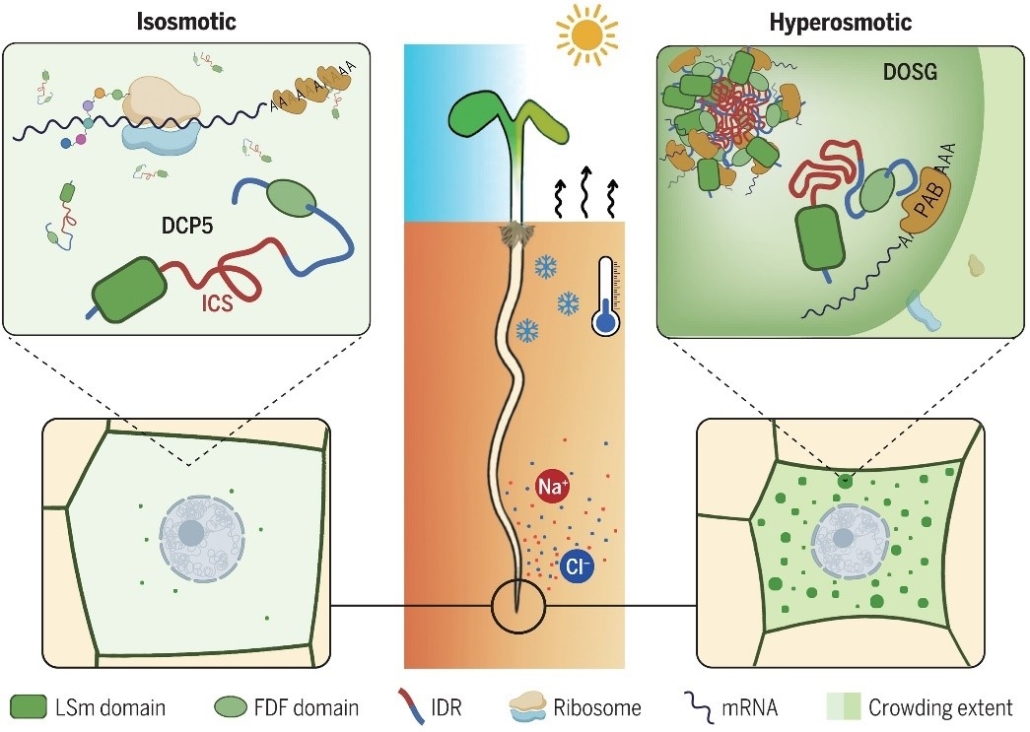
Crowd control by DCP5 - a new cytoplasmic osmosensor
Plant Science Research WeeklyOsmosis, driving water uptake and transport, is crucial for plants. It supports nutrient uptake, turgidity, and overall plant health. In hyperosmotic conditions, caused by drought, salinity, and cold stress, water loss triggers osmotic responses. A key question is: what sensors detect osmotic changes?…
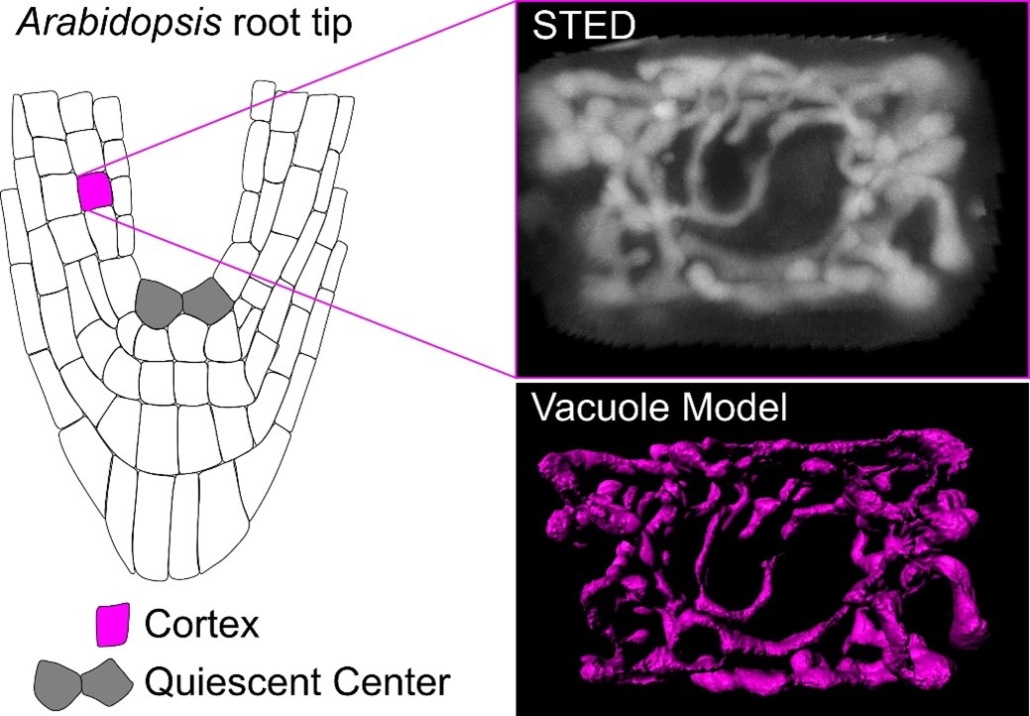
Unveiling vacuole biogenesis: Tubular networks are present in plant meristem cells
Plant Science Research WeeklyA recent paper by Scheuring and colleagues investigates vacuole biogenesis in meristematic cells of Arabidopsis thaliana, challenging earlier models of vacuole formation. Vacuoles are crucial organelles responsible for various cellular functions, yet their formation has remained puzzling for quite some…

Review: Guidelines for studying and naming plant plasma-membrane domains
