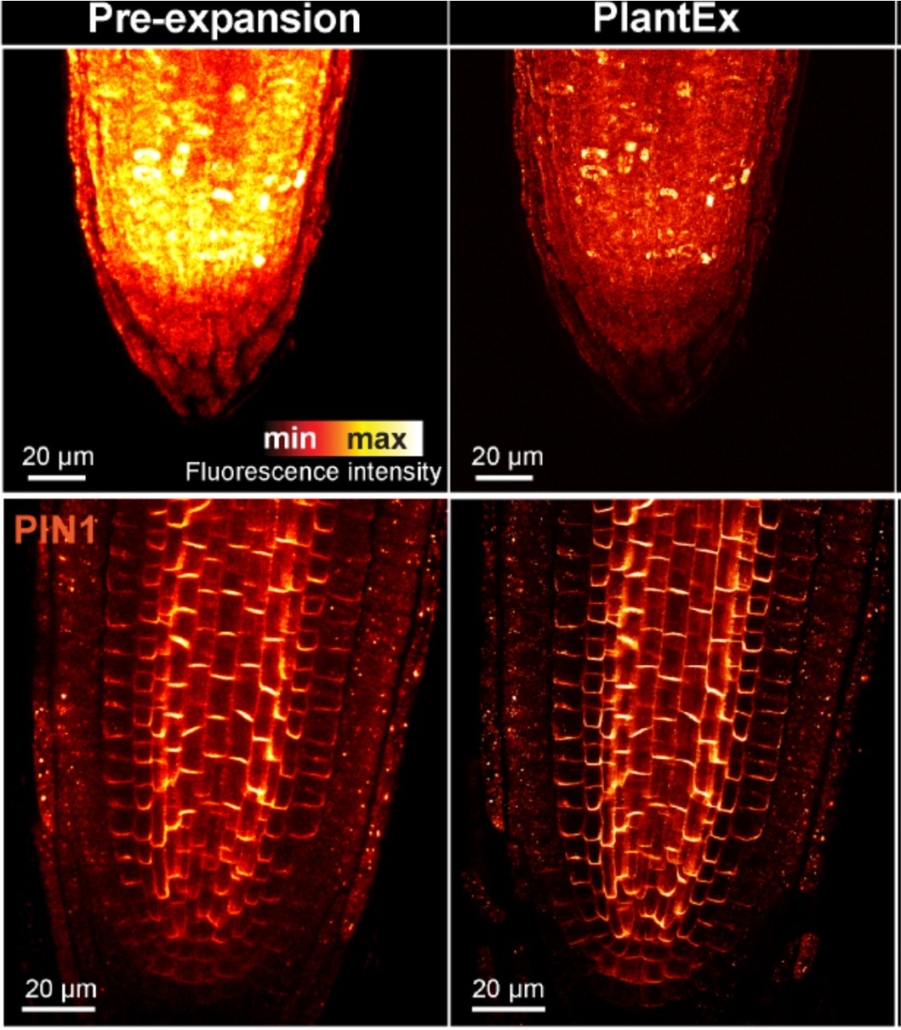

Expanding the resolution limits of conventional microscopy in whole plant tissues
Plant Science Research WeeklyHow can we precisely image plant tissues in super-resolution when approaching the optical limits of conventional microscopes? One solution lies in expansion microscopy, a technique that embeds tissue samples in an expandable hydrogel that proportionally increases the distances between structures, allowing…
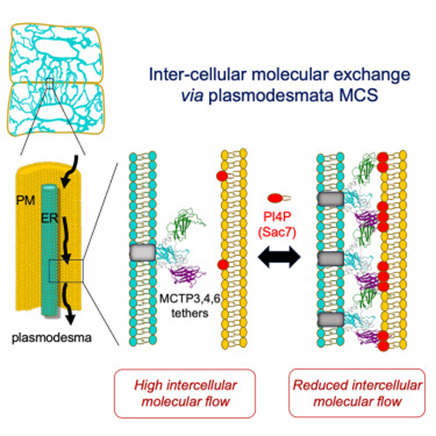
Plasmodesmata: A new frontier for membrane contact site intercellular communication
Plant Science Research WeeklyMembrane contact sites (MCSs) serve a critical role in intracellular communication, particularly between organelle membranes, enabling direct molecular transfer. Less clear is the role MCSs play in intercellular communication. New evidence from Pérez-Sancho et al. implicates plasmodesmata in this function…
