
Insights into Calmodulin-Interacting Proteins
0 Comments
/
Calmodulin (CaM) and closely related CaM-like polypeptides are principal sensors of Ca2+ signals. The plant-specific IQ67 DOMAIN (IQD) family has emerged as possibly the largest class of CaM-interacting proteins with undefined molecular functions and biological roles. Bürstenbinder et al. (Plant Physiol.…
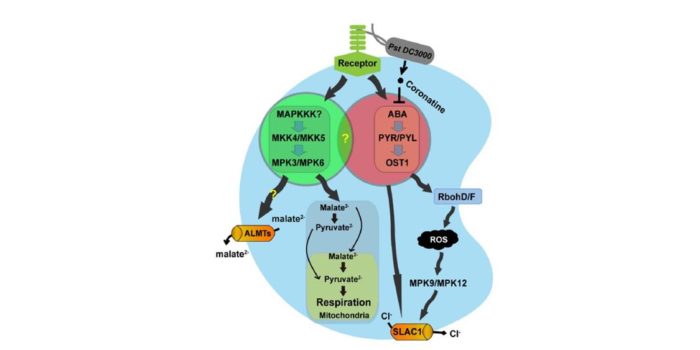
Stomatal immunity: Roles of MAP kinases and cytokinin
When a pathogen is perceived, plants have the ability to induce stomatal closure to prohibit the pathogens from passing into the inner tissues; this response is known as stomatal immunity. Two new papers in The Plant Cell investigate mechanisms by which pathogen perception is transduced into stomatal…
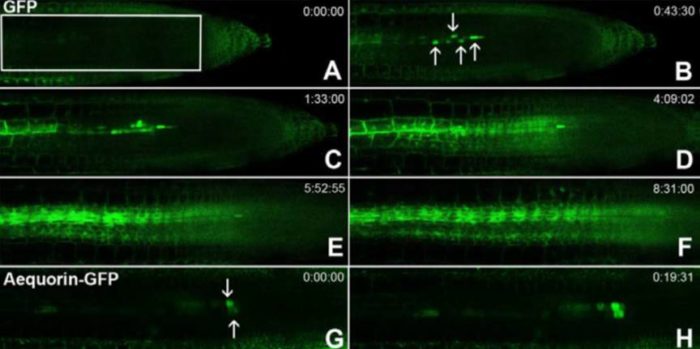
Phloem unloading in Arabidopsis roots
It is well known that long distance transport and movement of molecules is enabled by phloem, but the precise mechanism of loading/unloading of phloem mobile compounds is not known. In this article, Ross-Elliott et al. used a combination of approaches (non-invasive imaging, 3D-electron microscopy, and…
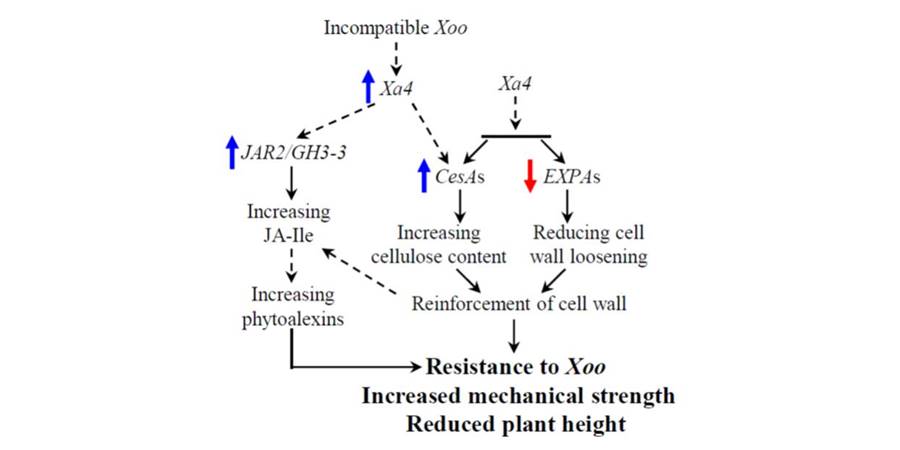
Durable resistance gene Xa4 encodes a cell wall-associated kinase
Xa4 is a durable rice disease resistance gene that confers resistance against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo), causal agent of bacterial blight. Hu et al. show that Xa4 encodes a wall-associated kinase (WAK) that promotes cellulose synthesis and suppresses wall loosening, thereby strengthening the…
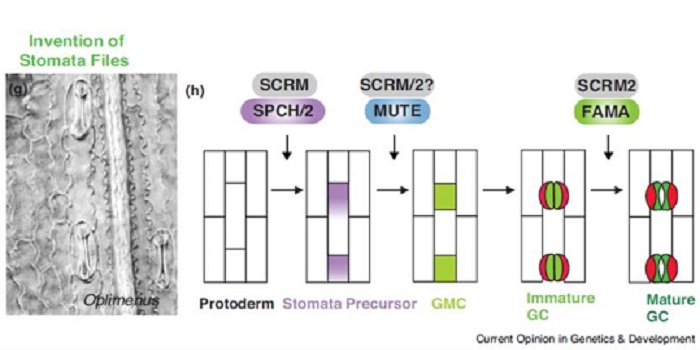
Review: Stomatal development in time: the past and the future ($)