Plant Science Research WeeklyNumerous studies have highlighted the critical importance of plasma membrane heterogeneities in regulating cell functions, leading to a proliferation of overlapping and contradictory terminologies. Here, Jaillais and others in the field propose a new system of nomenclature. It really is a must-read for…
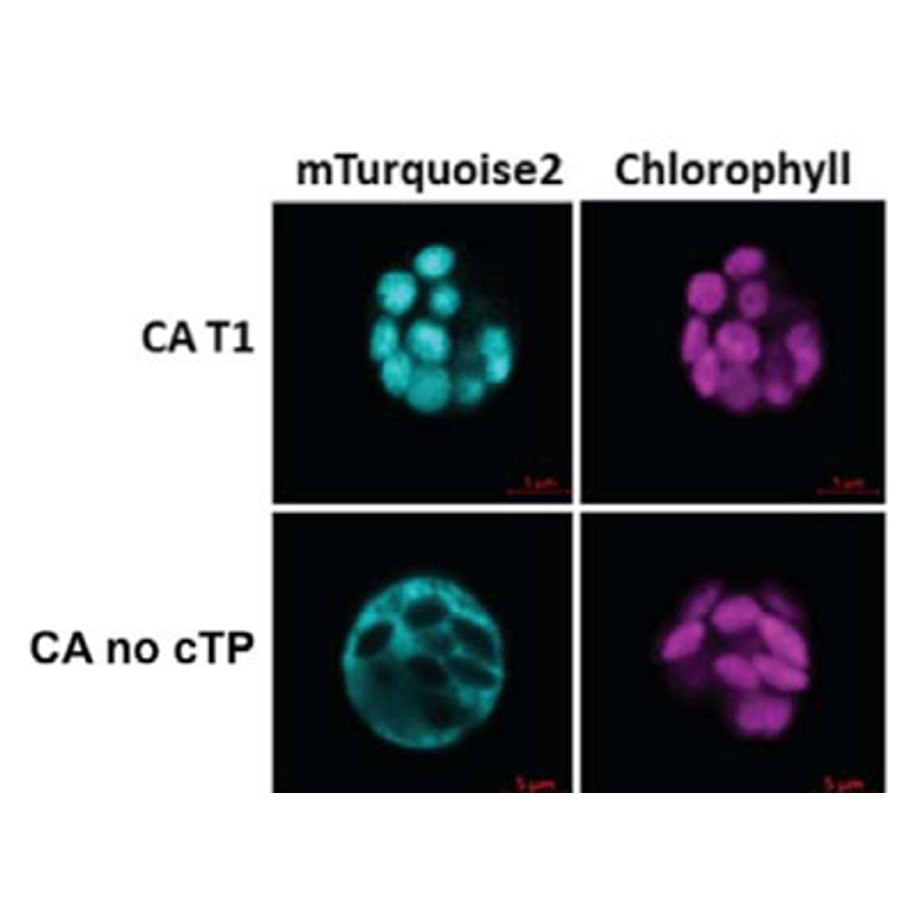
Engineering cytosolic carbonic anhydrase to establish C4 photosynthesis in rice
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn mesophyll cells, carbonic anhydrase is mainly located in the chloroplast, however it is in the cytosol in plants with a C4 carbon concentrating mechanism. There is interest in relocating carbonic anhydrase to the cytosol of C3 plants as a first step in the introduction of a carbon concentrating mechanism.…
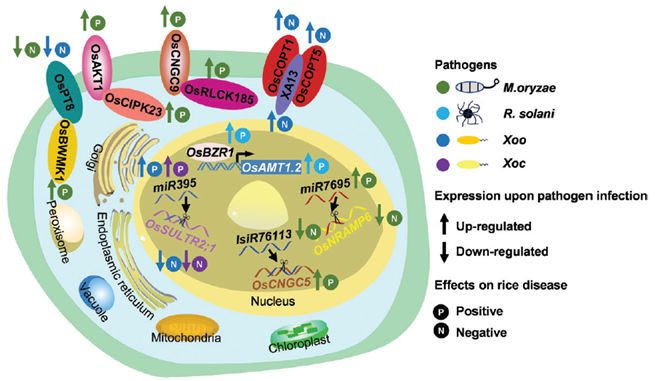
Review: Optimizing nutrient transporters to enhance disease resistance in rice
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants rely on an array of mineral nutrients for their growth, development, and reproductive processes. The molecular mechanisms governing