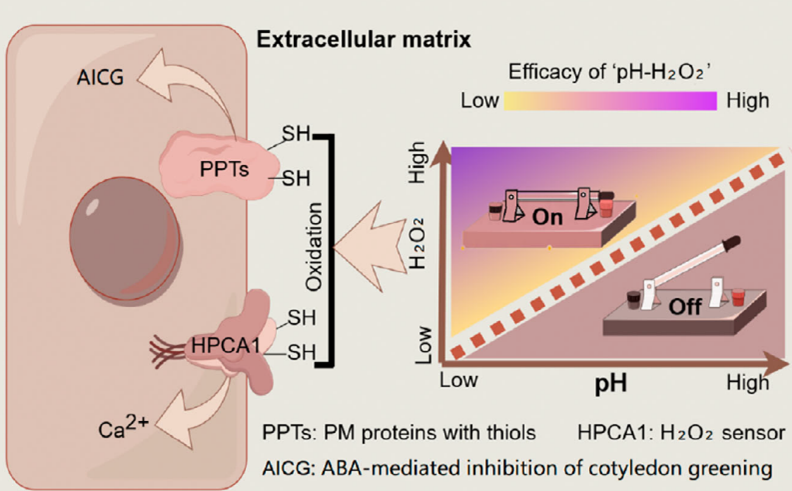
Apoplastic pH acts as a chemical switch in plants by modulating H2O2 redox potential
Plant Science Research WeeklyEnvironmental stimuli, such as drought and salinity, alter cellular conditions including apoplastic pH (pHApo) in plants. These stimuli often lead to an elevation in pHApo which is closely associated with cell functions and plant growth. However, the mechanism behind is largely unexplored. A recent study…
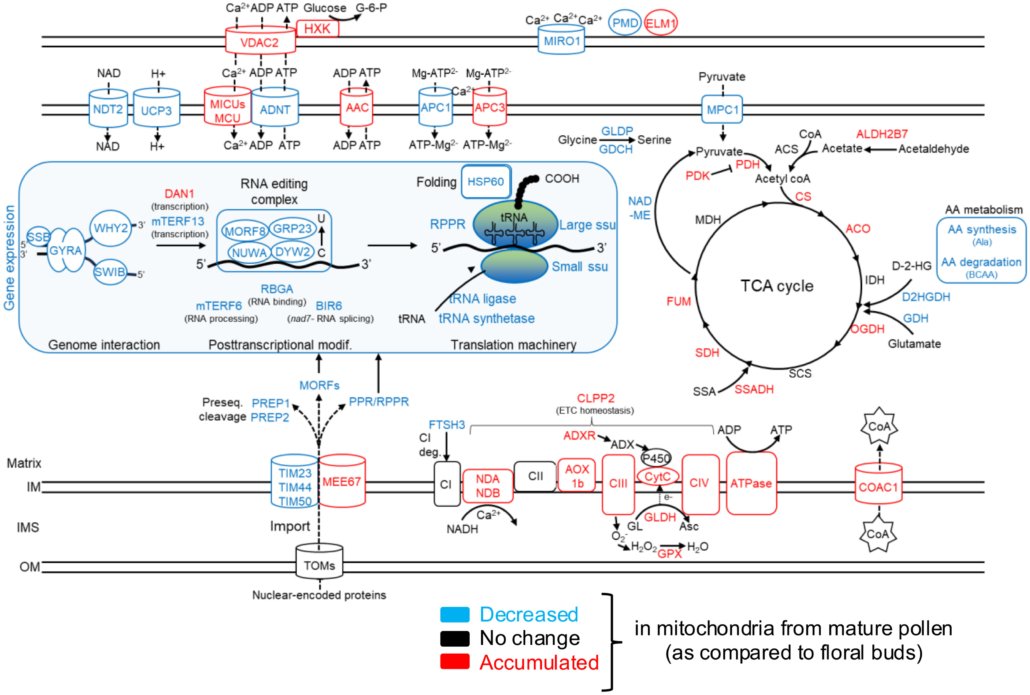
High-energy requiring pollen grains have specialized mitochondria
Plant Science Research WeeklyImagine you’re on a quest to deliver a package, racing against the competition. How do you prepare? Pollen grains and the pollen tubes that they form are essentially package-delivery systems. Their purpose is to deliver genetic information (sperm cell nuclei) to the ovule. Once the task is completed,…
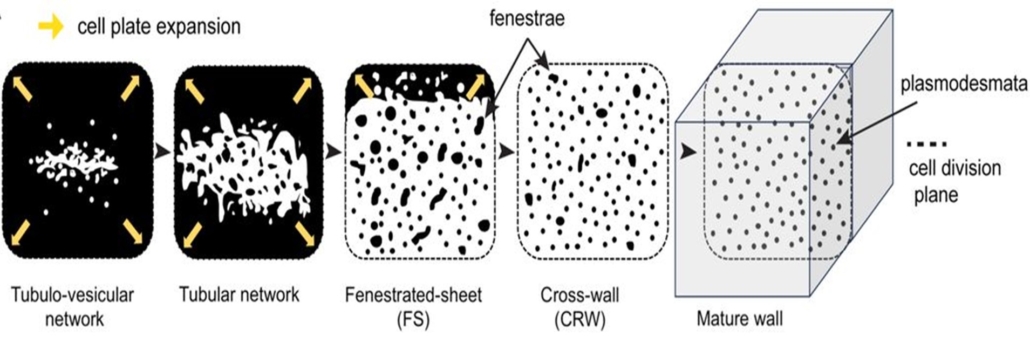