Stomata, epidermal pores for gas exchange, first appeared about 400 million years ago. Since then, there has been functional and structural diversification. Qu et al. synthesize the developmental genetics underpinning diverse stomata, spanning from bryophytes through monocots and the astomatous (without…

Generation of shape complexity through tissue conflict resolution
It’s easy to visualize how a sheet of cells grows, but how does a sheet of cells form a complex, three-dimensional structure? Rebocho et al. describe how differential growth rates between cell layers and across the growing surface can produce a variety of complex shapes. As a model for shape complexity,…
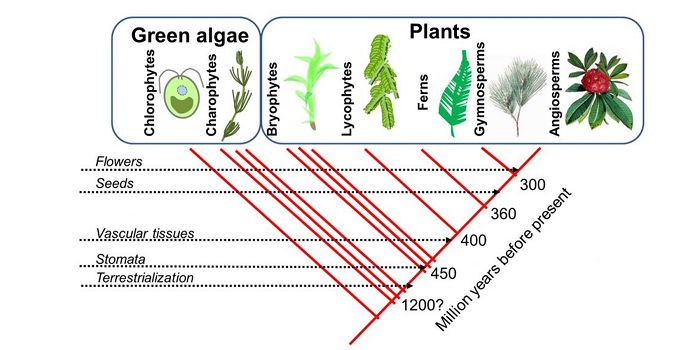
From LUCA to Lily: 12 perspectives for teaching about plants
The other day I was talking to a friend about the need to demystify plants, so that teachers feel as confident in their teaching of plant biology as they do about animal biology. I wonder if sometimes we teach plants too much in isolation, so it’s not always clear how plants relate to other organisms…
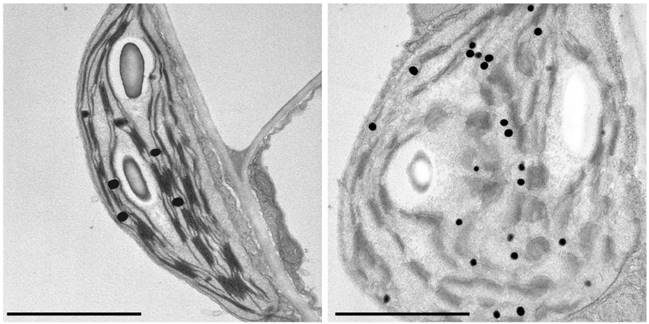
Photodamaged Chloroplasts Are Targets of Cellular Garbage Disposal
IN BRIEF by Gregory Bertoni gbertoni@aspb.org
Autophagy, or "self eating," is the process cells use to consume unwanted intracellular structures such as damaged organelles, excess membranes, and unneeded cellular proteins (Mizushima and Komatsu, 2011). Typically, the unwanted structure becomes surrounded…
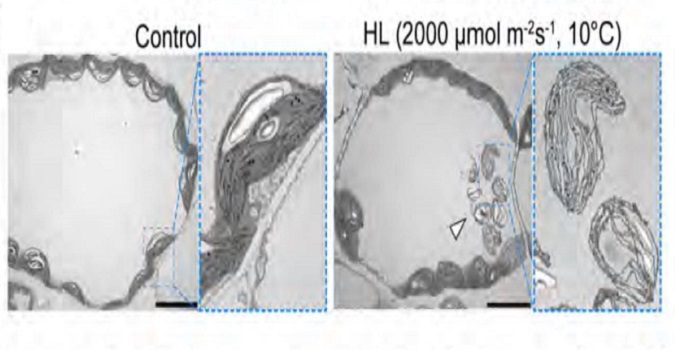
Entire photodamaged chloroplasts are transported to the central vacuole by autophagy
Autophagy is the process by which macromolecules and organelles are recycled. Previously it was shown that during leaf senescence or energy starvation, chloroplasts are degraded piecemeal by autophagy. In this work, Izumi et al. examined the role of autophagy in UVB damaged chloroplasts, using wild-type…