the uptake, translocation, storage, and utilization of these essential minerals are orchestrated by specific nutrient transporters and their associated regulatory…
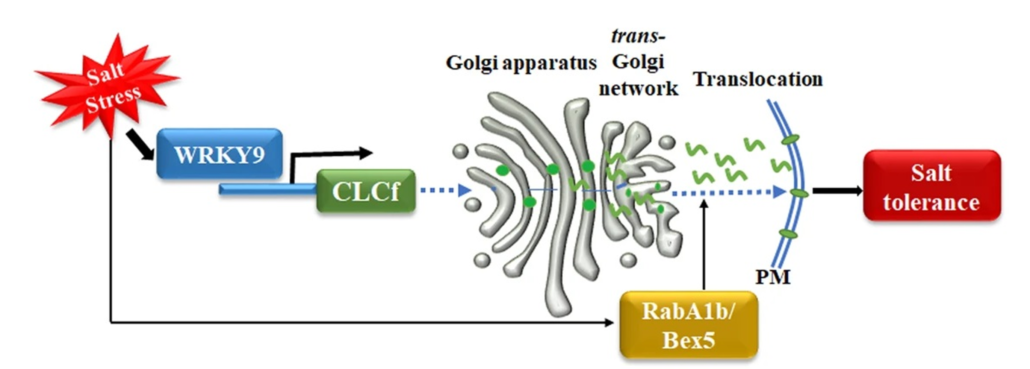
Translocation of a chloride channel from the Golgi to the plasma membrane helps plants adapt to salt stress
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants adapt to salt stress by maintaining ion balance using ion transporters. While much is known about cation transporters, the role of anion transporters is less clear. Rajappa et al. focus on the chloride channel gene AtCLCf in Arabidopsis thaliana, controlled by the transcription factor WRKY9 under…

Conjugation of ATG8 to vacuolar membranes as a response to cell wall damage
Plant Science Research WeeklyATG8 is a well-characterized protein involved in autophagy that binds to the double-membrane enclosed phagophore. In a new preprint, Julian et al. explore their finding that ATG8 binds to the single-membrane enclosed vacuolar membrane (tonoplast). They observed that this binding is enhanced by treatments…