Formation of plasmodesmata bridges through ER-dependent incomplete cytokinesis
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlasmodesmata are important for intercellular communication in plants. They are formed through incomplete cytokinesis during which there is no “final cut” of the communication between daughter cells. Unlike animal cells that have a single bridge between cells, plants create several hundreds of plasmodesmata…
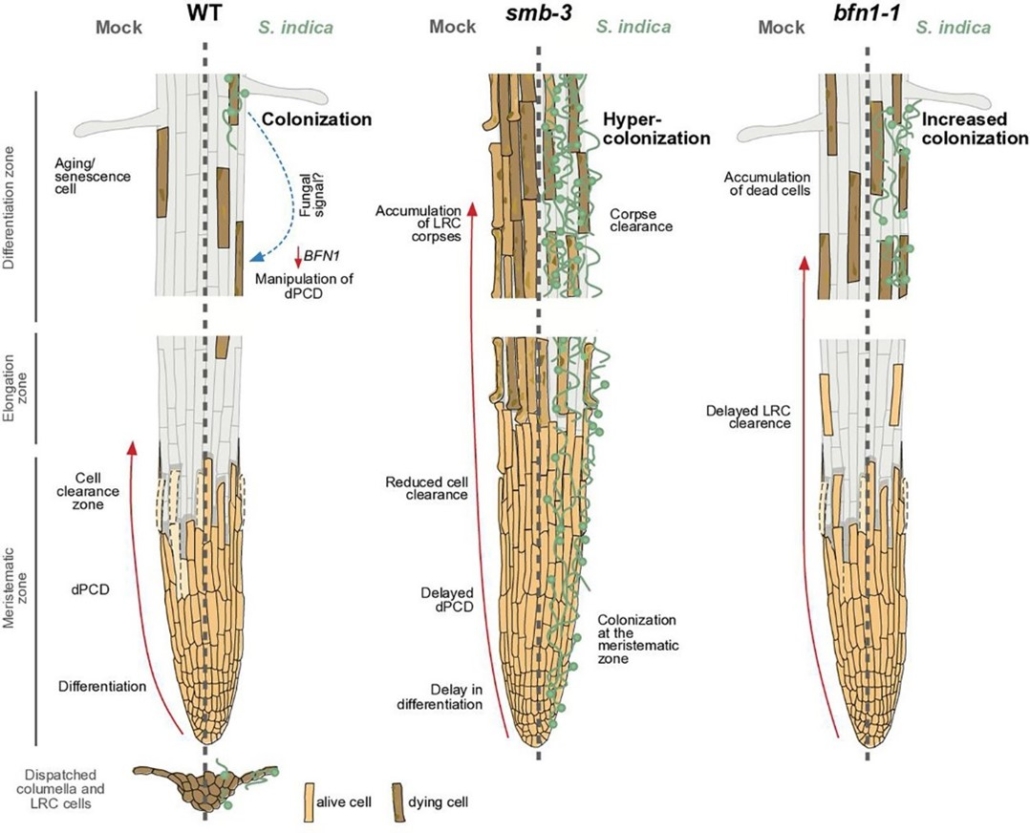
Capping your occupancy: programmed cell death as a mechanism to restrict microbial colonization of the root tip
Plant Science Research WeeklyThanks to the continued shedding and renewal of root cap cells, plant roots are able to extend into further reaches within the soil column overcoming physical barriers and potential microbial attacks, or so we assumed. Charura et al. explored the latter hypothesis showing that timely programmed cell…