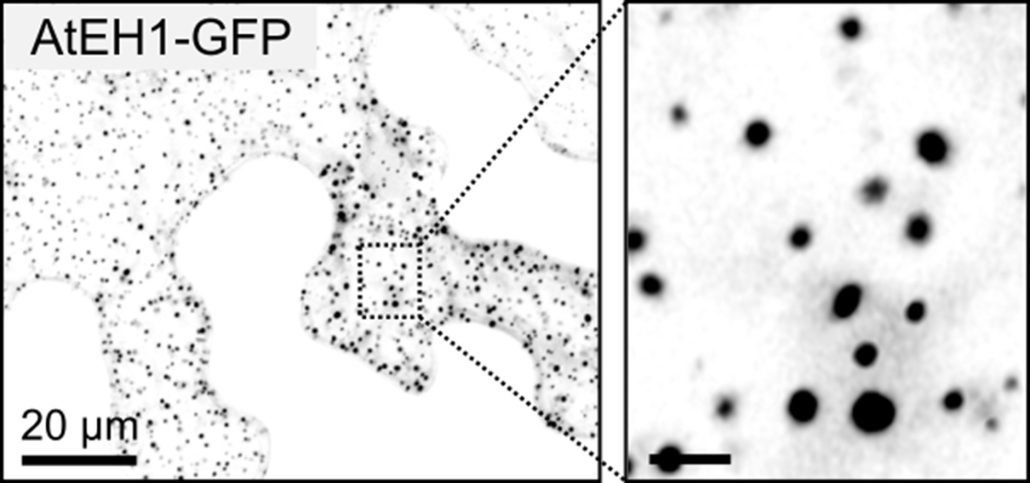
Functional insights into the TPLATE complex: A key player in clathrin-mediated endocytosis in plant cells
Plant Science Research WeeklyTransporting cargo within a cell may seem straightforward, but it is actually an intricate task. At the plasma membrane in plant cells, this complexity is navigated by a process known as clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Central to this process are two key players: adapter protein AP-2 and the TSET/TPLATE…
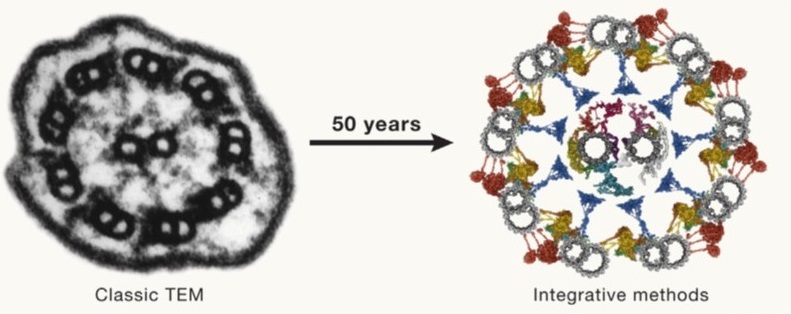
Review: Integrating cellular electron microscopy with multimodal data to explore biology across space and time
Plant Science Research WeeklyFifty years ago (1974), Albert Claude, Christian de Duve, and George Palade were awarded the Nobel Prize for their discoveries on the structural and functional organization of the cell, which Claude eloquently framed by writing, “We have entered the cell, the mansion of our birth, and started the inventory…

